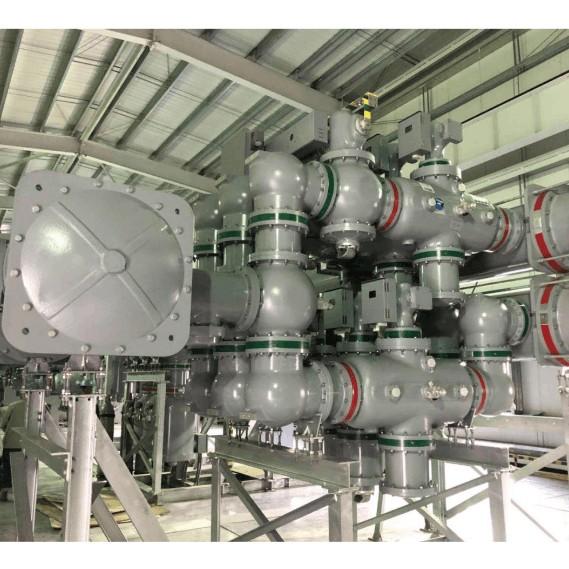
Ang GIS (Gas-Insulated Switchgear) naghatag og mga abilidad sama sa kompakto nga struktura, pahimutang nga operasyon, reliable nga interlocking, matagumpay nga serbisyo, walay maintenance nga operasyon, ug gamay nga footprint. Kini usab adunay daghang irreplaceable nga abilidad sa insulation performance, environmental friendliness, ug energy saving, ug gitukod na sa mas daghan nga industriya ug mining enterprises, airports, railways, subways, wind power stations, ug uban pang mga field.
Ang usa ka enterprise’s 35 kV indoor substation orihinal nga gipakita sa air-insulated switchgear nga may 10 bays. Kini nga upgrade magdugang og 4 bag-ong bays. Apan, ang orihinal nga site area dili makaya sa expanded bay requirements. Sa wala pa, hinumdumiha ang edad sa equipment ug safety performance, ang 35 kV substation gigamit sa SF₆ gas-insulated metal-enclosed switchgear. Ang kasagaran nga switchgear room area makaya ang expansion requirements, ug ang kabuok nga safety performance sa electrical equipment mahimong mapadako.
Ang maong article imong gi-study, batasan sa main components sa switchgear, ang sumala nga mga tests: enclosure ug busbar insulation tests, vacuum circuit breaker tests, voltage transformer tests, current transformer tests, metal oxide surge arrester tests, ug power cable tests.
1.Test Item Classification and Sequence Arrangement
Ang Bus Section III sa 35 kV substation gisumala sa double-bus system nga gihimo sa 14 ZX2-type SF₆ gas-insulated switchgear units. Tanang primary live parts sulod sa cabinets gisulob sa sealed gas-filled enclosures, mosulob sa direct preventive testing. Testing lisod pagbuhat tungod kay kinahanglan nga ibuo ang test circuits gamit ang adjacent switchgear units. Daghang conductive parts sama sa voltage transformers ug busbars, gisulob sa plug-in connections. Aron sigurado ang good contact sa tanang busbar plug joints, DC contact resistance measurements kinahanglan pagbuhat sa tanang joints. Sa panahon sa testing, temporary test plugs kinahanglan i-install sa cable sockets aron magsilbi isip test access points, mosulob sa test difficulty ug workload. Dili lang, ang test sequence kinahanglan reasonably arranged aron mapalito ang workload. Hinumdumiha ang uban pang mga factors, electrical equipment testing sa 35 kV Bus Section III gipatuman pinaagi sa duha ka methods: internal cabinet tests ug external cabinet tests.
2. Characteristic Tests of Equipment Inside the Switchgear
Ang internal cabinet tests gibuhat sa duha ka rounds. Sa unang round, low-voltage current injection test plugs ang gisulob; kini madali mogamit—basahan ang gi-insert directly sa cable installation sockets sa switchgear. Sa ikaduhang round, high-voltage test plugs ang gi-insert sa cable installation sockets sa switchgear ug secured pinaagi sa screws aron mailisan ang test voltage sa equipment under test.
2.1 First Round Tests
2.1.1 Vacuum Circuit Breaker Tests
Sa unang round, mechanical characteristic tests ug operating mechanism tests ang unang gibuhat, parehas gamit ang circuit breaker dynamic characteristic tester. Duha ka adjacent switchgear units gisulob sa group. Three-phase test leads gisulob sa usa ka end, ug ang uban nga end gi-ground. Ang mechanical characteristics ug coil operating voltages sa duha ka series-connected circuit breakers gisukol separado—i.e., sa panahon sa measurement sa mechanical characteristics sa usa ka circuit breaker, ang uban nga circuit breaker gisulob sa closed position aron magsilbi isip test path. Ang test method identical sa standard procedures. Para sa bus-tie breaker bay 9AH, ang bridge sa main ug auxiliary buses sa double-bus system, kini makasulob sa series sa left-side breaker 10AH ug right-side breaker 8AH (tulo ka breakers total) aron mouswag ang test paths sa 10AH ug 8AH.
2.1.2 DC Contact Resistance Test of Conductive Circuits and Bus Plug Joints
Arong sukli sa contact resistance sa tanang vacuum circuit breakers, main/auxiliary bus disconnect switches, ug main/auxiliary bus plug joints, adjacent switchgear units gisulob sa pairs, apan sequential—i.e., 1AH–2AH, 2AH–3AH, ..., 13AH–14AH. Para sa tanang pair, sa panahon sa main (o auxiliary) bus disconnect switches sa duha ka adjacent switchgear units gisulob sa closed, ang three-phase DC contact resistance sa corresponding main (o auxiliary) bus path gisukli. Loop resistance tester ang gisulob pinaagi sa test current nga approximately 100 A. Bisag unsa, para sa bus-tie breaker 9AH, kini makasulob sa series sa left-side 10AH ug right-side 8AH aron mouswag ang duha ka test paths: 10AH–main bus–9AH–auxiliary bus–8AH ug 10AH–auxiliary bus–9AH–main bus–8AH. Ang test method identical sa uban nga switchgear units, resistance values ranging from 200 to 300 μΩ.

2.1.3 Current Transformer Tests
Ang primary conductive parts sa gas-insulated dedicated current transformers gisulob sa cabinet sealed sa enclosure; dili lang, ang ilang tests kinahanglan kompleto sa panahon sa internal cabinet testing. Sa unang round, ratio tests, polarity checks, ug excitation characteristic curve tests ang unang gibuhat. Kini gibuhat gamit ang multifunctional fully automatic comprehensive transformer tester.
Para sa ratio tests ug polarity checks: ang test circuit configuration consistent sa circuit breaker mechanical characteristic tests—i.e., duha ka adjacent switchgear units gisulob sa group, ang ilang circuit breakers ug same-side bus disconnect switches gisulob sa closed. High current gi-inject phase by phase, ug secondary induced currents gikinahanglan sa corresponding secondary current terminals aron suklain ang ratio ug polarity sa tanang current transformers connected in series sa loop. Ang test method identical sa standard procedures.
Para sa excitation characteristic curve test: kini nga test nanginahanglan lang open ang primary circuit ug mahimong pagbuhat sa anytime. Hinumdumiha nga kini gisulob sa same test equipment ug shares sa same secondary current terminals sa ratio test—i.e., test current gi-inject pinaagi sa corresponding secondary current terminals—kini mahimong pagbuhat simultaneously sa ratio test aron mapadako ang work efficiency.
2.2 Mga Pagsulay sa Insulation sa Sulod sa Switchgear
Sa ikaduhang hugna sa mga pagsulay, ang insulation tests sa switchgear ug busbars gihimo og samotan, apil ang: mga pagsulay sa insulation sa live nga bahin sa circuit breaker ngadto sa ground ug taliwala sa mga contact, mga pagsulay sa insulation sa main/auxiliary bus disconnect switch nga live nga bahin ngadto sa ground ug taliwala sa mga contact, mga pagsulay sa insulation sa primary sa current transformer ngadto sa secondary ug ngadto sa ground, ug mga pagsulay sa insulation sa tanang internal nga main/auxiliary busbars ug conductive nga bahin ngadto sa ground ug taliwala sa mga phase.
Ang matag switchgear unit giilisan og boltahe duha ka higayon. Una, ang main ug auxiliary busbars sulod sa cabinet gi-ground pinaagi sa usa ka napili nga switchgear unit—nga nagpasabot nga ang circuit breaker ug ang main (o auxiliary) bus disconnect switch sa napili nga switchgear unit gitaklop. Dayon, ang bus-tie circuit breaker ug ang main/auxiliary bus disconnect switches gitaklop, ug usa ka temporaryong grounding wire ang gipahimutang sa cable socket sa maong switchgear unit, nga nag-ground sa tibuok main ug auxiliary nga sistema sa busbar sulod sa cabinet.
Ang switchgear unit nga gisulayan gamiton ang high-voltage test plug, nga masuyop nga gisudlan sa cable socket aron i-introduce ang test voltage.
Sa una nga pagbutang sa boltahe sa switchgear unit, ang circuit breaker niini bukas, ug ang three-position main bus disconnect switch gibutang sa grounding position (o gibutang sa service position samtang ang bus grounded sa lain nga lugar), nga mao ang nagtugot sa withstand voltage tests tali sa primary-to-secondary ug primary-to-ground sa current transformer, ingon man usab taliwala sa mga contact sa circuit breaker.
Sa ikaduhang pagbutang sa boltahe, ang circuit breaker taklubon, ug ang main ug auxiliary bus nga three-position disconnect switches anaa sa open position, nga makapahimo sa withstand voltage tests sa tibuok circuit breaker assembly ngadto sa ground ug taliwala sa mga contact sa main/auxiliary bus disconnect switch.
Alang sa espesyal nga bus-tie circuit breaker bay 9AH, ang mga pagsulay mahimong isiplan uban sa main ug auxiliary bus withstand voltage tests, nga nanginahanglan og total nga tulo ka pagbutang sa boltahe. Sa una nga pagbutang sa boltahe, ang bus-tie circuit breaker ug ang main bus disconnect switch gitaklop, samtang ang auxiliary bus disconnect switch ablihan. Ang auxiliary bus gi-ground pinaagi sa lain nga switchgear unit, ug ang test voltage giintroduce sa main bus pinaagi sa usa ka piho nga switchgear unit. Human niini, gihimo ang withstand voltage tests sa main bus system, sa tibuok bus-tie circuit breaker ngadto sa ground, ug sa auxiliary bus disconnect switch contact gap, sama sa gipakita sa Figure 1.
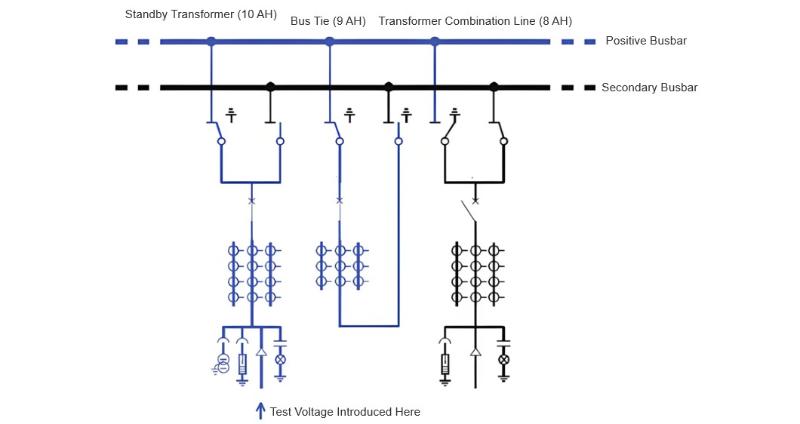
Sa ikaduhang pagbutang sa boltahe, ang bus-tie circuit breaker ug ang auxiliary bus disconnector gitaklop, samtang ang main bus disconnector giabli. Ang main bus gi-ground pinaagi sa lain nga switchgear unit, ug ang test voltage giintroduce sa auxiliary bus pinaagi sa usa ka piho nga switchgear unit. Gihimo dayon ang withstand voltage test sa auxiliary bus system, sa tibuok bus-tie circuit breaker ngadto sa ground, ug sa contact gap sa main bus disconnector.
Sa ikatulong pagbutang sa boltahe, ang contact gap sa bus-tie circuit breaker gisulayan pinaagi sa auxiliary bus. Ilabi na, ang bus-tie auxiliary bus disconnector gitaklop, ang bus-tie circuit breaker giabli, ug ang bus-tie main bus disconnector gibutang sa “ground” position. Ang test voltage giintroduce sa auxiliary bus pinaagi sa usa ka piho nga switchgear unit aron maghimo sa withstand voltage test sa contact gap sa bus-tie circuit breaker.
3. Mga Pagsulay nga Gihimo sa Gawas sa Switchgear
Alang sa mga ekipo sama sa surge arresters, voltage transformers, ug cables, natapos na ang tanan nga mga pagsulay sa wala pa ma-install.
3.1 Mga Pagsulay sa Metal-Oxide Surge Arrester
Ang tanan nga circuit breaker bays sa 35 kV Bus Section III (gawas sa bus-tie bay) adunay metal-oxide, walay gap, shielded, plug-in nga surge arresters. Ang pagsulay gihimo sa wala pa ma-install ang arrester. Ang insulation resistance gisukod sa dili pa ug human sa pagsulay. Gigamit ang DC high-voltage generator, ug gihimo ang mga pagsulay sumala sa mga detalye sa manufacturer:
Samtang nagasulay, usa ka dedicated insulating sleeve kinahanglan ipahimutang sa high-voltage terminal sa arrester; kon dili, sa palibot nga hangin, mahitabo ang surface flashover tungod sa taas nga boltahe ug gamay nga clearance, nga makadaot sa surface insulation sa arrester—naghimo sa pagsulay nga dili mahimo ug adunay risgo sa kadaot sa ekipo.
3.2 Mga Pagsulay sa Voltage Transformer (VT)
Adunay total nga 14 ka single-phase, plug-in, gas-insulated cabinet-specific nga voltage transformers nga gipahimutang sa 35 kV Bus Section III. Ang Bus VT lahi sa Line VT kay adunay dugang residual winding alang sa zero-sequence voltage measurement.
Mga Pagsulay sa Ratio ug Polarity: Gigamit ang multifunctional CT/VT tester aron masukod ang voltage ratio tali sa primary winding ug matag secondary winding (apil ang residual winding) ug i-verify ang polarity relationships.
Excitation Characteristic Curve: Menggamit sa samang tester, ang excitation voltage gipakaon sa secondary winding, ug ang excitation curve i-record sa 20%, 50%, 80%, 100%, ug 120% sa secondary rated voltage (i.e., 20 V, 50 V, 80 V, 100 V, ug 120 V).
Samtang nagasulay, usa ka temporaryong insulating cap (inner cone insulator) kinahanglan ipahimutang sa primary high-voltage terminal; kon dili, mahitabo ang surface flashover, makadaot sa insulation ug dili maabot ang test voltage.
DC Resistance sa mga Winding: Ang DC resistance sa primary ug secondary windings sa matag VT gisukod.
Prueba de Voltaje de Soporte AC: Pwedi ra ang VTs nga anaa ni sa gas-insulated switchgear ang idiseno, dili na sila makapugos og mataas nga test voltage kon isulod sa gawas sa cabinet. Mas maayo nga dili na ipahimulos ang power-frequency AC withstand test sa primary winding. Ang induced voltage test ang gamiton. Kini nga induced test mahimo molihok uban ang excitation characteristic test—ang pag-apply og 120 V nga voltage sa secondary side ngadto sa usa ka minuto.
Ipahimulos ang 3 kV AC (power frequency) ngadto sa usa ka minuto tali sa primary winding terminal N ug tanang uban pang windings/ground.
Ipahimulos ang 2 kV AC (power frequency) ngadto sa usa ka minuto tali sa bawg secondary (o residual) winding ug tanang uban pang windings/ground.
Tests on Auxiliary Components: Sukdi ang DC resistance sa primary-side fuse sa bawg VT ug checki ang insulation resistance sa neutral-point spark gap protector.
4.Precautions During Testing
4.1 Basic Conditions Before Testing
Ang SF₆ gas pressure gauge kinahanglan mosulti nga adunay normal nga green range.
Ang switchgear enclosure kinahanglan reliably grounded, ug ang grounding resistance nagpauli sa requirements.
Verifyi nga ang actual positions ug status indicators sa three-position disconnectors ug circuit breakers maong correct.
Tanang unused sockets sa equipment under test kinahanglan moseal pinaagi sa insulating plugs.
Durante sa AC withstand tests, ang cable termination holes, arrester mounting holes, ug VT mounting holes sa bays receiving voltage kinahanglan moseal pinaagi sa dedicated insulating plugs; ang non-energized areas wala nanginahanglan moseal.
Konfirmi nga ang busbar ends moseal pinaagi sa insulating plugs ug ang both end cabinets fully enclosed.
4.2 Special Characteristics of High-Voltage Tests
Ang insufficient external insulation strength sa VTs gawas sa cabinet, ang induced voltage test sa primary winding kinahanglan molihok uban ang excitation test sa reduced voltage, wala na maka-replicate sa standard withstand conditions. Sa dihang gi-measure ang DC contact resistance, ang total resistance sa entire series path—inclusive sa circuit breakers, disconnectors, bus plug joints, ug CT primaries—mahimo mas daghan ang specific component nga exceed sa allowable limits kon ang total value wala na sa specification.
4.3 Special Nature of High-Voltage Test Methods
Kon di posible ang direct testing sa equipment sealed inside gas-filled enclosures, ang test circuits kinahanglan ibuo pinaagi sa adjacent switchgear units ug busbars. Busa, ang comprehensive testing sa entire 35 kV Bus Section III mahimo lang kapag ang bus system walay energy. Apan, ang certain tests mahimo molihok sa individual de-energized bays:
Tanang CT tests (except ratio tests)
Withstand tests sa circuit breaker contact gaps ug line-side sections
Mechanical characteristic tests sa circuit breakers (except the bus-tie breaker)
Tanang tests sa removable components sama sa cables, surge arresters, ug VTs
4.4 Special Considerations for Test Standards
Durante sa internal AC withstand tests, tungod kay ang circuit breakers, disconnectors, CTs, ug busbars gitest simultaneously, ang test voltage kinahanglan limitahan sa lowest withstand rating sa kanila—76 kV (the CT standard)—resulting sa lower-than-optimal stress levels para sa uban pang components. Pagkatapos sa pag-remove sa secondary windings para sa testing, ang original wiring kinahanglan mabalik kasagaran aron malikayan ang poor contact o open circuits.
5.Conclusion
Ang high-voltage testing sa compact gas-insulated switchgear involbiha unique challenges ug highly complex operational requirements. Busa, ang thorough understanding sa equipment characteristics essential. Ang pagpili sa appropriate test equipment ug methodologies tailored sa kini nga features, ug ang pag-summarize sa effective testing procedures ug standards, maghatag og valuable reference ug technical basis para sa pag-resolve sa similar engineering challenges.























