IEE-Business solid insulated ring main unit (RMU) na nufin ɗaya ɗan takamfi da take ƙunshi external solid encapsulation, insulated busbar, da kuma compact combined unit technology. Switches da high-voltage live components suna cikin epoxy resin, wanda yana ƙunshi primary insulation daga live parts zuwa ground, da kuma daga phases. A matsayin ɗan takamfi mai kyau zuwa SF₆ gas-insulated equipment, 12kV solid insulated RMU na iya ba da faɗa amma yana da mafi nasararsa ta shiga hawa.
A 12kV solid insulated RMU da aka bincike, main conductive loops suna cikin epoxy da silicone rubber materials. Idan disconnecting switch yana amfani da air insulation, yana kan space mai kusa daidai daidai da cikakken hawa. Wannan yana taka shi da kyau zama da shiga hawa. Ya kamata da tsawon lokaci da hawa, za su iya haɓaka da abubuwan da ake gina su don hawa da kuma thermal aging. Wannan ya zama da yake haɗa da insulation performance, wanda yake haɗa da quality da reliability. A wasu lokutan, yana iya haɓaka da electrical accidents, wanda ke saukar da operation.
Saboda muhimmancin da rasu a wannan batu, an yi research masu inta. An yi structural optimizations don samun margin da ya shiga hawa, don haske product's long-term stable operation. Insulation of the solid insulated RMU na iya amfani da air da solid insulation. A prototype based on the initial design underwent temperature rise research testing. Key test point data is shown in Table 1.
|
No.
|
Measurement Point Location
|
Standard (K)
|
Equilibrium Temp. (°C)
|
Temp. Rise (K)
|
Margin from Std. (K)
|
Remark
|
|
1
|
A-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
86.1
|
73.0
|
-8.0
|
Exceeded
|
|
2
|
A-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
78.2
|
65.1
|
-1.1
|
Exceeded
|
|
3
|
B-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
86.4
|
73.3
|
-8.3
|
Exceeded
|
|
4
|
B-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
88.0
|
74.9
|
-9.9
|
Exceeded
|
|
5
|
C-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
80.6
|
67.5
|
-2.5
|
Exceeded
|
|
6
|
C-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
81.6
|
68.5
|
-3.5
|
Exceeded
|
Daga cikin Table 1, temperature rise testing on the prototype based on the initial design revealed severe exceedances of limits at both the disconnecting knife pivots and tips. To resolve this issue, optimization efforts focused on the following two aspects:
- Magnetothermal Coupling Simulation (Using ANSOFT): Perform magnetothermal coupling simulation to optimize conductor contact methods, the shape of irregular conductors, and the conductive cross-sectional area. This reduces internal heating by minimizing joule heat generation at the source.
- Cabinet-Level Thermal Simulation (Using ICEPAK): Conduct cabinet-level thermal simulation to establish effective heat dissipation pathways, increase the heat dissipation coefficient of the conductors themselves, and efficiently dissipate the generated heat. This approach aims to lower the temperature of the conductive loops through a dual approach of blocking and dissipating heat.
Magnetothermal Coupling Simulation
Since the applied current was less than 1000A, this simulation solely modeled the joule heating generated by the loop resistance in the conductive path. The simulated temperature distribution directly reflects joule heating effects, excluding scenarios involving heat dissipation through radiation or convection. This makes the results suitable for analyzing the impact of conductor structure on temperature distribution. Key product technical parameters are listed in Table 2.
|
No.
|
Parameter Name
|
Value
|
|
1
|
Rated Voltage (kV)
|
12
|
|
2
|
Rated Current (A)
|
700
|
|
3
|
A-phase Loop Resistance (μΩ)
|
190 (Assumed)
|
|
4
|
B-phase Loop Resistance (μΩ)
|
190 (Assumed)
|
|
5
|
C-phase Loop Resistance (μΩ)
|
190 (Assumed)
|
Simulation Results
Figure 1 shows the magnetothermal coupling temperature distribution of the insulation module. Figure 2 shows the overall magnetothermal coupling temperature distribution of the internal conductive path. Magnetothermal coupling simulation using ANSOFT software revealed that the primary locations of elevated heat generation were the tips of the disconnecting knives and the contact points with the stationary contacts. The B-phase disconnecting knife, in particular, exhibited consistently higher temperatures. Structural optimization is required to reduce constriction resistance and homogenize the conductive cross-sectional area.
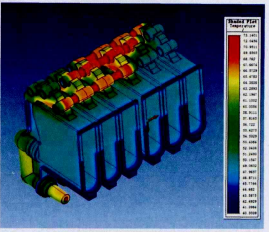
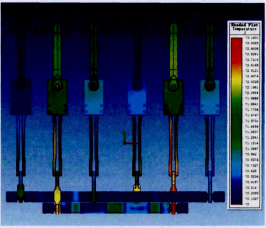
Cabinet-Level Thermal Simulation
Cabinet-level thermal simulation using ICEPAK software examined the distribution and forms of heat dissipation from the conductive paths after current flow, as well as the impact of the enclosure on heat transfer.
Technical Requirements
The temperature rise standard follows GB/T 11022-2011 "Common specifications for high-voltage switchgear and controlgear standards." As stipulated by the relevant standards:
- Maximum temperature for touchable enclosures: 70°C (max. temp. rise 30 K above ambient).
- Maximum temperature for non-touchable enclosures: 80°C (max. temp. rise 40 K above ambient).
- Maximum conductor temperature: 115°C (max. temp. rise 75 K above ambient).
- Maximum contact temperature: 105°C (max. temp. rise 65 K above ambient).
For temperature rise tests, a test current of 1.1 times the rated current is typically used to account for solar radiation effects.
Software Settings
Initial Temperature: 20°C; Three-phase current phase angles: 0°, 120°, -120°.
Simulation Results
The cabinet-level thermal simulation results (Figure 4) showed that due to the small clearance between the top plate of the sealed enclosure and the upper part of the insulation module, the effective heat dissipation area on the upper part of the cabinet is very limited. Consequently, heat concentrates at the top, making it difficult to dissipate, leading to persistently high busbar temperature rise. To provide more heat dissipation space within the sealed cabinet, the cabinet height was increased and a heat-dissipating coating was applied to its inner surfaces.
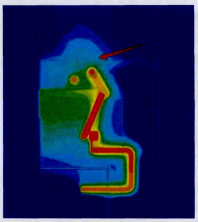
Temperature Rise Test After Structural Optimization
Following the simulation studies and initial temperature rise test findings, modifications were made to the cabinet and certain components. A subsequent temperature rise test was conducted (refer to Table 4).
|
No.
|
Measurement Point Location
|
Standard (K)
|
Equilibrium Temp. (°C)
|
Temp. Rise (K)
|
Margin from Std. (K)
|
Remark
|
|
1
|
A-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
72.4
|
55.2
|
+9.8
|
Compliant
|
|
2
|
A-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
73.7
|
56.5
|
+8.5
|
Compliant
|
|
3
|
B-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
73.6
|
56.4
|
+8.6
|
Compliant
|
|
4
|
B-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
73.6
|
56.4
|
+8.6
|
Compliant
|
|
5
|
C-phase Disconnect Knife Pivot
|
65.0
|
69.6
|
52.4
|
+12.6
|
Compliant
|
|
6
|
C-phase Disconnect Knife Tip
|
65.0
|
70.7
|
53.5
|
+11.5
|
Compliant
|
As shown in Table 4, the temperature rise values for the prototype retested are now compliant with requirements. Furthermore, a design margin of at least 8.5 K has been achieved.
Subsequent Optimization and Rectification
Given the critical importance of temperature rise and the potential consequences of non-compliance, further optimization is warranted to enhance prototype performance, even after meeting the standard. The goal is to achieve a controlled temperature rise margin between 12 K and 15 K. For instance, specific modifications on the insulation module require testing (Original Table 5 was incomplete; logically incorporated). Simulation results suggest that optimizing the structure of the main insulation module creates a more reasonable internal heat dissipation pathway, offering significant potential for further reducing the overall internal conductive loop temperature rise. This potential requires further experimental validation.
Conclusion
A combined design approach utilizing computer simulation technology and temperature rise testing enabled structural optimization of the solid insulated ring main unit. The optimized product complies with the temperature rise requirements stipulated in GB/T 11022-2011 "Common specifications for high-voltage switchgear and controlgear standards" and achieves a significant safety margin.

























