Ang substation sa 110kV sa among planta gipagtukod ug gisulbaran sa operasyon sa Pebrero 2005. Ang sistema sa 110kV nagamit og ZF4-126\1250-31.5 type SF6 GIS (Gas-Insulated Switchgear) gikan sa Beijing Switchgear Factory, na may pitong bay ug 29 ka SF6 gas compartments, kung diin lima niini mao ang mga circuit breaker compartments. Kada circuit breaker compartment adunay SF6 gas density relay. Ang aming planta nagamit og MTK-1 model oil-filled density relays gikan sa Shanghai Xinyuan Instrument Factory. Ang mga relays niini adunay duha ka range sa presyon: -0.1 hangtod 0.5 MPa ug -0.1 hangtod 0.9 MPa, na may usa o duha ka set sa contacts. Nagamit sila og Bourdon tube ug bimetallic strip isip mga sensing elements. Kapag ang gas leakage moadto sa usa ka level, ang electrical contacts magtrigger og alarm o lockout signals, nagsiguro sa uban pang mga protective functions. Sa Oktubre 17, 2015, sa usa ka routine inspection, ang mga on-duty electricians nakadiskubre og varying degrees sa gas leakage sa density relays sa compartments 11, 19, ug 22. Nihighlight kini ang operational risks nga gihatagan sa oil leakage sa SF6 density relays.
1. Hazards of Oil Leakage in SF6 Density Relays
Ang oil leakage sa density relays naghatag og significant damage sa power equipment:
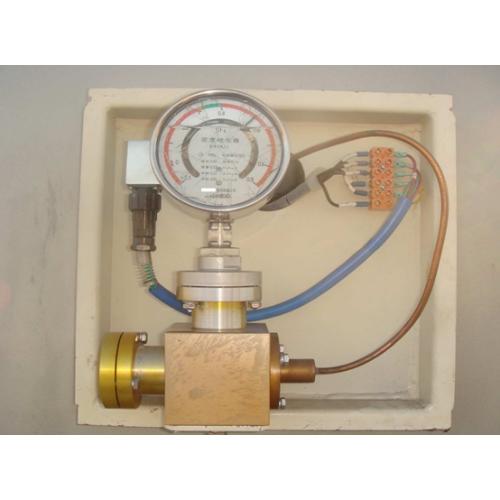
1.1 Bisag unsang oras ang anti-seismic oil sa density relay mawala kompletamente, ang iyang shock-absorbing capability madaghan ang pagbawas. Kon ang circuit breaker mogamit (opens or closes) sa sulod sa matang nga kondisyon, mahimong mosabot kini sa contact failure, excessive deviation from standard values, pointer jamming, ug uban pang malfunctions (see Figure 1: Oil-filled density relay).
1.2 Tungod sa specific characteristics sa mga contacts sa SF6 density relays—low contact force ug long operational duration—mahimong mag-occur ang contact oxidation sa panahon, mosabot kini sa poor o interrupted contact. Sa mga SF6 density relays nga mawala ang ilang oil, ang magnetic-assisted electrical contacts exposed sa air, promoting oxidation ug dust accumulation, na resulta sa poor contact sa contact points. Sa operasyon, gisulti nga 3% sa mga SF6 density relay contacts failed to conduct effectively, primarily due to insufficient anti-seismic oil. Kon ang pointer sa SF6 density relay mohimo og stuck, o kon ang contacts failed o dili makapag-conduct properly, ang safety ug reliability sa power grid directly threatened.

2. Causes of Oil Leakage in SF6 Density Relays
Ang primary cause sa oil leakage sa SF6 density relays mao ang failure sa seals sa duha ka locations: ang junction tali sa terminal base ug ang surface, ug ang seal tali sa glass ug ang case. Kini nga seal failure mainly due sa aging sa sealing rings. Ang anti-seismic oil seals sa SF6 density relays typically made of nitrile rubber (NBR). Ang NBR mao ang synthetic elastomer copolymer composed of butadiene, acrylonitrile, ug emulsion, na may molecular structure nga featuring an unsaturated carbon chain. Ang acrylonitrile content directly affects the properties sa NBR: higher acrylonitrile content increases oil, solvent, ug chemical resistance, as well as strength, hardness, wear resistance, ug heat resistance, pero reduces low-temperature flexibility, elasticity, ug increases gas impermeability. Factors affecting the aging sa NBR seals can be categorized into internal ug external factors.
2.1 Internal Factors
2.1.1 Molecular Structure of Nitrile Rubber
Ang NBR dili saturated hydrocarbon rubber; ang iyang polymer chains adunay unsaturated double bonds. Sa panahon sa various external influences, ang oxygen reacts sa kini nga double bonds, forming oxides. Kini nga oxides further decompose into rubber peroxides, leading to molecular chain scission. Simultaneously, small amounts sa active groups generated, promoting cross-linking sa rubber molecules. This significantly increases cross-linking density, making the rubber brittle ug hard. The number of double bonds directly influences the rate of aging.
2.1.2 Rubber Compounding Agents
The selection of vulcanizing agents during rubber manufacturing is critical. An increase in sulfur cross-linking concentration accelerates the aging process of the rubber.
2.2 External Factors
2.2.1 Oxygen is a primary cause of rubber aging. Oxygen molecules cause chain scission and re-cross-linking. Another factor is ozone, which is highly reactive. Ozone attacks the double bonds in rubber molecules, forming ozonides that decompose and break the polymer chains. Since the anti-seismic oil seal is in direct contact with air, and oxygen/ozone can dissolve into the oil, they participate in aging reactions within the oil.
2.2.2 Thermal Energy accelerates the oxidation rate. Typically, a 10°C increase in temperature doubles the oxidation rate. Additionally, heat accelerates reactions between rubber chains and compounding agents, causing volatile components in the rubber to evaporate, significantly degrading rubber performance and shortening its service life.
2.2.3 Mechanical Fatigue. Under sustained stress, rubber undergoes strain, leading to mechanical-oxidative effects. Combined with thermal energy, this accelerates oxidation. Over its service life, rubber gradually loses elasticity, leading to mechanical aging. Aged rubber seals lose their sealing capability, resulting in oil leakage.
2.2.4 Insufficient Initial Compression of the Seal. Rubber seals rely on deformation during installation to create a tight fit between the seal and the sealing surface, preventing leakage. Insufficient initial compression is most likely to cause leakage. Design issues—such as selecting a seal with a small cross-section, using an oversized installation groove, or improperly tightening the case cover during installation—can all result in inadequate initial compression. In practice, tightening the relay case cover is often done by feel, making it difficult to achieve the optimal position, thus leading to insufficient compression. Moreover, rubber has a cold-shrink coefficient more than ten times greater than metal. At low temperatures, the rubber seal cross-section contracts and the material hardens, further reducing compression.
2.2.5 Excessive Compression Rate. To ensure sealing performance, rubber O-rings require a certain compression rate. However, this cannot be increased blindly. Excessive compression can cause permanent deformation during installation, generate high equivalent stress in the seal, lead to material failure, shorten service life, and ultimately cause oil leakage. Again, the practice of tightening the relay cover by feel often results in excessive compression due to difficulty in achieving the correct position.
3. ZDM-Type Oil-Free, Anti-Seismic Density Relay
3.1 Shock Absorption and Operating Principle of the ZDM-Type Relay
The ZDM-type oil-free, anti-seismic density relay (see Figure 2) achieves shock absorption by incorporating a shock-absorbing pad between the connector and the case. This pad buffers vibrations generated during circuit breaker operation. The impact and vibration from the switch operation are transmitted through the connector to the shock-absorbing pad, which then dampens the energy before passing it to the relay case. Due to this buffering effect, the vibrational and impact energy reaching the relay case is greatly reduced, resulting in excellent anti-seismic performance.
Additionally, the operating principle of the ZDM-type relay relies on a spring tube as the elastic element, with a temperature compensation strip correcting for pressure and temperature variations to reflect changes in SF6 gas density. The output contacts use a micro-switch mechanism. The control of the micro-switch signal is performed by the temperature compensation strip and spring tube, combined with the buffering effect of the shock-absorbing pad. This design prevents false signals due to vibration, ensuring reliable and effective system operation. It significantly enhances the anti-seismic performance of the pointer-type density relay, making it a high-performance device.

3.2 Features of the ZDM-Type Oil-Free, Anti-Seismic Density Relay
3.2.1 Full stainless steel enclosure with excellent waterproof and corrosion-resistant properties, and an attractive appearance;
3.2.2 Accuracy: 1.0 class (at 20°C), 2.5 class (at -30°C to 60°C);
3.2.3 Operating ambient temperature: -30°C to +60°C; operating ambient humidity: ≤95% RH;
3.2.4 Anti-seismic performance: 20 m/s²; anti-impact performance: 50g, 11ms; sealing performance: ≤10⁻⁸ mbar·L/s;
3.2.5 Contact rating: AC/DC 250V, 1000VA/500W;
3.2.6 Enclosure protection rating: IP65;
3.2.7 Oil-free design, resistant to vibration and impact, and permanently leak-proof;
3.2.8 Stable and highly consistent performance of the temperature-sensing element.
The above features demonstrate that the ZDM-type oil-free, anti-seismic density relay completely eliminates the problem of oil leakage. By utilizing a unique structural design and shock-absorbing pads instead of anti-seismic oil, it fundamentally prevents oil leakage during operation.
4. Conclusion
The main causes of oil leakage in density relays stem from manufacturing, operation, and maintenance issues. When equipment density decreases, not only is the dielectric insulation strength reduced, but the circuit breaker’s interrupting capacity is also compromised. Therefore, timely replacement of oil-leaking density relays is essential. To ensure safe and reliable operation, it is recommended to use ZDM-type oil-free, anti-seismic density relays or similar devices in future applications.