Overview
Ang mga lumang distribution network kasagaran radial ang istraktura, uban sa daghang incoming ug outgoing lines nga overhead. Ang switching equipment kasagaran gisulay sa air-insulated vacuum circuit breakers o minimal-oil circuit breakers. Kini nga mga network adunay pakauban nga mga pagkamalas, mataas nga operating costs, ug mahimong makapahinungdan og prolonged, widespread power outages kon may suliran, nga nagpabugha sa ekonomiya.
Sa rapid economic growth ug implementasyon sa urban grid renovation, ang demand para sa mas taas nga power supply reliability nahimong daghan. Ang fully insulated, fully sealed, maintenance-free, ug compact SF₆ Ring Main Units (RMUs) muli naging importante isip guarantee sa reliable power supply.
1 Mga Tipo ug Structural Features sa SF₆ RMUs
1.1 Mga Tipo sa SF₆ RMUs
Ang SF₆ RMUs mahimong ikategorya sa duha ka pangunohan nga tipo batas sa istraktura: Common Tank Type ug Modular Unit Type. Ang maong Common Tank Type RMUs kasagaran adunay usa ka inlet, usa ka loop, ug usa ka outlet, angay sa gamay nga loads. Apan, tungod sa daghan nga load demands, ang expandable Modular Unit Type mibuntog, na offer og maximum distribution capacity nga makapahimong 10 MVA.
Ang SF₆ RMUs mahimong ikategorya batas sa function sa Cable Type, Fuse Type, ug SF₆ Circuit Breaker Type:
- Cable Type: Ginagamit para sa cable inlets/outlets. Ang rated current mao ang 630A.
- Fuse Type: Mahimo nimong direkta mo connect sa transformers. Ang rated current mao ang 200A. Apan, sa pag consider sa temperature rise effect sa fuses, ang bawat RMU praktikal limitado sa supply sa transformers hangtod sa 1600 kVA sa real-world applications.
- SF₆ Circuit Breaker Type: Ginagamit para sa protection sa transformers nga mas taas sa 1600 kVA. Kini mahimo usab mag-serve isip incoming o bus section unit nga may overcurrent ug instantaneous trip protection. Ang rated current mao ang 630A, ug ang total fault interruption time mao ang 95ms.
Ang basic configurations sa SF₆ RMUs gitakda sa figure sa ubos.
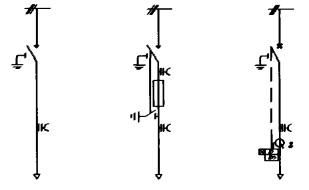
1.2 Structural Features sa SF₆ RMUs
Ang Common Tank Type SF₆ RMU kasagaran gisulay sa gas tank, operating mechanism compartment, ug cable connection compartment. Ang Modular Unit Type lisod pa ngadto sa busbar connection compartment.
Ang SF₆ RMUs adunay apat ka major features:
- Gas Tank: Kini ang pinaka-critical part sa RMU. Ang gas tank naglaman sa load switch, busbars, switch shaft, ug SF₆ gas.
- Ang load switch mao ang 3-position switch, kinahanglan sa isolating knife switch ug arc chute.
- Ang moving contact sa knife switch adunay duha ka special rivets gihimo sa Nichrome alloy, na serve og duha ka purposes:
- Naghatag og dry lubrication sa panahon sa switch opening/closing, siguradohon nga ang contact resistance sa moving ug fixed contacts dili mag-increase human sa long-term use.
- Tungod sa taas nga melting point sa Nichrome alloy, ang moving contact dili mag-melt tungod sa heat generated sa short-circuit currents sa panahon sa closing o withstand periods.
- Ang arc chute naglaman sa deionizing plates nga nag-stretch sa arc, reduce arc energy, ug minimize ang amount sa metal vapor ug SF₆ decomposition products generated sa panahon sa load switch interrupts load current.
- Ang bahin sa busbar nga nakontak sa knife switch mao ang fixed contact. Sa dihang meet sa rated current capacity ug dynamic/thermal stability requirements, ang busbar design ug manufacturing consider usab ang electromagnetic field effects aron mapahimulos ang magnetic field impact.
- Ang switch shaft penetrates sa gas tank ug connect sa operating mechanism compartment, allowing operators sa wala sa compartment mogamit sa switch's closing, opening, ug grounding states. Ang double-seal structure ginamit sa penetration point (ang unom nga moving connection sa tank ug wala), strictly ensuring sa tank's airtightness sa panahon sa vacuum evacuation ug gas filling.
- Ang annual leakage rate sa SF₆ gas mao lang 0.0035%. Kini nga low leakage rate importante para sa long-term safe operation sa RMU.
- Sa wala sa SF₆ gas para insulation ug arc quenching, ang gas tank adunay Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃), nga accelerate sa SF₆ gas regeneration ug act as an excellent desiccant, maintaining sa quality sa SF₆ gas ug minimizing arc faults. Kon may suliran, ang explosion-proof diaphragm sa wala sa tank protect sa personnel sa pag vent sa hot gases directly sa cable trench sa wala o likod sa unit, away sa operators sa front.
- Ang gas tank gisulay sa 3mm thick stainless steel plate, double-sided welded.
- Operating Mechanism Compartment: Ang operating mechanism sa wala connect sa load switch ug earthing switch pinaagi sa switch shaft. Pinaagi sa pag-operate sa operating rod insert sa operating hole, ang operators mahimo mosimple perform sa closing, opening, ug earthing operations nga walay effort (only 60 N·m required).
- Kon ang switch contacts dili visible, ang operating mechanism adunay position indicator directly linked sa switch shaft, clearly showing ang current state sa load switch ug earthing switch.
- Ang mechanical interlocks sa tibuok load switch, earthing switch, ug front cover plate installed, satisfying ang lima ka safety interlock requirements (anti-misoperation functions).
- Ang load switch ug earthing switch adunay quick-make/quick-break mechanisms, ensuring ang opening/closing speeds independent sa speed sa operator.
- Ang switches sa fuse protection (TS Type switchgear) adunay automatic trip device, available sa mechanical o electrical versions. Ang mechanical trip principle: Sa panahon sa short-circuit fault sa unit's circuit, ang fuse melts sa unom nga half-cycle (~10ms) sa fault current. Ang fuse's striker pin impacts sa trip mechanism, causing ang load switch to open. Ang total fault interruption time mao lang 35ms, effectively protecting ang unit ug preventing fault propagation sa adjacent units. Furthermore, tungod sa excellent mechanical performance, ang transfer current sa Fuse Type switchgear makapahimong 2300A.
- Ang padlocks mahimo mosulay sa operating levers sa front panel sa operating mechanism compartment aron maprevent ang unauthorized operation.
- Para sa safe operation, ang gas pressure gauge, directly connected sa gas tank ug sealed against moisture (preventing fogging sa dial), installed sa compartment, allowing ang maintenance personnel accurately monitor ang status sa RMU sa bisan unsa nga oras.
- Ang voltage indicator installed usab sa operating mechanism compartment, allowing ang operators monitor ang circuit energization (neon bulb indicator) ug verify phasing (using test sockets).
- Cable Connection Compartment: Located sa front sa RMU nga may height sa 1220mm, providing ample space sa cable termination.
- Ang cable connections sa RMU's bushings use either Asbestos-free Touching Screened (AFTS) o Asbestos-free With Kit (AWK) silicone rubber cable accessories.
- Ang copper o aluminum cable cross-sections range gikan sa 25–240 mm² (para sa Fuse Type switchgear) o 35–400 mm² (para sa Cable Type switchgear).
- Busbar Connection Compartment (Modular Units): Positioned sa wala sa gas tank. Tulo ka bushings arranged sa staggered "step-up" configuration, effectively minimizing space requirements ug facilitating busbar connections.
- Ang bushings mao ang hollow conductive type, allowing ang copper tube busbars direct bolt sa busbars sa wala sa gas tank.
- Ang silicone rubber-insulated copper tube busbars used, effectively increasing current-carrying capacity ug reducing phase spacing (only 110mm).
- Ang connections sa tibuok busbars ug bushings use silicone rubber connectors (E-type terminal connectors ug T-type extension connectors) ug screw-on caps para sa electrically seamless connections directly sa bushings. Kini nga mga busbars withstand harsh conditions sama sa moisture condensation, conductive dust, ug salt deposits without failure.
- Additionally, ang front sa busbar compartment shielded sa separate grounded steel plate, separating kini sa cable connection compartment.
2 Technical Parameters ug Applications sa SF₆ RMUs
2.1 Technical Parameters
|
Item
|
Cable-type Switchgear
|
Fuse-type Switchgear
|
Fuse-type Switch Cabinet
|
|
Rated Voltage / kV
|
12
|
12
|
12
|
|
Rated Current / A
|
630
|
200
|
630
|
|
Power-frequency Withstand Voltage / kV·min⁻¹
|
50 - 60
|
42 - 48
|
42 - 48
|
|
Impulse Withstand Voltage / kV
|
125 - 145
|
75 - 85
|
75 - 85
|
|
Rated Breaking Current / A
|
630
|
200
|
630
|
|
Rated Transfer Current / A
|
-
|
2300
|
-
|
|
Rated Short-circuit Breaking Current / kA
|
-
|
20
|
20
|
|
Breaking Capacitive Current / A
|
45
|
10
|
50
|
|
Breaking Inductive Current / A
|
16
|
16
|
-
|
|
Rated Peak Withstand Current / kA
|
50
|
-
|
50
|
|
Rated Short-time Withstand Current / kA·3s⁻¹
|
20
|
-
|
20
|
|
Rated Closing Current / kA
|
50
|
-
|
50
|
|
Number of Operations (630 A) / time
|
>100
|
>100
|
3000
|
|
Number of Closing Operations (50 kA) / time
|
5
|
5
|
5
|
|
Number of Mechanical Operations / time
|
2000
|
2000
|
4000
|
|
Ambient Temperature / °C
|
-
|
-25 - +55
|
-
|
|
Degree of Protection
|
IP65/IP4X
|
IP65/IP4X
|
IP65/IP4X
|
|
Leakage Rate / %, per year
|
-
|
0.0035
|
-
|
2.2 Applications sa SF₆ RMUs
Tungod sa ilang compact size, maintenance-free nature, ug high reliability, ang SF₆ RMUs kasagaran angay sa power distribution sa critical facilities, high-rise buildings, residential complexes, ug urban grids. Kini significant reduce sa operating costs ug footprint.
- 3-Unit Common Tank Type: Dimensions only 980mm × 635mm × 1050mm, making it ideal para sa kiosk transformers ug outdoor applications.
- Modular Cable Type: Mahimo mosulay sa switching tap-off boxes, supporting configurations hangtod sa one incoming ug three outgoing feeders (i.e., incoming via the busbar compartment, with three outgoing feeders connected in parallel via the cable connection compartment).
- Modular Fuse Type: Angay sa locations far sa substations kon may usa ra ka transformer nga operational. Para achieve local transformer control without needing an additional incoming unit, ang incoming cable mahimo mosulay diretso sa busbar compartment sa TS Type switchgear unit, providing ang same functionality.
- Circuit Breaker Type Switchgear: Equipped sa overcurrent ug instantaneous trip protection. Kini mahimo mag-serve isip transformer protection unit, incoming unit, o busbar section unit. Para enable remote tripping o tripping upon transformer gas protection relay operation (for Fuse Type switchgear), simply add an electromagnetic trip coil sa operating mechanism ug provide a 220V AC o 24V DC power supply sa circuit.
Motorized Operation:
- Para sa distribution automation, ang electric motor mahimo mosulay sa operating mechanism compartment, together sa 350mm high control box mounted sa top. Local push-button operation (open/close) remains possible.
- Adding an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) device enables automatic switching sa tibuok duha ka incoming supplies, with or without a defined primary/standby configuration.
- Electric motors kasagaran available sa various voltage levels (220V AC, 220V DC, 110V DC, 48V DC, 24V DC) para sa user selection.
- A short-circuit fault indicator mahimo mosulay sa front panel sa operating mechanism compartment, sa signals transmitted sa remote control room. Kini nga indicator mahimo reset automatically, manually, o remotely.
- Low-voltage through-core Current Transformers (CTs) mahimo mosulay sa cable connection compartment para sa current measurement.
- Surge arresters mahimo usab mosulay sa within Cable Type switchgear units para sa RMU protection.
Distribution automation functions primarily focus sa five areas: Data Acquisition, Monitoring & Control, Fault Isolation & Service Restoration, Geographic Information System (GIS), ug Data Statistics & Reporting.
- Implementing distribution automation requires primary equipment sa motorized operating mechanisms ug Feeder Terminal Units (FTUs) o Remote Terminal Units (RTUs).
- Fiber optic cable ang preferred communication medium. Communication protocols should be internationally recognized standards familiar sa users, sama sa IEC 870, DNP 3.0, o TCP/IP.
- Ang control room SCADA software platform should be multi-tasking ug multi-user capable, sama sa UNIX.
- Ang database recommended stable sa sufficient processing capacity, sama sa Oracle.
Kini nga solution kasagaran angay sa RMUs located sa outdoors o far sa low-voltage power sources, tungod sa kini guarantees simultaneous operation sa duha ka 150W motors over 50 times.
3 Lifecycle
Ang lifespan sa SF₆ RMUs kasagaran 25–30 years, ug mahimo convenient retrofit sa distribution automation equipment. Therefore, ang SF₆ RMUs should be ang preferred choice para sa urban grid renovation projects.























