1 פריטי אבחון לאחר כשל
1.1 זיהוי סיבות לכשל וקביעת יחידות מבחן
כדוגמה, בנק קONDנסטורים המותקן על רצפת rack, כל יחידת קONDנסטור היא בדרך כלל מצוידת בFusible פלט חיצוני מסוג ejection שמשמש כמכשיר הגנה ראשי. אם קONDנסטור בודד חווה כשל, קONDנסטורים מקבילים משחררים דרך נקודת הכשל. הפוזה והאלמנט הנמס של הקONDנסטור שניזוק עשויים להתפוצץ במהירות, מעבירים את החלק המושחת כדי להבטיח המשך פעילות הבנק.
עם זאת, אם לקONDנסטורים מתפתחים מעגלים פתוחים או תקלות אחרות, הם עשויים להמשיך לפעול ללא התפוצצות הפוזה. סיכון קASCADE קריטי: התפוצצות מוקדמת של פוזות סמוכות מפעילה תהליכים שרשרת. ניתוק יתר של קONDנסטורים גורם לאיזון העולה על הגבולות המתוכנים, בסופו של דבר גורם לכישלון של כל הפוזות בבנק. לדוגמה, בבנק קONDנסטורים 10kV מספר 2 של פאזה B בתחנת 220kV, קONDנסטור עם רק abweichung messung von 14% יזם כזו שרשרת, מה שהוביל לכישלון של כל קבוצת הפוזות.
מסקנה: כאשר מתרחשת התפוצצות של קבוצת פוזות, כל קONDנסטור חייב לעבור בדיקה ובדיקה אישית כדי לזהות:
- חדירת לחות פנימית
- תקלות ברכיבים/קצר מעגלים
- הידרדרות מבודדת
זה מזהה יחידות פגומות, מפחית את שיעור הכשלונות ומפחית סיכונים מבצעיים.
1.2 בחירת פריטי מבחן לחקירת כשל
1.2.1 בדיקה חזותית
מוקד הבדיקה:
- נקיון/ חלקות הגוף
- דליפות שמן, צלעות, סימני שחרור
- איבוד חום, שינוי צבע
- נפיחות/עיוות מקומי
“These issues indicate internal structural changes, component damage, or capacitance drift that create operational risks. Discoloration particularly necessitates disassembly for overheating/failure analysis, increasing inspection complexity.”
1.2.2 מדידת 저נגד מבודד בין הסוף לעטיפה
מטרת המבחן: זיהוי הידרדרות מבודדת כתוצאה מחשיפה לחומצה, הידרדרות או כשל על ידי מעקב אחר ירידת ההתנגדות.
ограничения: Этот тест служит только в качестве вспомогательного справочника, когда присутствуют другие дефекты.
Applicability:
- ✅ מבוצע על קONDנסטורים דו-קצה
- ❌ אינו נדרש עבור קONDנסטורים חד-קצה (המקרה פועל כאלקטורוד)
Testing method illustrated below:
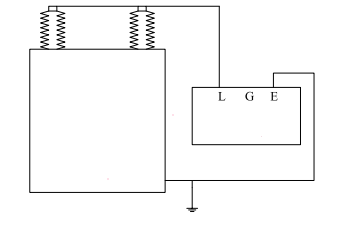
1.2.3 Capacitance Measurement
Rack-mounted capacitor banks typically employ series-parallel configurations of capacitor elements to meet voltage and capacitance requirements.
- Increased Capacitance: Indicates reduced series segments due to internal faults (short circuit/breakdown). Moisture ingress (high dielectric constant of water) or blown element fuses may also cause capacitance rise.
- Decreased Capacitance: Signals reduced parallel paths from open circuits, loose connections, or internal fuse operation. ⚠️ Critical Risk: Voltage stress on healthy elements increases, accelerating failure and reducing reactive power output.
- Oil Leakage Impact: Higher dielectric constant of oil vs. air causes measurable capacitance drift.
Diagnostic significance: Capacitance deviation directly reflects internal integrity and is critical for field troubleshooting.
Acceptance Range: ±5% to +10% of nameplate value.
Measurement Protocol:
- Rule out residual charge interference
- Repeat with multiple capacitance bridges
- If deviation persists:
- Disconnect fuse links
- Remove HV-side connections
- Re-measure. Consistent deviation confirms internal fault.
Case Study: 110kV Substation 10kV 11A Capacitor Bank (Unit B2)
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
|
Nameplate Capacitance (Cₓ)
|
8.03 μF
|
|
Measured (Cᵧ) with HV connected
|
10.04 μF
|
|
Measured (Cᵧ) after HV disconnection
|
10.05 μF
|
|
Deviation
|
+25.16%
|
|
Conclusion: Unit B2 exceeds tolerance limits → Failed.
|
|
1.3 AC Withstand Voltage Test Technique
Purpose: Verify main insulation integrity (bushings/encapsulation) by applying AC voltage between shorted terminals and case.
Test Value: Detects:
- Low oil levels
- Internal moisture
- Damaged bushings
- Mechanical defects
Terminal Handling:
- Short both terminals together
- Apply voltage between shorted terminals and grounded case
Industry Note: Routine AC withstand testing is often unnecessary due to capacitors’ inherent high terminal-case insulation strength.
2.Rational Selection of Capacitance Measurement Methods
Common Techniques:
|
Method
|
Typical Use Case
|
|
Ammeter/Voltmeter (I/V)
|
Field testing ★ Preferred
|
|
Digital Capacitance Meter
|
Field testing
|
|
Capacitance Bridge
|
Factory acceptance
|
I/V Method Superiority:
- Voltage advantage: Applied test voltage > capacitor’s operating voltage
- Detects masked faults: Activates breakdown points where:
- Failed elements retain residual insulation resistance
- Capacitance meters show false-normal readings
- Procedure: See Figure 2 (Voltage-controlled reactance testing)
|
Equipment Tag No.
|
B2
|
|
Nameplate Capacitance, Cₓ (μF)
|
8.03
|
|
Measured Cᵧ (μF) Before Disconnecting High-Voltage Lead
|
10.04
|
|
Measured Cᵧ (μF) After Disconnecting High-Voltage Lead
|
10.05
|
|
% Discrepancy (vs. Nameplate Value)
|
25.16%
|
3. Key Technical Points for Ammeter/Voltmeter Testing
3.1 Standard-Compliant Test Power Supply Waveform & Frequency
- Voltage selection: ≤5× rated voltage (based on source capacity & meter range)
- Frequency stability: Maintain steady sinusoidal waveform
- Measurement protocol:
- Stabilize voltage at rated value
- Synchronously record voltage, current, and frequency
- Calculate capacitance:
Cx=I2πfVC_x = \frac{I}{2\pi f V}Cx=2πfVI
- Critical requirements:
- Pure sine wave voltage (±3% THD limit)
- Frequency fluctuation ≤±0.5%
- Prefer line voltage (reduces 3rd harmonics)
Non-compliance risks >10% measurement error due to capacitor's XC∝1/fX_C \propto 1/fXC∝1/f characteristic.
3.2 Selection of High-Precision, Noise-Immune Instruments
- Minimum specifications:
- Accuracy class: 0.5 or better
- Electromagnetic compatibility: IEC 61000-4 compliance
- Case study - 220kV substation:
|
Instrument
|
Test Outcome
|
|
T51 AC/DC milliammeter
|
84 units show >20% deviation
|
|
T15 AC milliammeter
|
Deviation within limits
|
|
Root cause: T51 susceptibility to EMI from non-linear loads causes waveform distortion.
|
|
3.3 Controlled Voltage Ramp-Up Protocol
- Healthy capacitor response:
- Linear current rise with voltage increase
- Fault indicators:
- Current stagnation below 60V → cold solder joints
- Sudden current surge at >60V → weak insulation breakdown
Safety-critical procedure:
- Ramp voltage at ≤100 V/s rate
- Continuously monitor dIdV\frac{dI}{dV}dVdI gradient
- Abort if non-linear response detected
Rapid voltage application masks faults and risks catastrophic failure.
3.4 Safety Procedures
|
Step
|
Requirement
|
|
Pre/post-test discharge
|
Ground terminals with insulated rod (≥3×)
|
|
Safety distance
|
≥0.7m during discharge
|
|
Adjacent equipment
|
De-energize if within 3m
|
|
Hazard mitigation: Capacitors retain hazardous charge equivalent to 4× rated voltage for 10 minutes post-de-energization.
|
|
- Conclusive Guidelines
Accuracy determinants:
A[Test Accuracy] --> B[Visual Inspection]
A --> C[Power Supply Quality]
A --> D[Instrument Selection]
A --> E[Test Methodology]
A --> F[Safety Implementation]
Field-proven practices:
- Pre-test: Verify ambient EMI levels <30V/m
- During test:
- Record voltage/current waveforms (oscilloscope recommended)
- Validate linearity at 25%, 50%, 75%, 100% voltage steps
- Post-test:
- Cross-verify capacitance with 2 methods
- Trend results against historical data
Statistical finding: 68% of capacitor failures originate from moisture ingress or voltage stress - detectable through rigorous capacitance testing and IR monitoring.
Operational recommendations:
- Implement quarterly capacitance deviation trending (±3% alert threshold)
- Use IRIS(Infrared Inspection System) for thermal anomaly detection
- Maintain capacitor bank unbalance protection at <5% setting
This comprehensive protocol enhances grid reliability while reducing capacitor bank failure rates by ≥37% (per IEEE 1036 case studies).























