1. Pungway ng mga Temperature Controller sa Transformer
Karon, ang mga power transformers adunay duha ka pangunahon nga klase: ang oil-immersed ug dry-type transformers. Ang mga dry-type transformers gigamit pinaagi sa ilang daghang abilidad—tulad sa natural nga seguridad, resistance sa apoy, zero pollution, walay kinahanglan og pag-amping, low losses, minimal partial discharge, ug long service life—sa mga power plants, substations, airports, railways, intelligent buildings, ug smart residential communities.
Ang usa ka key advantage sa dry-type transformers mao ang ilang design life, na kasagaran mas taas sa 20 years. Ang mas matagal ang operational lifespan, ang mas baba ang total cost of ownership. Sa praktikal, ang safe operation ug longevity sa usa ka dry-type transformer labi nga depende sa reliability sa ilang windings. Ang usa sa primary nga kadahomon sa pag-abot sa failure sa transformer mao ang insulation degradation resulta sa winding temperatures nga mas taas sa thermal endurance limit sa insulation material.
Bisan pa, ang service life sa dry-type transformer kasagaran limited sa iyang "thermal life." Aron makamit ang maximum operational life, importante nga imonitor ang winding temperature gamit ang temperature control system ug implementar ang timely protective measures—tulad sa forced cooling o alarm warnings—kung kinahanglan.
2. Mga Klase sa Temperature Controllers sa Transformer
2.1 Sumala sa Temperature Sensing Method: Mechanical vs. Electronic
Ang mga mechanical temperature controllers mao ang expansion-type devices nga gigamit og oil-filled bulb isip sensing element, operasyon sumala sa principle sa thermal expansion ug contraction. Tungod sa ilang bulky oil bulb ug inconvenient installation, kasagaran gigamit sila lamang sa oil-immersed transformers.
Ang mga electronic temperature controllers gigamit og temperature sensors tulad sa resistance temperature detectors (e.g., Pt100, PTC) o thermocouples. Tungod sa ilang high technological sophistication, comprehensive functionality, high accuracy, ug user-friendly operation, ang mga electronic controllers karon giwasto nga gipamatok sa parehas sa oil-immersed ug dry-type transformers.
2.2 Sumala sa Installation Method: Embedded vs. External-Mounted
Ang mga embedded controllers direktang gipamatok sa clamping frame sa transformer (para sa mga unit nga walay enclosures) o integrated sa enclosure sa transformer.
Ang mga external-mounted (wall-mounted) controllers gipamatok sa walls (para sa non-enclosed units) o gipamatok sa outer surface sa enclosure sa transformer.
Ang mga dry-type transformers mogenerate og significant heat, low-frequency vibration, ug electromagnetic interference sa panahon sa operasyon—conditions nga severe nga impact sa embedded temperature controllers nga gipamatok sa clamping frames o within enclosures.
Gitawag nga ang mga electronic components, sama sa mga dry-type transformers mismo, adunay finite "thermal life." Ang embedded installation method significantly reduces the controller’s service life ug reliability. Kontra, ang mga external-mounted controllers effectively isolated gikan sa harsh environment, ensuring better protection ug longevity.
3. TTC Series Dry-Type Transformer Temperature Controller
Ang JB/T 7631-94 “Resistance Thermometers for Transformers” usa ka standard nga gihatagan sa China’s Ministry of Mechanical Industry niadtong 1994, specifically para sa temperature indicators ug controllers nga gipamatok sa dry-type transformers. Igiincorporate nia ang requirements gikan sa GB/T 13926-92 “Electromagnetic Compatibility for Industrial Process Measurement and Control Equipment.”
Ang TTC series temperature controllers compliant sa updated standard GB/T 17626-1998 “Electromagnetic Compatibility – Testing and Measurement Techniques” (equivalent to IEC 61000-4:1995).
3.1 Working Principle
3.1 Circuit Block Diagram & Temperature Sensing Principles (Pt100 and PTC)
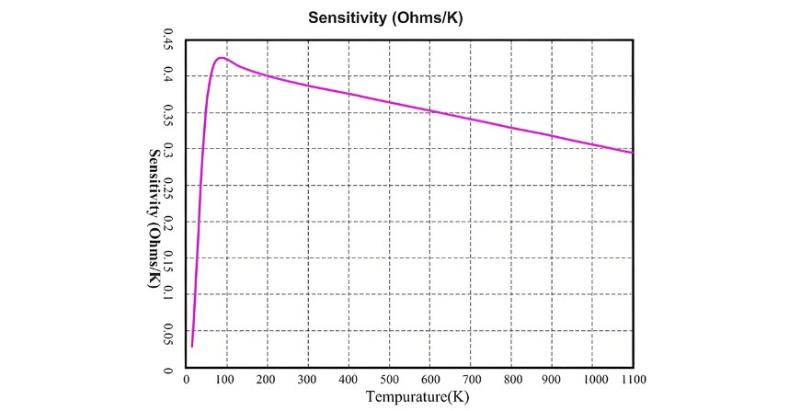
Ang Pt100 temperature sensor nagoperasyon sumala sa principle nga ang iyang electrical resistance magbabago approximately linearly sumala sa ambient temperature. Sumala sa resistance–temperature curve (right), ang resistance sa Pt100 platinum resistor madugay ug nearly linear nga mosaka samtang mosaka ang temperatura.
Ang temperature controller mogamit kini nga characteristic aron mobaton sa continuous, accurate temperature monitoring sa transformer. Ang displayed temperature value gikinabat direkta gikan sa measurements gikan sa Pt100 sensor.
Tungod sa iyang excellent repeatability ug one-to-one correspondence tali sa resistance ug temperature, ang Pt100 enables precise point-by-point temperature measurement, typically achieving an accuracy class of 0.5.
3.2 Ensuring Pt100 Temperature Measurement Accuracy
Ang Pt100 temperature sensor mahimo gigamit sa two-wire, three-wire, o four-wire configurations. Sa most industrial temperature control applications, ang three-wire connection gigamit tungod kay efektibo kini sa pag-compensate sa measurement errors resulta sa lead wire resistance.
Puliha: ang amplifier circuit kasagaran usa ka Wheatstone bridge. Sa manufacturing ug calibration, shorting links gipamatok alang sa adjustment. Pero sa real-world operation, kon gipamatok ang sensor cables, ang inherent resistance nila mag introduce og measurement errors. Ang three-wire configuration minimize kini nga error pinaagi sa balancing sa bridge circuit.
Bagama't ang kurba sa resistensya-temperatura sa Pt100 maayo usabon, dili kini perfekto linear. Aron mapadako ang akurate, ang atong mga temperature controller naghahatag og lima ka segmento alang sa 0–200°C Pt100 resistance-temperature curve. Sa dako sa matag segmento, gigamit ang straight line aron mapadugay ang tun-aw nga kurba pinaagi sa linear fitting, na nagpadako sa kabuok nga kasinatian sa pagsukol.
3.3 PTC Thermistor isip Alternative Sensor sa TTC-300 Series Controllers
Ang PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) thermistor usa ka temperatura sensor nga gigamit sa among TTC-300 series transformer temperature controllers. Ang mga PTC thermistors gihimo gikan sa barium titanate-based polycrystalline ceramic materials, doped aron makab-ot ang partikular nga "trip" o "switching" temperatures.
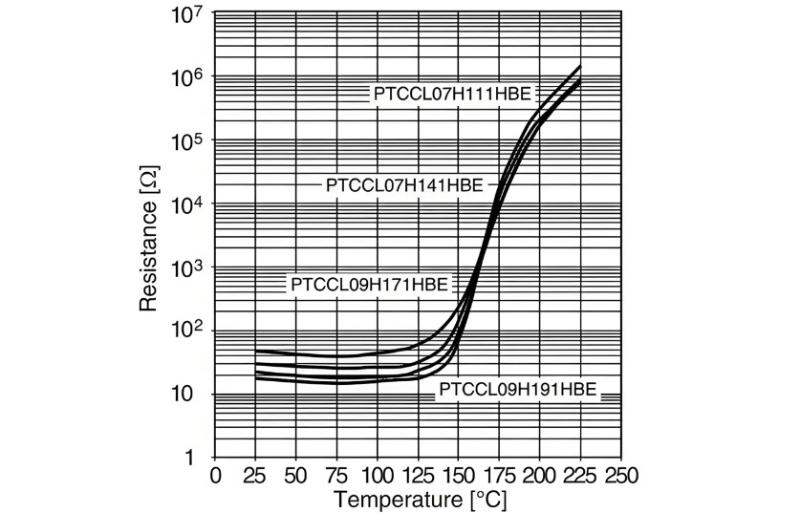
Kunbag-o sa platinum resistors (Pt100), ang PTC thermistors nagpakita og distinct nonlinear behavior: ang ilang resistensya giyahan sa relatyibong stable sa mas mababa nga temperatura apan nagpakita og sharp, almost step-like increase kon ang temperatura makarating sa predefined threshold—known as the Curie point o action temperature. Kini nga katangian gilumulop sa resistance-temperature curve sa ubos.
Gisurat, sa babaw sa action temperature, ang PTC resistance gibago gamay lamang sukad sa temperatura. Apan kon ang temperatura makadakpon ug lampa sa kritikal nga punto, ang resistensya magdagan dramatiko—sulod sa daghang orders of magnitude.
Ang operasyon nga prinsipyong PTC-based temperature detection mao ang pagdetect sa kini nga abrupt nga pagbago sa resistensya aron masayri kon ang specific nga temperatura threshold makarating. Taliwala, ang PTC sensors mahimong mosulti og usa ra ka temperatura point—dili sila mahimo mobigay og continuous, full-range temperature measurements sama sa Pt100.
Ang among produkto naggamit kini nga on/off characteristic sa PTC sensors aron implementar ang over-temperature alarms ug trip protection alang sa transformers. Aron masigurado ang konsistensiya, reliability, ug high quality sa produkto, kami naggamit og PTC components gikan sa Siemens–Matsushita Electronic Components Co., Ltd.
3.4 TC Temperature Sensing Principle
Ang temperature controller mogahin og temperatura signals gikan sa PTC ug Pt100 sensors pinaagi sa iyang internal circuitry ug mogamit og logical judgment aron masayri kon motrigger ba og over-temperature alarm o over-temperature trip signal. Kini nga dual-protection mechanism efektibo sa pagpreventa sa failures to act o false triggering.
Ang temperatura sa transformer windings (Phases A, B, C) ug core (D) gimonitor pinaagi sa Pt100 ug PTC sensors. Kon ang temperatura magbag-o, ang resistensya sa mga sensors magbag-o usab. Ang controller magconvert kini nga resistensya isip voltage signal, nga magproseso pinaagi sa filtering, analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion, ug advanced algorithms aron makalkula ang corresponding temperature value.
Batasan sa kini duha ka klase nga temperatura inputs:
Ang controller magdisplay sa channel number ug real-time temperature value sa front-panel screen.
Sa parehas, iya magapply og logical algorithms aron ikumpara ang measured temperature batasan sa user-defined setpoints. Kon ang temperatura lampa sa threshold, ang controller magactivate sa appropriate outputs—such as starting/stopping cooling fans, triggering alarms, o initiating a trip command.
Ang users mahimo mogamit sa front-panel buttons aron iconfigure ang system parameters—inclusive sa fan start/stop temperatures, core overheat alarm thresholds, ug uban pang settings.
Bisan pa, ang sistema nagperform sa continuous self-diagnostics. Kon may sensor failure o internal hardware fault sa temperature controller, iya magissue og audible ug visual alarms sama sa fault signal aron alertan ang operators.























