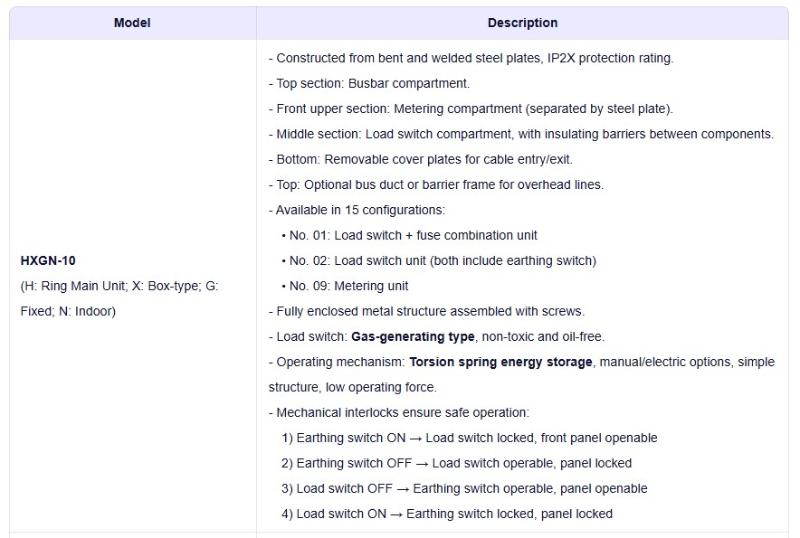
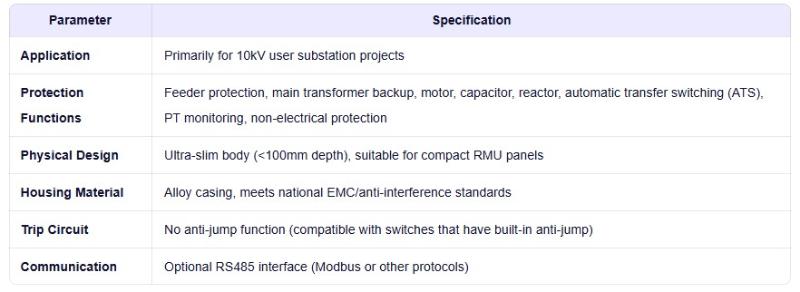
- Product
- Suppliers
- Manufacturers
- Solutions
- Free tools
- Knowledges
- Experts
- Communities
Search
-
Ingyenes eszközök
-
IEE Business ingyenes AI-alapú eszközöket kínál villamosmérnöki tervezéshez és energiaellátási költségvetés-tervezéshez paraméterek bevitelével és azonnali eredményekkel transformátorokkal kapcsolatban vezetékesítéssel motorokkal energiaszerelvények költségeivel stb világszerte mérnökök hitelesítették
-
-
Támogatás
-
IEE-Business támogatja a vezető megoldásokat vállalkozásokat és szakértőket - egy olyan platform kialakítása ahol az innováció találkozik az értékkelKiváló technikai tudásCsatlakozás és technikai ismeretek megosztása sponzoroktól származó bevételhezKiváló üzleti megoldásokCsatlakozás és üzleti megoldások létrehozása szponzoroktól származó bevétel eléréséhezKiemelkedő Egyéni SzakértőkTalánj megjelenítése támogatóknak jövő megszerzéséért
-
-
Közösség
-
Építsd fel szakmai közösségedKeresse meg és lépjen kapcsolatba iparági szakemberekkel, lehetséges partnerekkel és döntéshozókkal az IEE-Business növelése érdekébenSzemélyes hálózat kibővítéseCsatlakozzon iparági szakemberekhez, lehetséges partnerekhez és döntéshozókhoz a növekedés felgyorsítása érdekébenTovábbi szervezetek felfedezéseCéltársaságok, együttműködők és iparági vezetők feltárása az IEE-Business új üzleti lehetőségeinek kibontakoztatásáhozDiverzifikált közösségekhez csatlakozásVéleményeket cserélhetsz, iparági információkat oszthatsz meg és erőforrásokat használhatsz fel hatékonyságod növelése érdekében
-
-
Együttműködés
Partner
-
-
Csatlakozás az IEE Business Partner ProgramhozÜzleti Növekedés Támogatása – Technikai Eszközöktől a Globális üzleti kiterjesztésig
-
-
IEE Business
-
magyar nyelv
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
További szervezetek felfedezése
-
magyar nyelv
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
Ingyenes Elektrotechnikai Számológépek
További szervezetek felfedezése