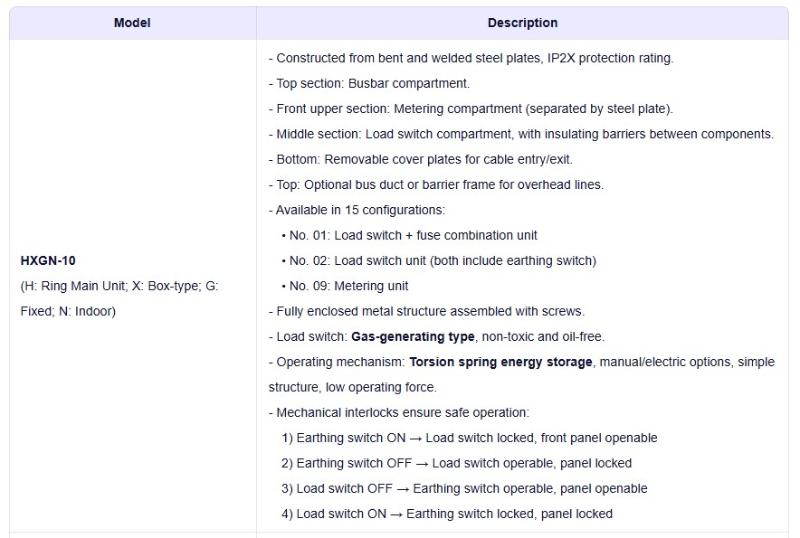
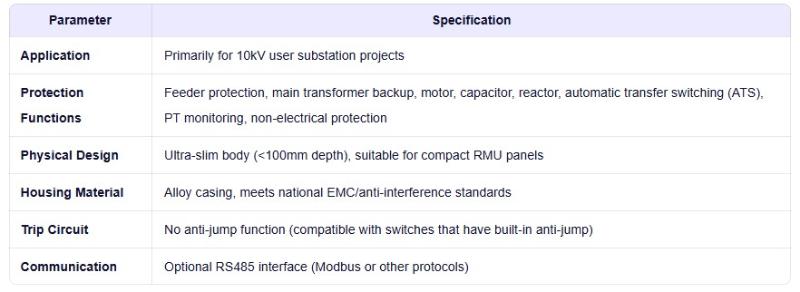
- Product
- Suppliers
- Manufacturers
- Solutions
- Free tools
- Knowledges
- Experts
- Communities
Search
-
Vabad tööriistad
-
IEE Business pakub tasuta, AI-ga töötavaid vahendeid elektroonikainseneri disaini ja elektriostu eelarve koostamiseks: sisestage oma parameetrid, klõpsake arvutamise nuppu ja saage kohe tulemused trafode, juhtmete, mootorite, elektriseadmete kulude jms kohta — usaldatud üle maailma insenerite poolt
-
-
Toetus ja sponsorlus
-
IEE-Business toetab juhtivaid lahendusi ettevõtetele ja ekspertidele lootes platvormile kus innovatsioon kohtub väärtusegaVäga hea tehniline teadmisteLiitu ja jaga tehnilist teadmist, et teenida sponsooridelt tulu.Värskeid äri lahendusiLiitu ja lo äri lahendusi sponsori tulu teenimiseksErakordsed isiklikud eksperdidEsitage oma talendit sponsoreile võidake oma tuleviku!
-
-
Kogukond
-
Looge oma professionaalne ühendusLeidke ja ühenduge IEE-Businessiga, et arendada oma äriLaienda oma isiklikku võrgustikkuÜhendu oma valdkonna kolleegidega, potentsiaalsete partnerite ja otsustajatega, et kiirendada oma kasvu.Avasta rohkem organisatsiooneSihtfirma, koostööpartnerite ja tööstusjuhtide uurimine uute äri võimaluste avamiseksLiitu mitmekesiste kogukondadegaTegele teemakohaste arutelude, tööstusharude vahetustega ja ressursside jagamisega, et suurendada oma mõju
-
-
Meiega koostöö
Partner
-
-
Liitu IEE Business Partner ProgrammisEttevõtte kasvu tugevdamine teknilistest tööriistadest kuni globaalse bisneslaienemiseni
-
-
IEE Business
-
Eesti keel
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
Erakordsed isiklikud eksperdid
Laienda oma isiklikku võrgustikku
-
Eesti keel
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
Erakordsed isiklikud eksperdid
Laienda oma isiklikku võrgustikku