Tungod sa segundo bahin sa siglo sa 19, ang tanging materyales nga insulate sa maayo ang mga linya sa pagpapadala sa mataas nga kuryente mao ang ceramika ug bato. Sumala sa 1940s, tungod sa pag-ila sa mga polymer materials, dili na ang ceramika ug bato ang gipili, nagpuyo ang mga nasod sa Europa ug Amerika aron magsugyot og pananaliksik sa mga polymer insulators. Human niini, gibutang ang damo nga mga pag-aaral sa mga pisikal nga katangian, elektrikal nga karakteristikas, dugay nga reliabilidad, ug pinakamaayo nga hugis sa mga electrical insulators, ug nagpadayon sa pag-improve sa efektibidad sa pagbuhat.
Sa mga high-molecular-weight materials nga makapalit sa ceramika ug bato, ang silicone rubber nakaipil ang praktikal nga paggamit sa 1960s ug nakatun-an sa uban nga mga polymer. Ang mga silicone rubber insulators adunay daghang abilidad higayon sa ceramic insulators: unang, sila mas light, mas sayon sa pagbutang, ug mas safe; ikaduha, ang mga ceramic insulators masusulob sa pagkabagbag sa impact, pero ang mga silicone rubber insulators makapahimulos sa mekanikal nga shock sama sa pagbagon sa mga sasakyan sa mga poste sa utility.
Bag-o may iba pang polymer materials usab nga adunay ang nabanggit nga abilidad, ang silicone rubber lang ang minimoy nga naghatag og kalambigit sa kalimutan. Ang mga polymer insulators water-resistant, nagpapahinay sa leakage current ug surface arcing gikan sa mga tubig. Gihapon, ang hydrophobicity sa silicone rubber insulators mas sayon nga mobalik kon parehas sa uban nga mga polymer insulators, kasagaran sila usa ka matibay nga materyal nga angay sa dugay nga paggamit sa harsh nga environment. Kini nga artikulo ipahibalo ang mga katangian sa silicone rubber nga gamiton sa high-voltage electrical insulation ug ipakilala ang kamakaron nga mga trend sa pagbutang.
1 Katangian sa Silicone Rubber
1.1 Kimikal nga Katangian sa Siloxane Bond
1.1.1 Kimikal nga Stable Bond
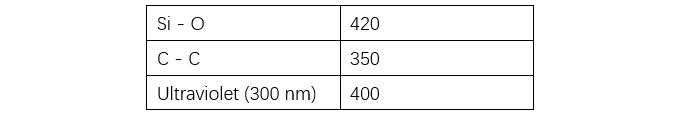
Ang backbone sa silicone rubber gitukod sa siloxane (Si-O) bonds. Tungod sa significant nga difference sa electronegativity tali sa Si (1.8) ug O (3.5), gihatag ang polarized structure, gisubli sa Figure 1 (omitted), nga nagpakita ionic bond characteristics. Konsekwensiya, ang bond energy sa Si-O mas taas kay sa C-C (tan-aw Table 1). Gihapon: (1) tungod sa ionic nature sa main chain, ang polarity sa methyl C-H groups sa side chains gireduce, mas sayon nga mogamit sa attack sa uban nga molecules, resulta ang excellent chemical stability; (2) tungod sa Si dili readily mag-form og double or triple bonds, ang main chain mas sayon nga mobreakdown, ug ang Si-C bonds resulta labi nga stable, gihatagan pa ang stability sa backbone sa silicone rubber.
1.1.2 High Flexibility Polymer
Ang bond angle sa siloxane (Si-O-Si) mas taas (130°–160°), naghatag sa iya mas taas nga freedom kay sa organic polymers (C-C bond angle ~110°). Gihapon, ang Si-O bond length (1.64 Å) mas taas kay sa C-C (1.5 Å). Kasagaran ang overall polymer molecule mas mobile ug mas sayon mopagbago.
1.1.3 Helical Structure
Tungod sa helical structure sa polysiloxane, ang siloxane bonds sa main chain gihatud sa loob pinaagi sa ionic attraction, samtang ang outer side gitukod sa methyl groups nga adunay weak intermolecular interactions, resulta ang weak intermolecular forces.
1.2 Properties of Silicone Rubber
Baton sa kimikal nga katangian gisulti sa Section 1.1, ang silicone rubber adunay mosunod nga properties angay sa high-voltage electrical insulation.
1.2.1 Heat and Cold Resistance
Tungod sa iyang high bond energy ug excellent chemical stability, ang silicone rubber adunay mas maayo nga heat resistance kay sa organic polymers. Gihapon, tungod sa weak intermolecular forces, adunay low glass transition temperature ug excellent cold resistance. Kaylapos, ang iyang performance maasoy wala mahimong mapaslan sa geographic region diin gigamit.
1.2.2 Water Resistance
Ang surface sa polysiloxane gitukod sa methyl groups, naghatag sa iya hydrophobic properties ug mas maayo nga water resistance.
1.2.3 Electrical Properties
Ang silicone rubber adunay mas kaunti nga carbon atoms kay sa organic polymers, resulta ang excellent arc resistance ug tracking resistance. Gihapon, bisan kapagburn, gi-form ang insulating silica, nagpahimulos pa sa superior electrical insulation performance.
1.2.4 Weather Resistance
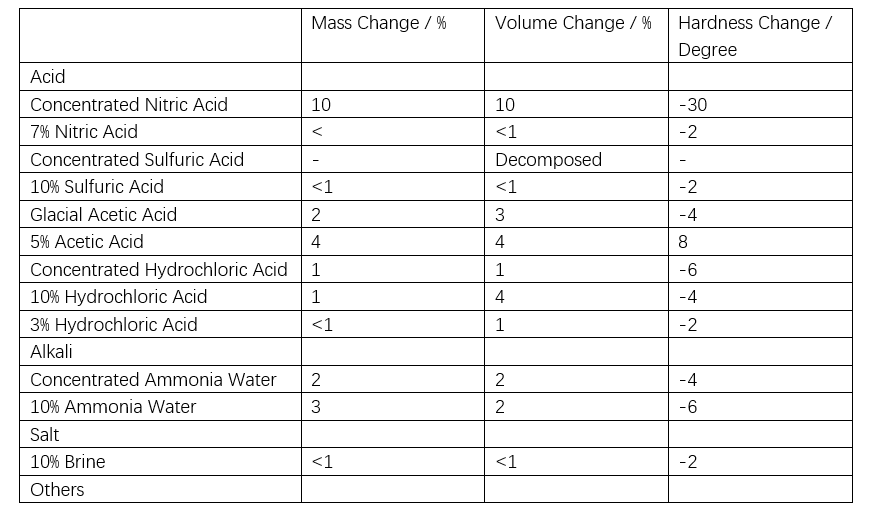
Gisubli sa Table 1, ang bond energy sa siloxane mas taas kay sa energy sa ultraviolet (UV) light, nagpahimulos sa resistensya sa UV-induced aging. Sa accelerated ozone resistance tests, ang organic polymers mogamit sa seconds hangtod sa hours, samtang ang silicone rubber nagpakita sa slight reduction sa strength human sa apat ka semana sa aging, walay cracking natun-an, nagpahimulos sa excellent ozone resistance (tan-aw Table 2). Ang acid rain usa ka mixed ionic solution nga adunay pH nga humoltog sa 5.6. Gibuhat ang 500x concentrated artificial acid rain test pinaagi sa solution listahan sa Table 3. Ang silicone rubber nagpakita sa excellent chemical resistance gisubli sa Table 4. Bisag exposed sa mixed solutions sama sa acid rain, posible nga maghatag og uban nga changes, apan ang impact expected nga kaunti ra.
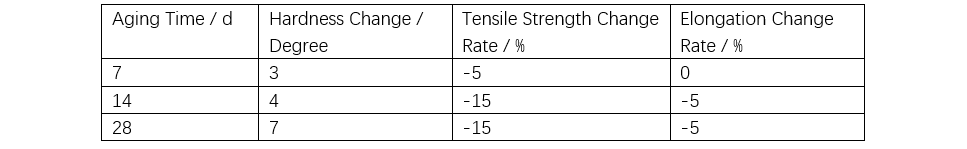
Note: Sa room temperature, pinaagi sa ozone concentration nga 200 ppm ug 50% tensile strain applied sa rubber, ang surface walay cracking human sa 28 days sa aging.
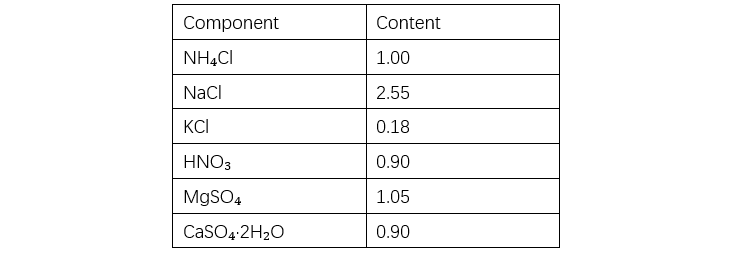
Unit: g per 2 L deionized water.
1.2.5 Permanent Deformation
Ang silicone rubber nagpakita sa mas maayo nga permanent deformation characteristics (kasagaran permanent elongation ug compression set) sa room ug elevated temperatures kay sa organic polymers.
2 Classification of Silicone Rubber
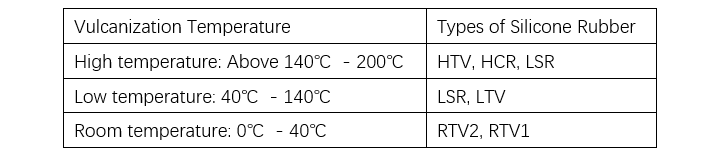
Ang silicone rubber mahimong isulat bilang solid ug liquid types batasan sa iyang estado human sa vulcanization, ug mahimong isulat bilang peroxide curing, addition curing, ug condensation curing types batasan sa vulcanization mechanism. Ang primary difference tali sa solid ug liquid silicone rubber nahimong molecular weight sa polysiloxane. Ang solid silicone rubber mahimo mong vulcanize pinaagi sa peroxide curing o addition curing, ug commonly referred to as high-temperature vulcanizing rubber (HTV) o heat-cured rubber (HCR) (tan-aw Tables 5 ug 6).
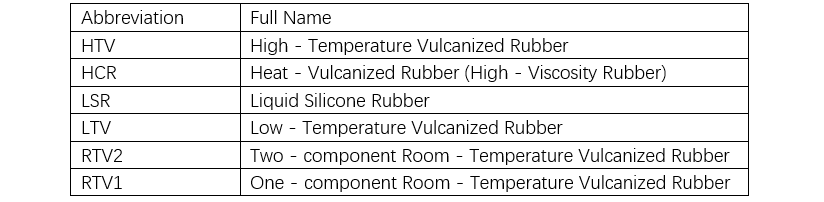
Bisan ang liquid silicone rubber cured pinaagi sa addition reaction mahimo usab mong vulcanize sa room temperature, designado kini isip liquid silicone rubber (LSR), low-temperature vulcanizing rubber (LTV), o two-part room-temperature vulcanizing rubber (RTV), depende sa processing method ug curing temperature. Sa manufacturing sa polymer insulators, common ang injection molding ug casting processes.
One-component condensation-type (moisture-cure) silicone rubber mahimong gamiton sa construction sealants, same sa electrical ug electronic products. Sa electrical applications, common ang solvent-diluted room-temperature vulcanizing (RTV) silicone rubber coatings nga gi-spray sa ceramic insulators isip protective materials.
2.1 Silicone Rubber with Aluminum Trihydroxide (ATH)
Mahimo mong kuha ang good tracking resistance ug arc resistance sa silicone rubber pinaagi sa pag-ila sa high loading sa aluminum trihydroxide (ATH). Ang silicone rubber filled sa 50 parts by mass sa ATH nagpakita sa acceptable resistance sa high-voltage (4.5 kV) tracking, samtang adunay excellent arc resistance, weather resistance, salt fog resistance, ug acid rain resistance, angay isip insulating material sa areas nga adunay severe salt fog. Apan, tungod sa high ATH loading, ang materyal nagdula sa high viscosity (poor plasticity) ug low mechanical strength.
2.2 Silicone Rubber without Aluminum Trihydroxide (ATH)
Sa inland areas sa Europe ug similar regions nga adunay minimal salt fog ug low pollution levels, mahimo mong gamiton ang silicone rubber without ATH filler. Sa mga kaso, ang appropriate selection sa base silicone rubber, surface treatment sa fumed silica, ug addition sa compounding agents nga enhance tracking resistance mahimo mong improve hydrophobicity aron mapaslan ang high-voltage tracking resistance requirements. Comparing sa ATH-filled silicone rubber, ang type niini adunay lower viscosity ug superior mechanical ug electrical properties.
2.3 For Outdoor Cable Accessories
Bisag exposed sa harsh nga environment, ang outdoor cable accessories kinahanglan adunay good tracking resistance. Mahimo mong achieve ang materials nga adunay low permanent elongation pinaagi sa paggamit sa polymers nga optimized crosslinking density, angay sa ambient-temperature shrinkable (cold-shrink) products.
2.4 For Indoor Cable Accessories
Walay posibilidad nga ang indoor cable accessories mogamit sa salt fog, kaya ang tracking resistance dili gyud required. Apan, bisan unsa, sa paggamit sa ambient-temperature shrinkable (cold-shrink) applications, kinahanglan pa gyud ang low permanent deformation characteristics.
2.5 Coating Applications
Pag-spray sa silicone rubber coatings sa heavily polluted areas mahimo mong maintain ang good hydrophobicity sa long term. Ang coatings mahimo usab mong apply sa already-installed insulators depende sa pollution levels, enabling continued service ug cost savings. Recent reports nagpakita nga ang coating sa silicone rubber insulators mahimo mong enhance pa ang retention sa hydrophobicity. Karon, duha ang primary types exist: coated insulators ug rubber-type insulators.
3 Conclusion
Kini nga paper ipahibalo ang silicone rubber materials para sa polymer insulators. Ongoing research ug testing gibuhat sa iba't ibang institusyon ug manufacturers. Bisag high reliability mahimo mong demonstrate pinaagi sa durability ug uban pang performance tests, ang application sa silicone rubber insulators expected nga expand pa.


























