1. Patalim sa Klasipikasyon sa Cable nga Flame-Retardant
Ang sistema sa pamantayan sa flame-retardant gisulay sa duha ka pangunahon nga kategoriya. Ang unang kategoriya mao ang "Klasipikasyon sa Burning Behavior para sa Electric ug Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247. Ang mga cable nga sumala sa sistemang pamantayan ini gamiton sa dako nga populasyon sama sa high-speed railways ug subways. Ang pamantayan niini nagpatuman sa mahigpit nga mga parametro sama sa density sa usok, heat release, ug total smoke production, ug ang mga cable adunay paggamit sa low-smoke, halogen-free materials.
Ang ikaduhang kategoriya mao ang "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666. Bago mapasabot ang GB 31247, ang pamantayan niini gamiton sa tanang tipo sa mga pasilidad sa China. Ang sistema sa GB/T 19666 usab naghatag og mga balore sa mga parametro sama sa density sa usok, ug sa bidding, madalas maghatag og daghang prefix sama sa WD (low-smoke, halogen-free). Ang nakaugalingong test standards para sa cable flame-retardant ratings makita sa table sa ubos:
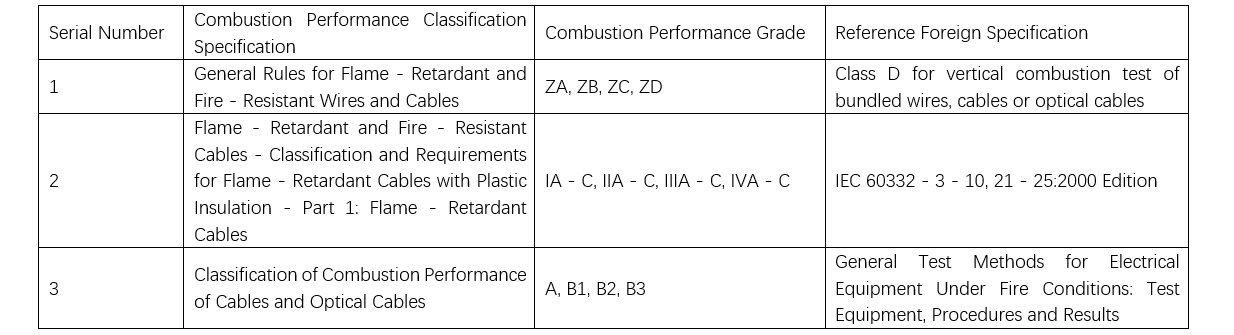
Klasipikasyon Standard para sa Item 1: Ang standard "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666 gigamit ang ZA, ZB, ZC klasipikasyon nga kasinat-on sa power design institutes. Apan ang iyang gireferensyahan nga test method, "Test on the vertical flame propagation for bunched wires or cables under fire conditions – Part 3: Test methods for bunched wires or cables" GB 18380.3-2001, gipawas na. Ang test standard niini gipahigayon pinaagi sa IEC 60332-3-25:2000, "Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions – Part 3-25: Test for vertical flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched cables – Category D."
Klasipikasyon Standard para sa Item 2: Ang standard "Flame-retardant and Fire-resistant Cables – Part 1: Flame-retardant Cables" GA 306.1-2007, migkategorya sa cables batas sa updated test methods GB 18380.31~36-2008, nga migbatasan sa GB 18380.3-2001. Ang ilang pipila ka distinksiyon mao ang pag-inclusion sa daghang criteria sama sa toxicity sa usok (GB 20285), light transmittance, ug corrosion resistance, mas nadugangan pa ang A, B, ug C classes ngadto sa lima ka distinct grades.
Klasipikasyon Standard para sa Item 3: Ang "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247 mao ang pinakabag-o nga standard. Ang iyang corresponding test method mao ang "Flame spread, heat release and smoke production characteristics of cables or optical fiber cables in fire conditions" GB 31248, nga nagreferensiya sa EN 50399:2011, "Common test methods for cables under fire conditions – Measurement procedures of heat release and smoke production for the test of vertical flame spread of bunched wires and cables – Apparatus, procedure and general results." Ang key difference mao ang pag-evaluate sa flame spread, total heat release, peak heat release rate, ug total smoke production. Ang criteria sa duha ka klasipikasyon system giingon nga walay parehas. Ang GB 31247 system (B1 class) nagpasabot sa low-halogen ug low-smoke characteristics, mao nga ang klasipikasyon dili direkta equivalent. Kahit ang "B" class sa ZA/ZB/ZC system wala makapasa sa requirements sa B1 class.
2. Rason Kung Paano Maoy Wala sa B1 Class ang High-Voltage Cables
2.1 Kulang sa Low-Smoke, Corrosion-Resistant Materials
Ang pag-abot sa low-smoke performance kasagaran gibutangan sa bituminous paint. Apan, ang bituminous paint wala sumala sa corrosion resistance requirements, ug ang paggamit niini wala pay maopay sa European standards. Busa, ang low-smoke performance criterion wala makapasa. Ang high-voltage power cables gigamit sa metallic aluminum sheath nga may bituminous anti-corrosion structure, nga magbuhat sa dako nga usok sa combustion. Taliwala sa abroad, ang bituminous paint o hot-melt adhesive kasagaran gigamit, ang struktura wala pay gibutangan sa domestic manufacturer o gigamit sa engineering project. Busa, ang material field sa high-voltage power cable outer sheaths naglimita sa abilidad sa pag-abot sa low-smoke performance required sa B1 class.
2.2 Pagbaba sa Insulation Resistance sa Low-Halogen Cables
Ang importante nga kalainan tali sa high-voltage ug medium-voltage power cables mao ang pagpipili sa outer sheath material. Tali sa high current capacity, high overvoltage, ug single-core design sa high-voltage cables, ang outer sheath kinahanglan may excellent insulation properties alang sa operational safety. Busa, ang outer sheath sa high-voltage cables gisulay isip "insulation-grade," samtang ang medium-voltage cables gigamit "sheath-grade" material.
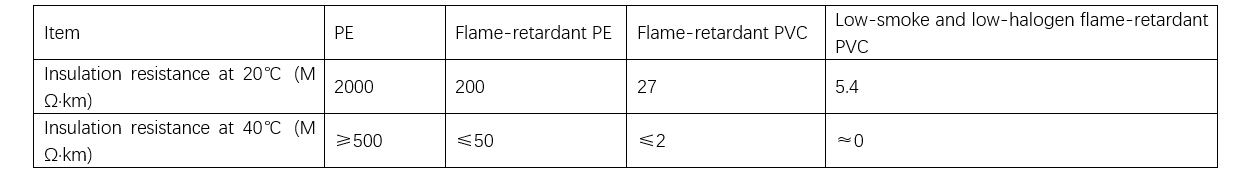
Pero, ang low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds adunay dako nga amount sa inorganic flame retardants, nga magresulta sa relatively poor insulation resistance sa sheath. Ang kasamtangang sheath material insulation performance sumala sa order: PE ≥ Flame-retardant PE ≥ PVC ≥ Low-smoke, halogen-free series. Tali sa niini, ang kasamtangang high-voltage cable standards sama sa GB/T 11017 ug GB/T 18890 wala pa gipasabot ang low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds sa ilang standard systems. Sa katitikan, sa medium-voltage cables, diin ang requirements sa sheath insulation performance wala ka strict, ang low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds gipasabot na sa standard system.
Ang power grid companies miorganisa og daghang cable industry conferences, tungod sa poor performance sa duha ka key indicators: ang water absorption rate sa outer sheaths sa saturated water absorption conditions ug ang insulation resistivity sa saturated water absorption conditions.
Ang fire prevention situation sa high-voltage power cable tunnels severe. Kasamtangang, ang high-voltage cables kasagaran gigamit sa flame-retardant models. As the name suggests, ang flame-retardant materials mao ang conventional sheath materials nga adunay added formulations sama sa flame retardants, nga nagdugang sa materials og flame-retardant properties. Ang flame-retardant performance sa common sheaths makita sa Table 3.
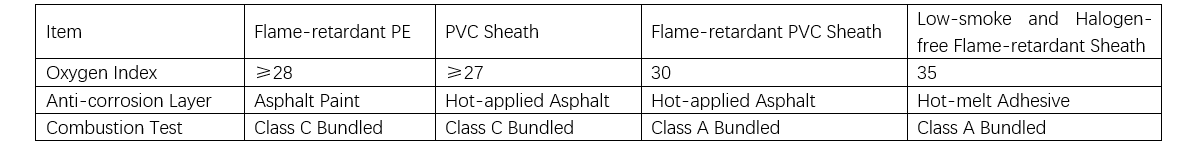
Tali sa example sa PE sheath, ang flame-retardant PE mao ang standard PE sheathing material nga adunay added flame retardants. Ang flame retardants gisulay sa inorganic ug organic types. Kasamtangang, ang most products sa market kasagaran gigamit sa inorganic flame retardants, nga adunay common types sama sa magnesium oxide ug aluminum oxide. Kini nga materials ready to absorb moisture ug undergo hydration reactions sa normal conditions. Busa, ang sheathing materials kasagaran immediate put into production human natapos ang procurement; otherwise, ang moisture absorption kasagaran mogenerate sa defects sama sa voids sa extrusion. Only after the flame retardant particles micronized, undergo surface modification, ug enhanced sa material compatibility, ang flame-retardant sheathing compounds makapahimulos sa good processability.
Ang waterproof cables kasagaran refer sa cables nga adunay complete, sealed metallic sheath. Kini nga plastic sheath gigamit isip waterproof layer, ang moisture kasagaran mopasok sa cable pinaagi sa plastic. Ang moisture ingress mao ang slow process. Sa actual cable operation, ang sheath surface temperature kasagaran molihok hangtod 60°C, nga mag-accelerate sa moisture penetration. Busa, sa newly commissioned cable sheaths, ang insulation resistance kasagaran sumala sa requirements. Pero, human sa period sa operation, ang sheath insulation resistance sa daghang lines mobaba gyud, ug ang problema kasagaran nakit-an sa several months to about a year. Human ang sheath insulation resistance mobaba hangtod sa certain level, ang rate of decline kasagaran stable ug mobaba gyud.
2.4 Poor Crack Resistance sa Low-Halogen Cables
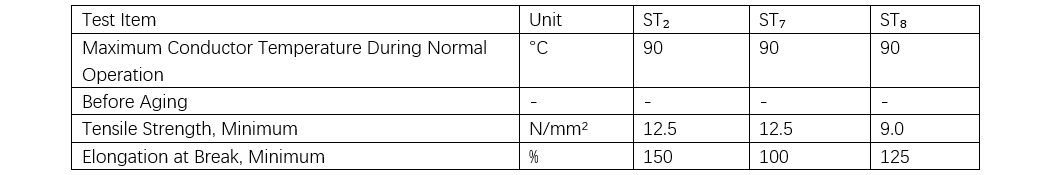
Sa Table 5, ST2 refers to PVC, ST7 to PE, ug ST8 to halogen-free, low-smoke material. Gikan sa perspective sa sheath mechanical properties, ang tensile strength ug elongation at break sa halogen-free, low-smoke materials significantly inferior. Ang installation sa halogen-free, low-smoke cables kasagaran strict, lalo na sa outdoor areas sa northern regions, tungod kay ang sheaths prone to cracking sa low temperatures ug posible mopasok sa cracking sa operation. Daghang similar quality incidents napahimulos na sa medium- ug low-voltage cables sa China. Ang some construction projects kasagaran gigamit halogen-free, low-smoke cables sa winter, partly because ang work conducted indoors where temperatures higher.
Ang halogen-free, low-smoke cables kasagaran gigamit sa indoor buildings ug densely populated areas sama sa stations, subways, ug public buildings. Ang power compartment sa utility tunnel wala belong sa densely populated area.
3 Conclusion
Batasan sa above analysis, ang halogen-free, low-smoke materials perform worse than the current insulation-grade flame-retardant sheathing materials ug more prone to problems. Tungod niini, ang current high-voltage cable standards sama sa GB/T 11017 ug GB/T 18890 wala gipasabot ang halogen-free, low-smoke sheathing materials sa ilang standard systems.
Ang "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247 strengthens fire behavior control. Ini appropriate sa densely populated areas sama sa subways ug high-speed rail stations, diin adunay dako nga combustible materials, tungod sa safety considerations sa life ug property. Ang most cables used sa areas niini medium- o low-voltage, diin ang electrical performance requirements wala ka strict as for high-voltage cables.
Importante nga butangan sa atensyon nga ang Class B rating sa "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666 wala equivalent sa B1 rating sa "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247. Ang duha ka standards adunay completely different fire performance criteria ug intended application areas. Dili sila dapat interchangeable. Recommended ang use sa high-voltage cables meeting GB/T 19666 Class B, ug not recommended ang use sa high-voltage cables meeting GB 31247 B1 o B2 ratings. Although both labeled "B," sila belong sa different standard systems, resulta sa completely different performance outcomes. Using high-voltage cables meeting GB 31247 B1 o B2 ratings maghatag og enormous pressure sa construction ug operation & maintenance departments.
Given the stringent fire protection requirements in power tunnels, after upgrading the flame-retardant rating to Class B:
Para sa conduits o direct burial installations diin wala required ang flame retardancy, mahimo ang selection sa PE outer sheaths (without flame retardant additives, providing stable insulation resistance).
Para sa high-voltage cables installed in tunnels, recommended ang PVC outer sheaths (ang disadvantage mao ang release sa toxic gases during combustion; ang advantage mao ang formulation can enhance water resistance, ug ang insulation resistance mas stable compared sa Class B flame-retardant PE cables).
Furthermore, recommended ang prompt initiation sa joint research sa sheath materials ug structures aron fundamentally resolve ang conflict tali sa insulation resistance ug flame retardancy.

























