1. Ma'adancin Kable mai Yawanci Tsirriyar
An koyar ma'adancin tsirriyar zuwa duwata. An koyar da karkashin "Ma'adancin Tsirriyar Da Turu Masu Bincike" GB 31247. Kable da take da wannan ma'adancin tsirriya suna yi amfani da su a wurare da mutane masu yawan adawa kamar hanyar tsiro daga cikin kasa da kwararren magunguna. Wannan ma'adancin tsirriya ya ba da shiga da saukar da abubuwan da kamar hanyar ruwan bincike, kisan karfi da kuma kadan ruwan bincike, kuma kable suna yi amfani da abubuwan da kamar hanyar ruwan bincike da kuma halogen-free.
Karkashin karshe na koyar da karkashin "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666. A lokacin da bayan bayan bayar da GB 31247, wannan ma'adancin tsirriya ta yi amfani da su a wurare da duk wuri a Najeriya. Ma'adancin tsirriya na GB/T 19666 tana da muhimmanci da hanyar ruwan bincike, kuma a lokacin da zabe, ana iya dogara siffar da kamar hanyar WD (low-smoke, halogen-free). Duka cikin kable da ke da shiga da ma'adancin tsirriya ta kula ne a cikin jerin:
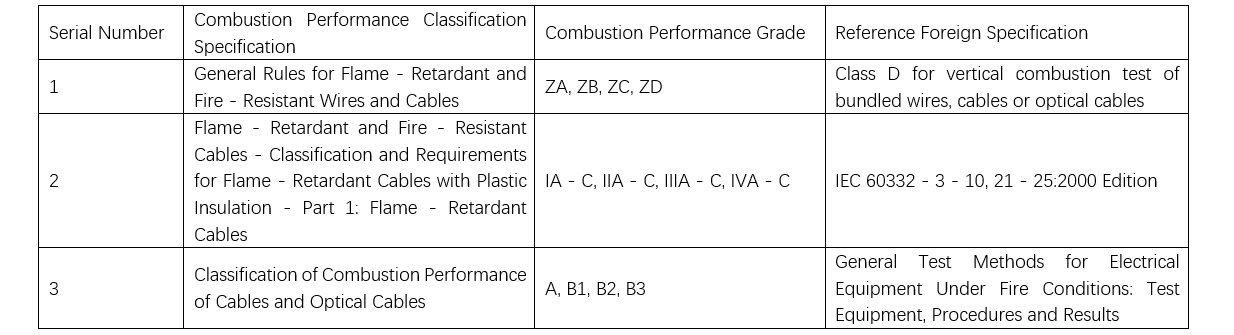
Ma'adancin Tsirriya na Item 1: Ma'adancin tsirriya "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666 tana da ZA, ZB, ZC da aka sanar da su a wurare da power design institutes. Amma, rikitarin yanayin da aka dogara da ita, "Test on the vertical flame propagation for bunched wires or cables under fire conditions – Part 3: Test methods for bunched wires or cables" GB 18380.3-2001, ta ci gaba. Wannan rikitarin yanayin ta kasance da IEC 60332-3-25:2000, "Tests on electric and optical fibre cables under fire conditions – Part 3-25: Test for vertical flame spread of vertically-mounted bunched cables – Category D."
Ma'adancin Tsirriya na Item 2: Ma'adancin tsirriya "Flame-retardant and Fire-resistant Cables – Part 1: Flame-retardant Cables" GA 306.1-2007, tana koyar kable da ke da shiga da rikitarin yanayin da aka dogara da su, GB 18380.31~36-2008, wanda ta kula da GB 18380.3-2001. Muhimman sakamakon da aka dogara da ita sun hada da toxicity da ruwan bincike (GB 20285), light transmittance, da kuma corrosion resistance, wanda tana koyar kable da ke da shiga da A, B, da C classes zuwa dubu masu dukkan addinin da suka dogara da su.
Ma'adancin Tsirriya na Item 3: "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247 tana da shiga da rikitarin yanayin da aka dogara da ita, "Flame spread, heat release and smoke production characteristics of cables or optical fiber cables in fire conditions" GB 31248, wanda ta kula da EN 50399:2011, "Common test methods for cables under fire conditions – Measurement procedures of heat release and smoke production for the test of vertical flame spread of bunched wires and cables – Apparatus, procedure and general results." Sakamakon da aka dogara da ita sun hada da flame spread, total heat release, peak heat release rate, da kuma total smoke production. Bayanai da ke da shiga da wannan ma'adancin tsirriya na B1 class tana da muhimmanci da low-halogen da kuma low-smoke characteristics, saboda haka, kable da ke da shiga da B1 class ba a iya kula da B class na ZA/ZB/ZC system.
2. Dalilai Da Ba Yi Amfani Da Class B1 Don Kable Masu Karfi
2.1 Rikicin Abubuwan Da Ba Sai Low-Smoke Da Kuma Corrosion-Resistant
Yadda ake bukatar low-smoke performance, har yanzu an iya amfani da bituminous paint. Amma, bituminous paint ba ta tabbata da rikicin corrosion resistance, kuma an iya amfani da ita a tarihin European standards. Saboda haka, ba za a iya tabbatar da low-smoke performance. Kable masu karfi suna amfani da metallic aluminum sheath da bituminous anti-corrosion structure, wanda tana yi ruwan bincike da kyau a lokacin da take da yawanci. Amma, a waje, an iya amfani da bituminous paint ko hot-melt adhesive, wanda ba a yi amfani da shi a Najeriya ko kuma a watsa wuri. Saboda haka, abubuwan da ke da shiga da outer sheaths na kable masu karfi suna ri kula da low-smoke performance da ke da shiga da B1 class.
2.2 Tabbatar Da Insulation Resistance Da Kable Masu Low-Halogen
Tsunanka da ke da shiga da kable masu karfi da kable masu tsakiya na wani babban matsala ta shiga da material da ke da shiga da outer sheath. Saboda kisan karfi da kuma single-core design na kable masu karfi, outer sheath ya bukata da insulation properties da ke da shiga don kula da operational safety. Saboda haka, outer sheath na kable masu karfi tana da shiga da "insulation-grade," amma kable masu tsakiya suna amfani da "sheath-grade" material.
Amma, low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds suna da inorganic flame retardants da kuma insulation resistance da ke da shiga. Current sheath material insulation performance follows the order: PE ≥ Flame-retardant PE ≥ PVC ≥ Low-smoke, halogen-free series. Saboda haka, current high-voltage cable standards such as GB/T 11017 and GB/T 18890 have not incorporated low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds into their standard systems. In contrast, for medium-voltage cables, where the requirements for sheath insulation performance are less stringent, low-smoke, halogen-free sheathing compounds have already been included in the standard system.
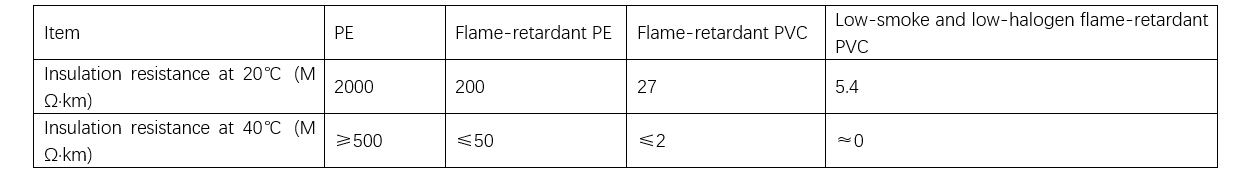
Power grid companies have organized multiple cable industry conferences, primarily due to the poor performance of two key indicators: the water absorption rate of outer sheaths under saturated water absorption conditions and the insulation resistivity under saturated water absorption conditions.
The fire prevention situation in high-voltage power cable tunnels is severe. Currently, high-voltage cables are mainly purchased in flame-retardant models. As the name suggests, flame-retardant materials are conventional sheath materials with added formulations such as flame retardants, endowing the materials with flame-retardant properties. The flame-retardant performance of common sheaths is shown in Table 3.
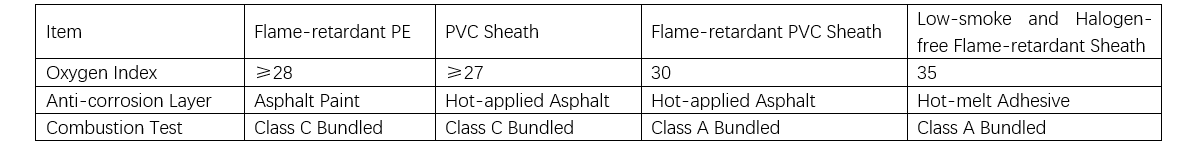
Taking a PE sheath as an example, flame-retardant PE is standard PE sheathing material with added flame retardants. Flame retardants are divided into inorganic and organic types. Currently, most products on the market primarily use inorganic flame retardants, with common types including magnesium oxide and aluminum oxide. These materials readily absorb moisture and undergo hydration reactions under normal conditions. Therefore, sheathing materials are typically put into production immediately after procurement; otherwise, moisture absorption can easily occur, leading to defects such as voids during extrusion. Only after the flame retardant particles are micronized, undergo surface modification, and have their material compatibility enhanced, can flame-retardant sheathing compounds achieve good processability.
Waterproof cables usually refer to cables with a complete, sealed metallic sheath. If a plastic sheath is used as the waterproof layer, moisture can penetrate into the cable through the plastic. Moisture ingress is a relatively slow process. During actual cable operation, the sheath surface temperature can reach as high as 60°C, which accelerates moisture penetration. Therefore, for newly commissioned cable sheaths, the insulation resistance generally meets requirements. However, after a period of operation, the sheath insulation resistance of many lines drops sharply, and this issue is typically discovered within several months to about a year. Once the sheath insulation resistance decreases to a certain level, the rate of decline tends to stabilize and slow down.
2.4 Poor Crack Resistance of Low-Halogen Cables
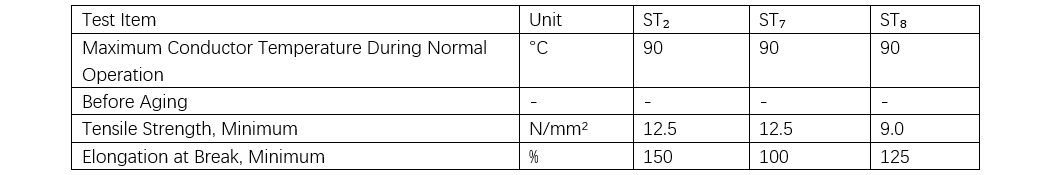
In Table 5, ST2 refers to PVC, ST7 to PE, and ST8 to halogen-free, low-smoke material. From the perspective of sheath mechanical properties, the tensile strength and elongation at break of halogen-free, low-smoke materials are significantly inferior. The installation of halogen-free, low-smoke cables has strict requirements, especially in outdoor areas in northern regions, because these sheaths are prone to cracking at low temperatures and may even develop cracking during operation. Numerous similar quality incidents have already occurred with medium- and low-voltage cables in China. Some construction projects use halogen-free, low-smoke cables during winter, partly because the work is conducted indoors where temperatures are higher.
Halogen-free, low-smoke cables are primarily used indoors in buildings and densely populated areas such as stations, subways, and public buildings. The power compartment of a utility tunnel does not belong to a densely populated area.
3 Conclusion
Based on the above analysis, halogen-free, low-smoke materials perform worse than the current insulation-grade flame-retardant sheathing materials and are more prone to problems. For this reason, current high-voltage cable standards such as GB/T 11017 and GB/T 18890 have not incorporated halogen-free, low-smoke sheathing materials into their standard systems.
The "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247 strengthens fire behavior control. This is appropriate for densely populated areas like subways and high-speed rail stations, where there are many combustible materials, due to safety considerations for life and property. Most cables used in these areas are medium- or low-voltage, for which electrical performance requirements are not as stringent as for high-voltage cables.
It is particularly important to note that the Class B rating in "General Rules for Flame-Retardant or Fire-Resistant Electric Wires, Cables, or Optical Cables" GB/T 19666 is not equivalent to the B1 rating in "Classification of Burning Behavior for Electric and Optical Fiber Cables" GB 31247. The two standards have completely different fire performance criteria and intended application areas. They should not be used interchangeably. It is recommended to use high-voltage cables meeting GB/T 19666 Class B, and not recommended to use high-voltage cables meeting GB 31247 B1 or B2 ratings. Although both are labeled "B," they belong to different standard systems, resulting in completely different performance outcomes. Using high-voltage cables meeting GB 31247 B1 or B2 ratings would place enormous pressure on construction and operation & maintenance departments.
Given the stringent fire protection requirements in power tunnels, after upgrading the flame-retardant rating to Class B:
For conduits or direct burial installations where flame retardancy is not required, PE outer sheaths (without flame retardant additives, providing stable insulation resistance) can be selected.
For high-voltage cables installed in tunnels, PVC outer sheaths are recommended (the disadvantage is the release of toxic gases during combustion; the advantage is that formulation can enhance water resistance, and the insulation resistance is more stable compared to Class B flame-retardant PE cables).
Furthermore, it is recommended to promptly initiate joint research on sheath materials and structures to fundamentally resolve the conflict between insulation resistance and flame retardancy.

























