Pagkabag-o sa Pagpahayag
Impormasyon sa Pagkabag-o ug Modo sa Operasyon Bago ang Pagkabag-o
Sa ika-17:53:50 ni Mayo 16, 2016, ang mga pananglitan sa dalan nga Jingchuan II nagsugyot sunod-sunod. Ang Phase B gipili aron mapatay, ug ang B-phase sa mga circuit breaker 7522 ug 7520 giopen. Ang pananglitan sa circuit breaker 7522 nakadetekta og permanenteng pagkabag-o sa dalan nga duol nga may delay nga 0.6s. Sunod dayon, ang ABC three-phase sa circuit breaker 7522 gipatay.
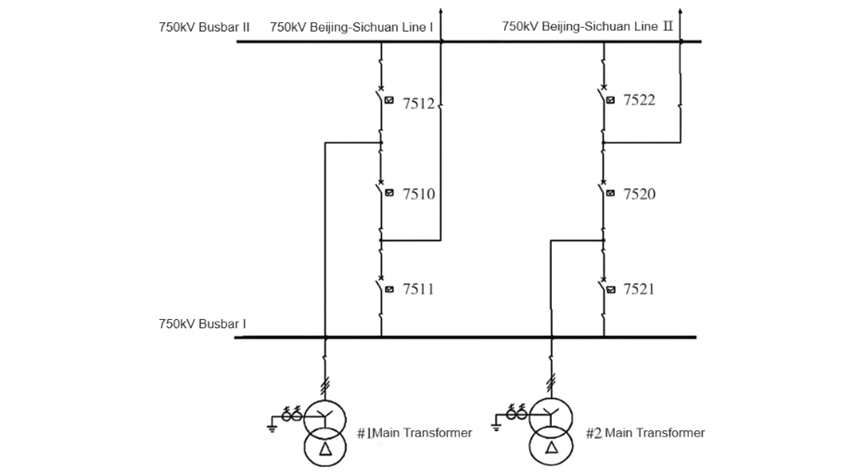
Sa proseso, ang pagprotekta sa B-phase sa circuit breaker 7522 gipasugyot ang differential protection sa Bus II, ug ang circuit breaker 7512 giopen, resulta niana ang pagkawalay kuryente sa 750kV Bus II. Ang pre-failure system operation mode ug unit operation conditions makita sa Figure 1. Ang active power sa Unit #1 adunay 645MW, ug ang Unit #2 adunay 602MW. Ang Jingchuan I ug II Lines nagoperar normal. Ang wiring mode sa step-up substation mao ang 3/2 wiring, ug ang step-up substation nagoperar sa loop-closing mode.
Sitwasyon sa Pagsusi sa Pagkabag-o
Pagtan-aw sa Lugar
Ang pagsusi sa lugar sa circuit breaker 7522 nagpakita nga ang mechanical open/close indicators para sa A/B/C phases nagpakita sa posisyon sa open, nga nasa "0" position. Ang hydraulic operating structure nasa spring compression position. Para sa WB - 2C circuit breaker, A/B/
Para sa phase C, ang pagsusi sa lugar sa panel sa operation box nagpakita nga ang red light sa TWJ indicator giluslit. Ang presyon sa SF₆ gas sa A/B/C three-phase circuit breakers 0.62MPa (relative pressure), ug walay obvious na anomalya sa circuit breaker 7522.
Impormasyon sa Action sa Proteksyon
Jingchuan II Line Protection IRCS - 931BM Protection Device: Sa ika-17:53:50:404 ni Mayo 16, 2016, ang B-phase current differential protection nagsugyot. Ang current differential protection gipatay ang A, B, ug C phases sa 767ms, ug ang tripping position contacts sa A, B, ug C phases nabalik sa 825ms.
Jingchuan II Line Protection IICS - 103C Protection Device: Sa ika-17:53:50:454 ni Mayo 16, 2016, ang B-phase current differential protection nagsugyot, ug ang phase-differential gipatay ang ABC phases sa 790ms.
7522 Circuit Breaker Protection Screen PRS - 721S Protection Device: Ang circuit breaker 7522 gipatay sa phase B. Ang follow-up tripping action nagsugyot. Pagkatapos og 0.6s, ang reclosing action gisugyot, ug ang three-trip action gipahibalo. Pagkatapos og 0.15s, ang failure-tripping sa circuit breaker mismo nagsugyot, ug pagkatapos og 0.25s, ang failure-tripping sa adjacent circuit breakers nagsugyot.
7520 Circuit Breaker Protection Screen PRS - 721S Protection Device: Ang circuit breaker 7520 gipatay sa phase B. Ang follow-up tripping action nagsugyot, ug ang three-phase follow-up tripping gisugyot. Tungod kay ang reclosing sa circuit breaker 7520 adunay delay nga 0.9s (upatong reclose sa faulty line ug pangutana sa impact sa unit), ang reclosing wala nagsugyot.
7512 Circuit Breaker Protection Screen PRS - 721S Protection Device: Ang circuit breaker 7512 gipatay sa three phases, ug ang return time sa three-phase tripping position contacts 1143ms.
II-Bus Mother Protection I Screen RCS - 915E Protection Device: Sa ika-17:53:51:258 ni Mayo 16, 2016, ang failure-tripping sa bus-line nagsugyot.
Pagtakda ug Pagsusi sa Katawan sa Circuit Breaker
Gikontak ang Ningxia Electric Power Research Institute aron ma-analisa ang komponente sa SF₆ gas sa three-phase circuit breakers sa 7522. Ang sulfur compound components sa SF₆ gas sa phase B sobrang labi sa standard. Ang decomposition product content sa gas chamber mahimong taas, nga nagpakita og presence sa high-energy partial discharge, nga nagresulta sa decomposition sa solid insulation materials, sama sa Table 1.
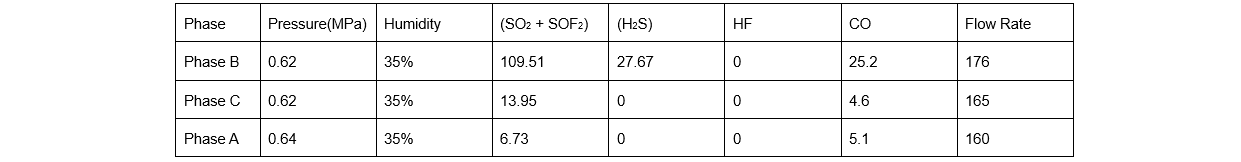
Pagkahuman sa pagmeasure sa breaking-circuit loop sa circuit breaker B, gitumpas nga ang loop open, nga nagpakita nga ang breaker naka-open-circuit state. Ang Ningxia Electric Power Research Institute mi-test ang opening time ug circuit resistance sa A ug C phases sa circuit breaker 7522, ug ang test results naka符合要求,以下是翻译内容的继续:
```html
ngadto sa standards.
Pagdisensambo ug Pagsusi Pagkatapos sa Pagkabag-o
Para sa circuit breaker 7522, ang SF₆ gas sa loob sa phase B gipalabas, ang nitrogen gipurgo, ug ang door sa breaker body gibuksan. Nahanap ang dust (arc-ablation decomposition products) sa loob. Pagdating sa mga teknisyano sa ABB factory, gipasab sa insulator, ug nahitabo ang 2 broken electrodes. Ang broken electrodes gibag-o sa outer wall. Ang connecting rod ug moving contact nahanap ang obvious na ablation marks, ug ang moving contact operating mechanism nahanap ang obvious na melting decomposition products. Ang operating mechanism sa hydraulic spring-type operating structure sa circuit breaker gisusi ug nahanap ang normal nga operasyon.
Analisis sa Dahon
Prinsipyong Pagpatay sa Arc
Ang pinaka maayo nga oras aron patayon ang AC arc mao kung ang arc current mag-cross zero sa bawat half-cycle. Sa panahon sa current zero-crossing period, ang arc mag-undergo sa 2 recovery processes:
Dielectric Strength Recovery Process: Tungod sa enhancement sa de-ionization process, ang dielectric strength sa pagitan sa arc electrodes gradual nga mag-recover.
Arc Voltage Recovery Process: Ang supply voltage muli mogamit sa contacts. Ang arc voltage mosubay sa arc-extinguishing voltage hangtod sa supply voltage. Kung ang dielectric strength recovery process mas rapido kaysa sa arc voltage recovery process, ug ang amplitude sa arc voltage recovery process dako, ang arc voltage recovery process mas rapido kaysa sa dielectric strength recovery process, resulta niana ang breakdown sa dielectric sa pagitan sa electrodes, ug ang arc muling mag-reignite. Kung ang arc voltage recovery process magsugyot bago ang dielectric strength recovery process magsugyot, ang arc muling mag-reignite.
Konklusyon
Sumala sa fault recording waveform sa CSL103 protection device, human sa re-closing sa B-phase sa 7522 circuit breaker, ang protection gipasugyot og three-phase tripping command sa 767 ms, ug ang three phases sa 7522 circuit breaker fully opened sa 825 ms, may action time nga 58 ms. Sa panahon sa arc-extinguishing process sa B-phase circuit breaker, ang current waveform wala mag-cross zero, ug ang arc nagpadayon sa pag-provide og short-circuit current sa loob sa circuit breaker.
Sumala sa analysis sa arc-extinguishing performance sa SF₆ gas: sa epekto sa arc, ang SF₆ gas mogamit og electrical energy ug giproduce og low-fluorine compounds. Pero, human sa arc current mag-cross zero, ang low-fluorine compounds mahimo gyud nga mabilis mopauli sa SF₆ gas. Ang dielectric strength sa arc gap mabilis nga mag-recover. Tungod kay ang arc current wala mag-cross zero, ang arc-extinguishing performance sa SF₆ gas nabag-o. Sa panahon na, ang circuit breaker failure protection lang ang mahimo mogamit aron matukod ang adjacent 7512 circuit breaker ug matukod ang fault current. Ang panahon gikan sa three-phase tripping position contact sa 7522 circuit breaker nabalik hangtod sa three-phase tripping position contact sa 7512 circuit breaker nabalik 317 ms total, nagpakita nga ang high-energy arc sa B-phase circuit breaker nagburn 317 ms. Human sa 7512 circuit breaker giopen, ang arc gipatay.
Sa konklusyon, ang line protection ug circuit breaker failure protection sa event na niini parehas normal nga nagsugyot, ug ang circuit breaker normal nga gipatay. Ang actions sa primary ug secondary equipment tanan correct. Para sa B-phase sa 7522 circuit breaker, sumala sa gas composition analysis, adunay high-intensity energy sa arc-extinguishing chamber, sufficient aron mapataas ang gas pressure. Pero, ang current sa 7522B phase wala mag-cross zero, ug ang arc wala gipatay. Pero, ang valve sa lower compression chamber gibuka, ug ang excess gas gipalabas sa lower part, posible nga gitangtang ang arc ug nagburn-out sa insulating tie-rod sa moving contact ug shunt capacitor.
Analysis of the Causes of the Burn-out of the Circuit Breaker Closing Resistance and the Breakdown of the Uniform Shielding Cover on the Outer Side of the Resistance
Ang operasyon sa circuit breaker mao ang dahon sa most switching over-voltages. Ang pag-install sa closing resistance mahimo efektibo limitar ang over-voltages during line closing ug single-phase reclosing. Ang 550/800PMSF₆ gas-blast circuit breaker nga giproduktahan sa ABB Company nga ginamit sa among kompanya adunay closing resistance nga gisunod silicon carbide resistance plates. Sumala sa instruction manual sa manufacturer, ang heat capacity sa closing resistance mao kini: human sa closing 4 times sa 1.3 times sa rated phase voltage, ang interval sa oras sa unang duha ka beses 3 minutes, ug ang interval sa oras sa katapusan duha ka beses 3 minutes; ang interval sa oras sa duha ka grupo sa tests (front ug back) wala mas dako sa 30 minutes.
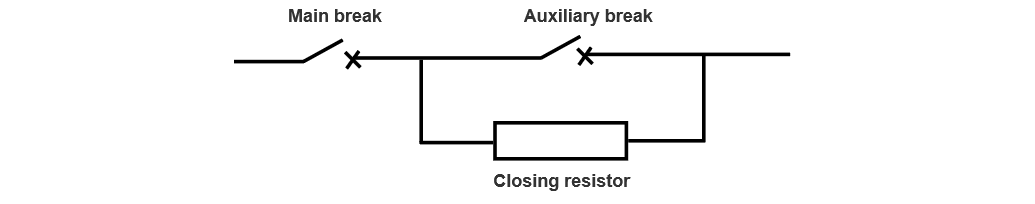
Ang breaker adunay series-type break structure, nga gisundan sa 3 main breaks, 1 auxiliary break, ug combined closing resistance, sama sa Figure 2. Ang primary feature sa series-type break mao kini: sa panahon sa closing operation sa circuit breaker, ang auxiliary break mocsure human sa main break sa arc-extinguishing chamber, ug sa panahon sa opening operation, ang auxiliary break moseparate human sa main break sa arc-extinguishing chamber.
Ngituyo, ang sequence sa action sa auxiliary break mao kini: closing later ug opening later. Ang working principle mao kini: sa panahon sa closing, ang main break mocsure unang, forming a current-conducting loop in series with the resistance, ug ang closing resistance connected. After about 8-11 ms (sumala sa instruction manual sa manufacturer), ang current-conducting loop formed through the closing contact of the auxiliary break, short-circuiting the closing resistance; sa panahon sa opening, ang main break moseparate unang, opening the main current loop, then the auxiliary break separates.
Kaya, ang auxiliary break carries the rated current ug short-circuit current sa panahon sa opening. Human sa B-phase mechanical opening, ang closing resistance connected to the circuit. Since the arc between the B-phase breaks lasted for 317 ms through the closing resistance, ug ang arc current was approximately 1620 A, according to the calculation, ang heat capacity borne by the closing resistance was greater than its rated capacity. This led to the over-limit heat capacity of the connection ring between the closing resistance and the auxiliary break, eventually causing fusing, discharging to the outer-wall grading ring, resulting in the breakdown of the grading ring and the blackening of the resistance.
Analysis of the Causes for the Operation of Circuit Breaker Failure Protection
In circuit breaker failure protection, when the current element is activated and meets the failure protection criteria, the failure protection will be initiated as long as the protection trip input is received and the corresponding phase current is greater than 0.05 In.
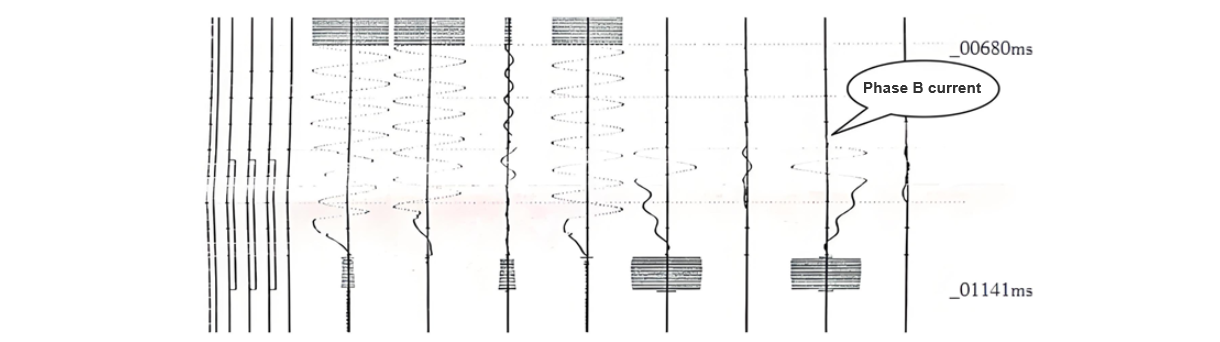
As can be seen from the reports of 7522, from 775 ms when the PRS - 721S protection device of the 7522 circuit breaker protection panel received the three-phase trip signal input from the IRC - 931BM protection device of the Jingchuan II line protection, to 925 ms when it tripped the local circuit breaker due to failure, and to 1025 ms when it tripped the adjacent circuit breaker due to failure, with a delay of 0.15 s for tripping the local circuit breaker and 0.25 s for tripping the adjacent circuit breaker respectively, which is in line with the operation logic of failure protection, and the protection operated correctly, as shown in Figure 3. In the oscillogram, it can be seen that although the B-phase tripping position contact of 7522 had returned at 825 ms, there was still current (arc) flowing between the moving and stationary contacts.
Conclusions
Due to the severe distortion of the fault current, the waveform shifted to the lower side of the time-axis. The fact that the waveform did not cross zero within the effective arc-extinguishing time of the circuit breaker was the main reason for the non-extinction of the arc. The failure of the gap insulation to recover after the circuit breaker opened and the decline in the arc-extinguishing performance of SF₆ gas were secondary reasons for the non-extinction of the arc.
The non-extinction of the arc and the expulsion of the remaining gas from the arc-extinguishing chamber, which carried out the arc, were the main reasons for the blackening of the insulating tie-rod and the outer wall of the capacitor.
After the mechanical opening of phase B, the closing resistance was connected to the circuit. Since the arc between the breaks of phase B flowed through the closing resistance for 317 ms, the heat capacity caused the heat capacity of the connection between the closing resistance and the auxiliary break to break down, eventually leading to fusing, discharging to the outer-wall grading ring, resulting in the breakdown of the grading ring and the blackening of the resistance.
The presence of arc current in phase B and its compliance with the operation logic of the circuit breaker failure protection were the main reasons for the tripping of the busbar.
```
























