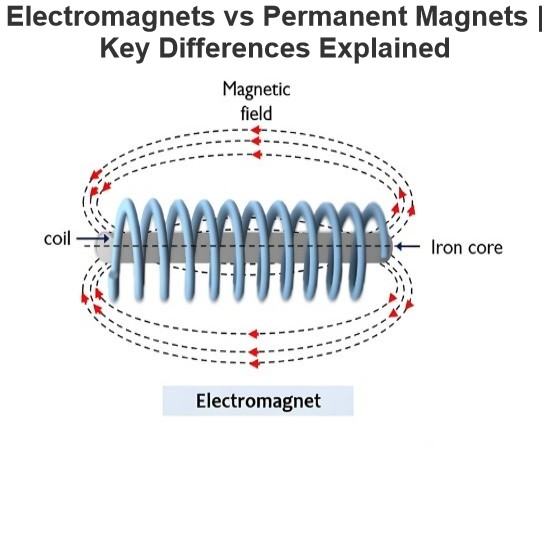
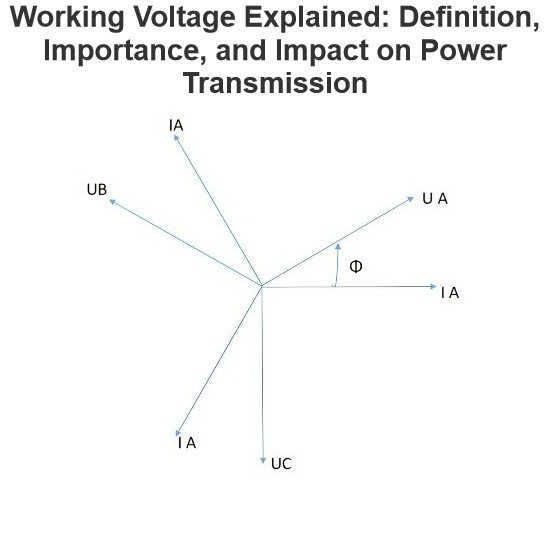
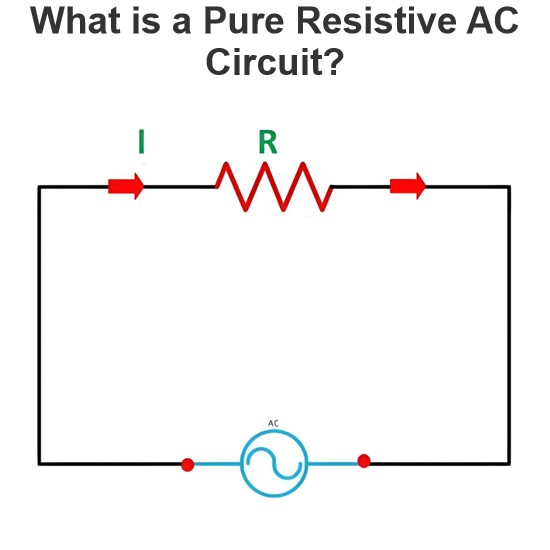
- Product
- Suppliers
- Manufacturers
- Solutions
- Free tools
- Knowledges
- Experts
- Communities
Search
-
Strumenti Gratis
-
IEE Business jipponi ħlasa l-għodod tal-inġinierija elettrika u tbattijiet għall-aċċizjoni ta' energija elektrika: daħħal parametri, ikklikkja kalkula, u oħroġ ir-riżultati immedjati għal transformers, wirings, motors, kosji tal-materjal elettriku, u aktar — fidati minn inġinieri f'dan il-mondo.
-
-
Support u Sponsorizzazzjoni
-
IEE-Business tispexxija soluzzjonijiet użwaljenti imprezi u esperti krei platforma fejn innoġazzjoni tinqeda mal-valurGħarxi TekniċiIkkunzola u tnejja u għallim tekniku biex tigħmlu flus minn sponsoriSoluzzjonijiet Bizantali EċċellentiIngħaqad u oħloq soluzzjonijiet tan-negozju biex tikseb flus mis-sponsorjiEsperti Individwali ĊapacitatiIpposta l-għaqda tiegħek għal is-sponsors ikseb il-futur tagħek
-
-
Komunità
-
Oħloq il-komunitajiet professjonali tiegħekSib u ħu kontatt ma’ persunalitajiet fl-industrija, possibbli partners u decisuri biex twassal il-biżness tiegħek.Espandiż netwerk personali tiegħekIkkannekta ma’ persuni fl-industrija, partniers potenzjali u deċiżjonijiet biex tispiċċa ż-żvilupp tiegħek.Discover Iktar OrganizzazzjonijietEsplora kumpaniji misti, kolaboraturi u raġel industrijali biex tiftaħ opportunitajiet kommersjali ġodda.Jingħaqdu komunitajiet diversiIngħaqad fid-diskussjonijiet bbażati fuq il-kwistjonijiet, b’bdaż-żewġ ta’ industrija u kondiviżjoni ta’ riżorsi biex tikkomplica l-impatt tiegħek.
-
-
Ħalq Ghaxaq Maħallna
Partneri
-
-
Iddoċa fil-Proġramm ta' Parteneri tal-IEE BusinessPotwen ta Tħabbur tas-Silġ -- Minn Strumenti Tekniċi għal Espansjoni Bisnis Ġlobali
-
-
IEE Business
-
Malti
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
Soluzzjonijiet Bizantali Eċċellenti
Esperti Individwali Ċapacitati
Espandiż netwerk personali tiegħek
Discover Iktar Organizzazzjonijiet
-
Malti
-
- English
- Afrikaans
- العربية
- Azərbaycan dili
- български
- বাংলা
- Català
- Cebuano
- čeština
- Dansk
- Deutsch
- Ελληνικά
- Esperanto
- Español
- Eesti keel
- Euskara
- دری
- فارسی
- suomi
- français
- Gaeilge
- Galego
- Hausa
- עברית
- हिन्दी
- Hrvatski
- magyar nyelv
- հայերեն
- Bahasa Indonesia
- Íslenska
- Italiano
- 日本語
- ქართული
- Қазақ тілі
- ಕನ್ನಡ
- 한국어
- Kurdî
- Latina
- Latviešu valoda
- македонски јазик
- Bahasa Melayu
- Malti
- नेपाली
- Nederlands
- Norsk
- ਪੰਜਾਬੀ
- polski
- پښتو
- Português
- Русский язык
- සිංහල
- Slovenščina
- српски језик
- Svenska
- Kiswahili
- தமிழ்
- తెలుగు
- ไทย
- Tagalog
- Türkçe
- українська мова
- اردو
- Oʻzbek tili
- Tiếng Việt
-
Soluzzjonijiet Bizantali Eċċellenti
Esperti Individwali Ċapacitati
Espandiż netwerk personali tiegħek
Discover Iktar Organizzazzjonijiet