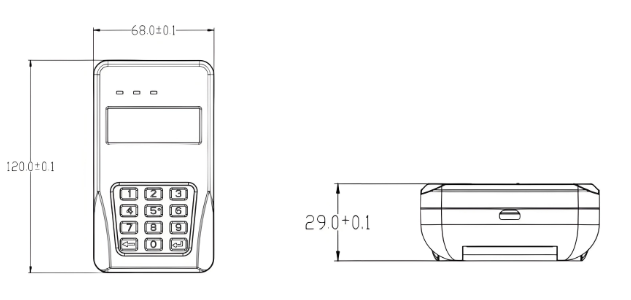
| Brand | Wone Store |
| Model NO. | Single-phase Keypad Smart Energy Meter GSD7666-G |
| Rated frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Series | GSD |
GSD7666 - G is an advanced single - phase smart meter with modular design to measure energy accurately for commercial & residential customers, with a wide range of functions, smart measurement & flexible communication modules for remote reading & management. It could be used for either prepayment (compliant with STS standard) or postpayment applications(optional), with outstanding anti - tampering functions like detection of terminal cover opening to help utilities in revenue protection. It could communicate with CIU or DCU (Data Concentrator Unit for AMR/AMI system) by different communication modes like PLC/GPRS/3G/4G/RF based on requirements.
Main Features
ELECTRICAL PARAMETERS |
|
VOLTAGE |
|
Nominal voltage Un |
230V |
Limited voltage |
70% ~ 120%Un |
FREQUENCY |
|
Nominal frequency fn |
50 ~ 60Hz |
Tolerance |
±5% |
CURRENT |
|
Basic current(Ib) |
5A |
Maximum current(Imax) |
60A (80A/100A optional) |
Starting current(Ist) |
20mA |
Active energy constant |
1000imp/kWh |
MEASUREMENT ACCURACY |
|
Active energy as IEC62053 - 21 |
Class 1.0 |
Power consumption |
|
Voltage circuit |
<2W <8VA |
Current circuit |
<1VA |
TEMPERATURE RANGE |
|
Operation range |
-25°C ~ +70°C |
Storage range |
-40°C ~ +85°C |
INSULATION |
|
Insulation level |
4kV rms 1min |
Impulse withstand voltage |
8kV 1.2/50 μs |
Insulation system classification |
Protection class II |
ELECTRO MAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY |
|
ELECTROSTATIC DISCHARGES |
|
Contact discharge |
8kV |
Air discharge |
15kV |
ELECTROMAGNETIC RF FIELDS |
|
27MHz to 500MHz typical |
10V/m |
100kHz to 1GHz typical |
30V/m |
Fast transient burst test |
4kV |
MECHANICAL REQUIREMENTS |
|
Meter case protection class |
IP54 |
Insulation system classification |
Protection class II |
Maximum cable size |
8 mm |
Split-type Structure for Anti-tampering Protection
The CIU (Customer Interface Unit) is optional, linking to the MCU (Metering & Control Unit) with communication modes of M-bus, PLC or RF based on requirements.
The CIU is installed inside the customer's home for inputting prepayment token and searching for information, while the MCU is normally installed in a meter enclosure away from the customer's home.