1 Current Grid Status
With the continuous deepening of rural power grid transformation, the health level of rural grid equipment is constantly improving, and power supply reliability basically meets user needs. However, regarding the current grid status, due to funding constraints, ring networks have not been implemented, dual power supplies are unavailable, and lines adopt a single radial tree-like power supply method. This resembles a tree trunk with many branches—meaning the lines have numerous branches. Therefore, when a fault occurs at any point on the line, the entire line shuts down completely, and the fault location is difficult to determine. This not only affects power supply but also wastes significant manpower and material resources for management departments dealing with accidents. Therefore, installing reclosers and sectionalizers on 10kV lines can effectively control the occurrence of accidents.
2 Characteristics of Reclosers and Sectionalizers
2.1 Reclosers
① Reclosers have automatic functions and can perform opening and closing operations without external power. The electronic control section obtains power through the bushing CT inside the recloser. A power-side current greater than 5A ensures normal operation of the electronic control section. They have small volume, light weight, and are easily installed on poles. Adjustment of the tripping current ampere-second curve can be achieved by replacing tripping resistors or ampere-second curve boards, which is very convenient.
② Reclosers can automatically detect line current and ground current. When current exceeds the preset minimum tripping current, they follow a pre-set sequence of opening, breaking, and reclosing with specific reclose intervals to interrupt fault current. If the fault is permanent, after 2, 3, or 4 preset tripping operations, the recloser locks out, isolating the fault area from the main circuit.
2.2 Sectionalizers
① The drop-out sectionalizer is a single-phase high-voltage electrical device. The product consists of insulators, contacts, conductive mechanisms, and other components forming secondary control lines and primary conductive systems. The control system comprises electromagnetic interlocking contacts, electronic controller components, and other elements. The tripping action system consists of an energy-storage permanent magnet mechanism, pallets, levers, and lock blocks.
② Sectionalizers are equipped with current transformers that detect circuit current values. When a line fault occurs, the electronic controller activates when current exceeds the rated starting current value and performs digital processing. The fault current is interrupted by an upstream recloser (or circuit breaker). The electronic controller can memorize the number of times the upstream switch has interrupted fault current and, after reaching the preset counting threshold (1, 2, or 3 times), when the upstream switch interrupts fault current and the line loses voltage with current below 300mA, the sectionalizer automatically segments within 180ms. This limits the fault area to the minimum range or isolates the fault section, allowing the recloser (or circuit breaker) to operate successfully.
③ Sectionalizers use a permanent magnet mechanism to complete the opening operation. When current in the sectionalizer exceeds the set value, the circuit breaker (or recloser) in the substation interrupts the fault current. After the line loses voltage, the electronic control board inside the sectionalizer tube sends a command, and the permanent magnet mechanism trip unit pushes the sectionalizer to open. After each segmentation, the trip unit doesn't require replacement of any components. After the sectionalizer drops out, it can be restored to working condition through manual energy storage via the stopper.
3 Coordinated Use of Reclosers and Sectionalizers
Based on the functions and characteristics of reclosers and sectionalizers, using them together installed on 10kV distribution networks will play a significant role. They can determine the fault range of lines, isolate faulty sections from healthy ones, thereby ensuring normal operation of non-faulty line segments. Specific application is shown in the figure below:
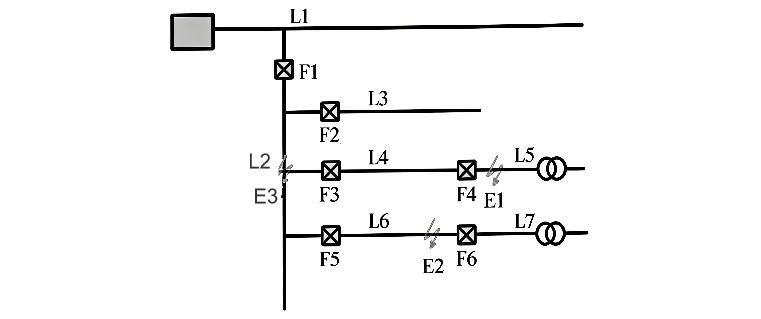
Reclosers are installed at the main line outlet or in substations, while six groups of drop-out automatic sectionalizers F1, F2, F3, F4, F5, and F6 are selected for branch lines, dividing them into segments L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6, and L7. The rated starting current value of the sectionalizers matches the starting current value of the recloser.
3.1 If fault E1 occurs in segment L5
The recloser and sectionalizers F1, F3, and F4 experience fault current. The recloser automatically trips, causing the line to lose voltage. F4 reaches its preset count threshold of 1 operation and automatically trips/drops out, isolating fault segment L5. After the recloser automatically recloses, power supply is restored to segments L1, L2, L3, L4, L6, and L7.
3.2 If fault E2 occurs in segment L6
The recloser and sectionalizers F1 and F5 experience fault current. The recloser automatically trips. If it's a temporary fault, the recloser successfully recloses and restores power supply. F1 and F5 remain closed as they haven't reached their preset count threshold. If it's a permanent fault, the recloser fails to reclose successfully, trips again, causing the line to lose voltage. F5 reaches its preset count threshold of 2 operations and automatically trips/drops out, isolating fault segment L6, while F1 remains closed as it hasn't reached its count threshold. After reclosing, the recloser restores power supply to segments L1, L2, L3, L4, and L5.
3.3 If fault E3 occurs in segment L2
The recloser and sectionalizer F1 experience fault current. The recloser automatically trips. If it's a temporary fault, the recloser successfully recloses and restores power supply. F1 remains closed as it hasn't reached its preset count threshold. If it's a permanent fault, the recloser fails to reclose, trips, attempts to reclose again but fails, and trips again. The line loses voltage, and F1 reaches its preset count threshold of 3 operations, automatically tripping/dropping out and isolating fault segment L2. After reclosing, the recloser restores power supply to segment L1 only.
4 Benefits of Coordinated Recloser and Sectionalizer Application
From the above discussion, it's clear that the coordinated use of reclosers and sectionalizers plays a significant role in power grid operation. They not only quickly isolate faulty line sections while ensuring normal operation of healthy sections, but also reduce the fault search area, enabling operating units to locate fault points in the shortest possible time. For users, this increases equipment utilization rates and reliably guarantees production and daily life.
As illustrated above, if the grid directly disconnects the faulty line section, maintenance personnel would only need to check one line segment, significantly reducing the fault search area. Maintenance staff can quickly locate the fault point and promptly restore power to the faulty line. Currently, when a fault occurs at one point, maintenance staff must check five different sections. This 1:5 relationship clearly demonstrates which approach benefits power supply enterprises more. Which grid structure both increases power supply quantity and improves power supply reliability? Therefore, the application of reclosers and sectionalizers will play a tremendous role in power grids.


























