Mfumo wa upimaji na uhifadhi wa mstari wa PMU ni mfumo mpya wa utumatiko wa umeme wa mstari.
unategemea kwa kutatua matatizo ya sasa hasa ya hitimisho la ardhi.
ambayo inebana kwenye Upimaji wa Phasor wa Mtandao wa Umeme wa Nchi - μPMU.
PMU (phasor measurement unit), kifaa au moduli bila msingi. Data za kipimo cha umeme/kivutio zote zina timestamp ya BDS/GPS yenye usahihi wa kiwango cha mikrosekunde.
Shughuli zisizohusika: • Phasor: amplitude, pembe ya angalau, • Kasi (f) na Mabadiliko ya Kasi (△f/△t)

Ramani ya Muundo wa Vifaa vya μPMU
Mfumo wa Upimaji wa Eneo Lefu (WAMS)
• Mapimo ya PMU yanaonekana kwa kutosha na Muda wa Kiwango cha Dunia (UTC)
• Upimaji wa eneo lefu wa tofauti ya PMU vilivyowekeka mahali mbalimbali
• Uhusiano wa hesabu wa ishara ya umeme/kivutio:

Sensor wa Kivutio wa Angani i-WCS - Single Channel Current PMU
Suluhisho la matatizo ya mtandao wa umeme linalotegemea kwenye PMU wa mtandao wa umeme na teknolojia ya upimaji wa phasor wa eneo lefu.
• Upimaji wa kivutio wa aina ya ufanisi na kiwango kikubwa
• Upimaji wa eneo lefu wenye kufanikiwa
• Upimaji wa kazi chanya, IP67
• Inastahimili mzunguko wa nguvu kwa kila upande au kazi ya mtandao wa ringi
• Mawasiliano ya 3G/4G/ 5G:
a. Ripoti kila harmoniki kwa wakati
b. Matukio ya mahali hutoa data
c. Kutuma na kutest tarehe maalum

• 1μs Upimaji wa eneo lefu
• 12.8kHz Kiwango cha upimaji
• 60 dakika Ripoti na kurudia data
• 0.5 Usahihi wa upimaji
• 3.5A Kiwango cha chini cha upimaji kwa ajili ya ufanisi kamili
Sensor wa Kivutio wa Kablai RCMU - Multichannel Current PMU

RCMU - Sensor wa kivutio wa kablai chini ya ardhi
• 1μs Upimaji wa eneo lefu
• 12.8kHz Kiwango cha upimaji
• 0.5 Usahihi wa upimaji
• 60 dakika Ripoti ya data
• Upimaji wa kivutio wa tatu
• Utumiaji wa mawasiliano rasmi au rasmi
• Kutafuta kivutio cha tatu, sawa na sera ya angani, inapatikana kwa kitengo cha ringi, steshoni ya kubadilisha, au steshoni ya umeme.
• Upimaji wa eneo lefu, induksi ya nguvu, au umeme wa DC 24V/48V
• Mbinu ya kupata hatari ya mahali kwa kutumia kivutio:
a. Kivutio kubwa
b. Kivutio cha kiwango cha zero
c. Kivutio cha tatu lisilo sawa
• Ripoti ya data ya kivutio, inastahimili kutafuta hatari ya eneo lefu
• Inastahimili mzunguko wa nguvu kwa kila upande au kazi ya mtandao wa ringi
• Mawasiliano ya 3G/4G/5G au mtandao
Kitengo cha Kutafuta Voliti BDCU - Single/Multiple Voltage PMU


Aina ya ndani na nje
• Umeme wa AC 220V/DC 24V • Safu ya mwanga, rasmi, au rasmi
• IEC 60870-5- 101/104/DNP3 • Inaweza kutumia sensori za kivutio 300
Upimaji wa Voliti:
• 1μs Upimaji wa eneo lefu
• 1.0 Usahihi wa upimaji
• 12.8kHz Kiwango cha upimaji
• 60 dakika Ripoti ya data
Kwa hatari ya tunda moja na kivutio cha ardhi kubwa zaidi ya 1A, upimaji na kutafuta hatari unaweza kufanyika kwa asili 100%, hakuna makosa
• Kutafuta voliti cha kiwango cha zero, kuanza ripoti ya hatari ya ardhi
• Kutafuta na kutathmini ripoti, na kutathmini hatari kwa ujumla
• Ingizo salama kwenye steshoni kuu ya umeme
a. Kutumika kama kituo cha kutathmini ustawi wa insulation
b. Kutumika kama kituo cha kutathmini ustawi wa insulation
c. Haitegemea steshoni kuu kwa kutatua hatari
Unganisho wa Mfumo wa Upimaji wa Hali ya Mtandao wa Umeme wa Kitaalamu Kubwa Unatumia Upimaji wa PMU

Viwango vya Matumizi vya Mtandao wa Umeme

Matumizi ya PMU - Tathmini ya Hali ya Mstari

Matumizi ya PMU - Ripoti ya Data ya Eneo Lefu

Data ya ripoti ya shambani na steshoni zote zinachapishwa kwa muda wa sekunde. Chombo chochote linaweza kuchukua ripoti wakati masharti ya kuanza yamepatakiwa. Inatoa "snapshot" ya mtandao kwa ujumla kulingana na muda wa kukabiliana na tukio lolote mahali popote hadi data ya ripoti ya sensori zote. Inatoa data za dunia kwa kutathmini tukio kwa undani, kusaidia kurejesha mchakato, kutathmini, na kutokomeza hatari ya hali isiyofaa, ndiyo.
Matumizi ya PMU - Upimaji wa Utendaji wa Umeme

Sensori inaweza kutathmini na kureport harmoniki kwa wakati. Kulingana na data ya upimaji wa eneo lefu, viwango vya utendaji wa umeme vingine kama vile ukosefu wa utaratibu wa tatu, kasi ya grid, na kiwango cha mabadiliko, na kuweka muhimu wa chanzo cha upaguzi.
Matumizi ya PMU - Upigaji wa Umeme

Kulingana na data ya mshirika wa kivutio wa upande wa high-voltage na mwendo wa kivutio, tabia za mshirika hupatanika na kuthibitishwa, na tabia ya umeme ya mtumizi wa mwisho inamonitoriwa, ambayo inaweza kutumika kwa uzoefu wa umbali na kutathmini hali ya vifaa vya umeme.
Matumizi ya PMU: Hatari, Kutokomeza, na Kurejesha Mchakato

Hatari:
• 2017-10-30 12:15:39:081719, mstari 115, pole 1# 64#, phase A to ground
• 2017-10-30 12:15:39:093125 , mstari 117, pole 29#, phase B grounded short circuit, peak flow exceeds 1000A
• 2017-10-30 12:15:39:115468 , Mstari 115, kati ya pole 1# na 64#, phase A na C short circuit, Peak current at pole 1# exceeds 5000A Feedback ya jiji na inversion ya mchakato wa hatari:
• Kupata majonzi ya gari kwenye pole 52# kwenye mstari 115
• Kupata alama ya kuchoma kwenye kabati la kablai kwenye eneo fulani nyuma ya pole 29# kwenye mstari 117
• Kuspekulizia kwamba conductor A kwenye mstari 115 amekwenda chini ya cross arm na kuchelewesha, na umeme wa phase siyo ya hatari ukawa mkubwa, ambayo inaweza kuchelewesha insulation weak point phase B nyuma ya pole 29# kwenye mstari 117, kujenga short circuit ya phase A na B kwa tofauti na mstari na kutoa current over 1000A
• Baada ya masaa kadhaa, conductor C kwenye pole 52# kwenye mstari 115 pia amekwenda chini ya cross arm, kuchelewesha short circuit ya Phase A na C. Waktu peak ya short-circuit current ikawa zaidi ya 5000A, protection relay kwenye outlet ya mstari ilikuwa imefanya kazi. Baada ya switch kumpata, system ilikuwa inafanya kazi vizuri, inaelezea kuwa insulation ya original breakdown point ya pole 29# kwenye mstari 117 imekurudi.
Matumizi ya PMU: Kutafuta hatari ya grounding ya kutofautiana

• 2018-10-05,15:27:45:395312, First alarm, the assignment notice is received.
“Allocation notice: 10kV Section 2 Phase A is connected to the ground at 15:29” “Allocation notice: 10kV Section 2 Phase A grounding disappear at 15:47 ”
• Patrol to confirm the break of 127-1-28# of Line 121 branch
• Timely discovery of broken wire contact, to avoid passers-by close to the electric shock. It is speculated that the ground jitter of the broken insulated conductor causes multiple grounding. After the metal core is retracted into the insulation layer, the phase loss operation will result in the bus voltage returning to normal
• During this time, typhoon "Connie" passed through, so it is speculated that the disconnected line was caused by typhoon.
Matumizi ya PMU: Big Data + AI Identification Guide to Find Fault Switches
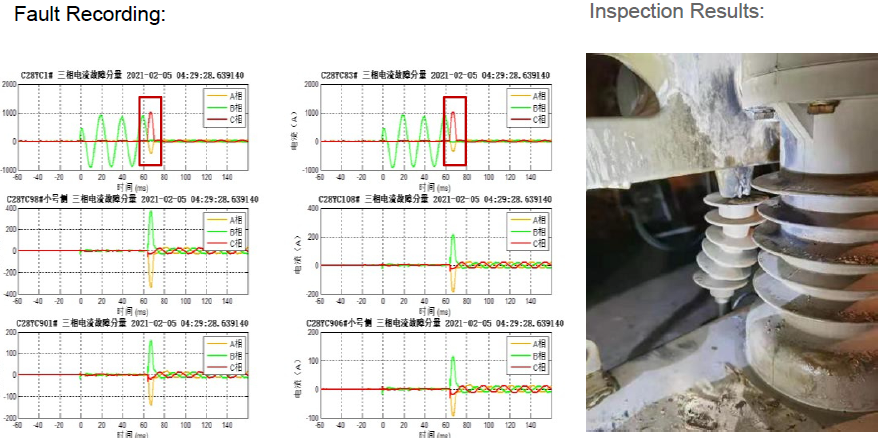
It is Small resistance grounding system, PMU sensor configuration.
whole process of fault identification and confirmation:
• 2020.11.25 - 2021.2.5, C28YC line had 5 grounding alarms, and all the alarm had the same characteristics, but the fault point could not be found during on-site inspection.
• The AI identified a match between the characteristics of the second half of the cycle and a type of waveform in the historical database, and deduced that it was a switch defect.
• On February 5, 2021, the on-site personnel had a target in mind and found the switch fault at pole 84.
Matumizi ya PMU: Line Insulation Warning - Reason: Meteorological Disaster

Line Neutral Grounding Mode: bus 1 arc suppression coil, bus 2 ungrounded PMU Sensor Layout Details:

System warning times: 13 times
Fault evolution process: on the afternoon of August 13, 2019, there were 13 disturbances, all indicating that they occurred in the same line section. The zero-sequence voltage rises continuously from 20V at the beginning of the warning to 30V at the end. The zero-sequence current increases from 3A to 5A, and the insulation of the line deteriorates. Due to the backlog of emergency repair tasks caused by typhoon one day ago, the priority of early warning and shortage elimination work has been postponed. After 9 hours deterioration into a short circuit, protective action trip, resulting in power failure.
Matumizi ya PMU: Line Insulation Warning - Cause: Conflict with Trees

Starting from 21 o 'clock on 2020.5.25, nearly one hundred weak disturbance events were perceived, all of which occurred in the same place.
The damping resistance of the arc suppression coil in the station is seriously heated.
The maintenance personnel patrolled the line according to the warning information.
After clearing the tree barriers and removing the defects, the insulation of about 14 points of the line was completely restored and the system returned to normal.
Matumizi ya PMU: Line Fault Warning - Cause: Bird Damage Line Neutral


System warning times: 10
Fault evolution process: From 19:57:41 to 22:48:18 on July 7, 2018, dozens of alarms were raised in the same place.
The time between two faults is getting shorter and the frequency is getting higher, which shows the trend of developing into permanent single-phase grounding faults. At around 10:50, the maintenance personnel manually pulled the switch on the site, destroyed the bird's nest in the fault section, closed the switch to restore power transmission, the fault disappeared.
Matumizi ya UCMU : Equipment Failure Warning - Cause: External Force Damage the Cable

Line neutral grounding mode: neutral grounding through arc suppression coil SMS warning times: 1
Fault Evolution Process: Multiple instantaneous grounding occurred since 15:22 on April 24, 2020, and the system pushed multiple warning information. In order to avoid frequent warning of short messages caused by instantaneous disturbance, the system sets three instantaneous grounding times within 20 minutes as the condition for pushing warning short messages. This condition can be improved through the accumulation and learning of big data by setting frequency. By 17:46, it became permanently grounded and lasted for 55 minutes.
Matumizi ya PMU: Equipment Failure Warning - Cause: Switchgear Insulation Deterioration

System Warning Times: 4
Fault Evolution Process: During the period of 2020.11.21 to 2020.11.24, there was 4 instantaneous grounding and 1 permanent grounding, and it eventually evolved into a short circuit fault. The system recorded 5 grounding faults with the same fault interval, similar waveform and obvious arc pull characteristics, which were judged to be insulation faults at the same location.










































