| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | DCEH Series Railway Vehicle Cable |
| Rated frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Series | DCEH series |
Standard
GB12528.4-90 JB8145.3-95
Application
For the transmission of power of railway vehicles. Rated AC voltage 3kV and below.
Property
a.The rated AC voltage 750V,1.5kV and 3kV.
b.Permissible contionuous operation temperature of the cable is 100℃ ,and the lowest temperature of installation is -25℃ .
c.The cables can be used in places contaminated by mineral oil and fuel oil.
d.Permissible radius for the installation of cable bending.
Overall diameter(D)20mm and below should not be less than 3D.
Overall diameter(D)20mm amd above should not be less than 5D.
e.The cable has single flame retardant property. It can pass the flame retardant test stipulated DZ-1 of GB12666 standard.
Type and Description

Construction of cable

Construction and Dimension
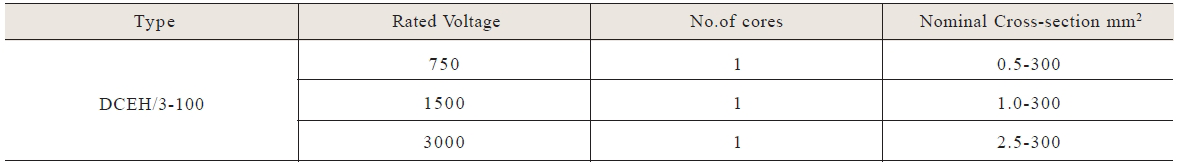
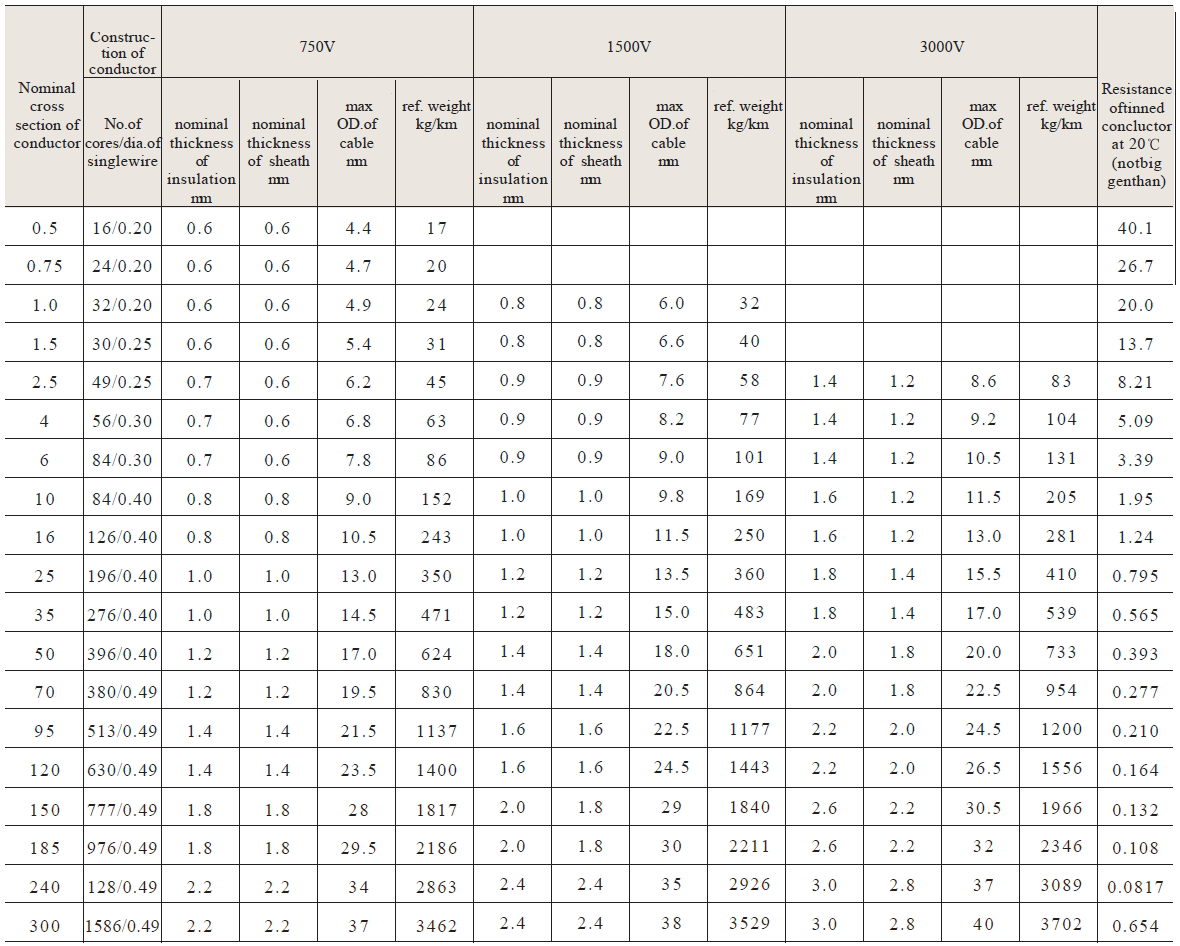
The technical requirement of the cable(wire)meets with the specification of the property and tests of GB12528.1-90 and GB12528.4-90.We canproduce cables of color sheathupon customer’s request.
Q: What is the special cable for rail transit?
A: Thin-wall insulated cable for rail transit vehicles is a cable used for electrical control equipment in locomotive. It adopts tin-plated soft copper conductor and halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant insulation material, and is produced by thin-wall manufacturing technology. It has the characteristics of small volume, light weight, heat resistance, oil resistance, acid and alkali resistance, cold resistance, wear resistance and ozone resistance. Especially suitable for high-speed and ultra-high-speed rolling stock relatively closed, personnel concentration and other environmental requirements of the rolling stock internal distribution cabinet and power supply system.
Q: What are the characteristics of the cable?
The cable is made of tin-plated soft copper conductor and halogen-free low-smoke flame-retardant insulating material, and is produced by thin-wall manufacturing technology. The product is small in size and light in weight, and has the characteristics of heat resistance, oil resistance, acid and alkali resistance, cold resistance, wear resistance and ozone resistance. It has excellent physical and mechanical properties, convenient installation, safe use and reliable operation. In the case of fire, it can effectively limit the spread of fire and the release of smoke to avoid danger to personnel.






