1 Paghahayag sa mga Kasinatian sa Smart Meter ug Ilang Epekto sa Grid sa Kuryente
1.1 Pagpapakilala sa Mga Katungkulan sa Smart Meter ug Ilang Mahalagang Papel sa Modernong Grid sa Kuryente
Ang smart meters nagpapadala og datos sa real time sa mga kompanya sa kuryente pinaagi sa dalihon nga komunikasyon, nagpadayon sa mga katungkulan sama sa remote meter reading ug dynamic tariff adjustment. Kini nga kapabilidad mahimo nga mobag-o ang mga user sa ilang pagkonsumo batas sa real-time pricing, nailhan sa energy savings ug pagbawas sa gasto. Samtang ang smart meters nagsuporta sa grid automation pinaagi sa paghatag og detalyado nga datos sa paggamit, nakatabang sa mga operator sa grid sa pag-optimisa sa load forecasting ug resource allocation, uban sa pag-improve sa operational efficiency sa power systems.
1.2 Pag-identify sa Common nga Mga Kasinatian sa Smart Meter ug Ilang Mga Sintomas
Sa panahon sa operasyon, ang smart meters maaaring magkaroon og iba't ibang kasinatian (isip gihatag sa Figure 1), kasama ang communication failure, display anomalies, ug inaccurate metering. Ang communication failure makita isip ang inability sa pag-connection sa backend system, nagpapahibaloog sa pag-disable sa data upload o reception ug nagdudulot sa pag-disrupt sa remote monitoring. Ang mga issue sa display, sama sa screen flickering o blackouts, naghadlok sa mga user sa pag-view sa impormasyon sa consumption. Ang inaccurate metering, madalas gipanggana sa hardware aging o software algorithm defects, direkta nga naapektuhan ang billing accuracy ug maaari mopasabot sa customer complaints. Ang pag-recognize sa mga sintomas sa kasinatian kay importante aron mas mapabilis ang troubleshooting ug pag-maintain sa stability sa grid.
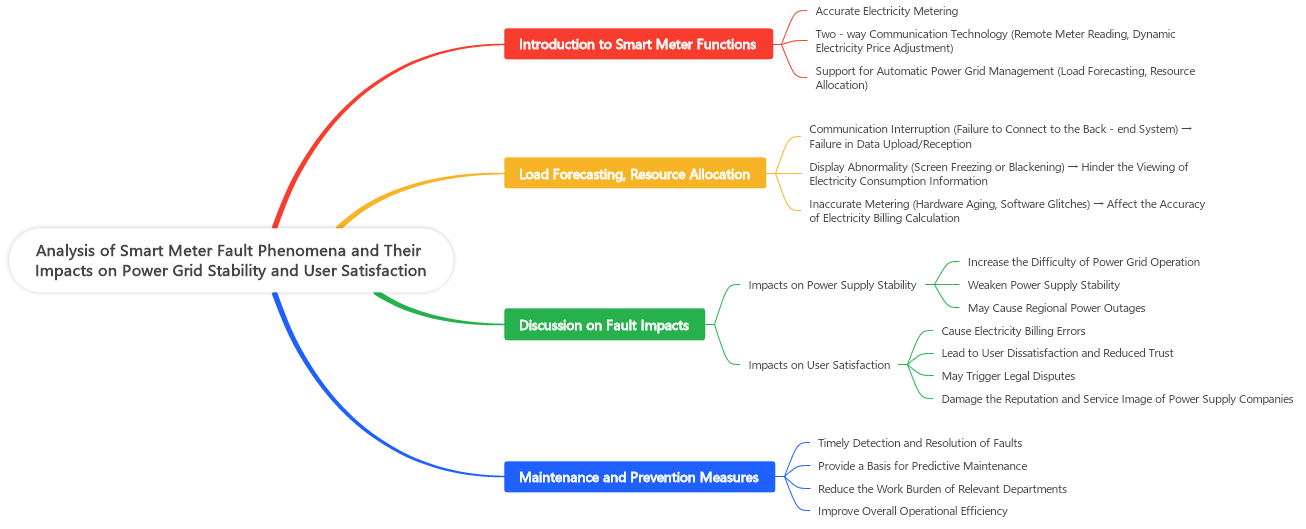
1.3 Pagdiskusyon sa Epekto sa Kasinatian sa Stability sa Power Supply ug Customer Satisfaction
Ang mga kasinatian sa smart meter maaaring mapahimutang sa utilities sa pag-collect sa accurate nga user data, nagresulta sa billing errors nga nag-undermine sa customer trust ug satisfaction. Lalo na sa peak periods, ang widespread communication failures maaaring komplikado ang grid dispatching, threatening sa power supply stability ug maaari mopasabot sa regional outages. Ang billing disputes gikan sa measurement inaccuracies dili lamang nagdisatisfy sa users apan maaari usab mopasabot sa legal issues, damaging sa reputation sa utility. Kini nga, ang pag-ensure sa reliable operation sa smart meters kay essential aron mapataas ang high service standards, enhance ang customer satisfaction, ug foster long-term customer relationships.
2 Paghahayag sa Underlying Causes sa Failures sa Smart Meter
2.1 Challenges sa Performance sa Meter Gikan sa Aging Hardware Components ug Environmental Factors
Ang aging sa hardware components sa smart meters, sama sa circuit boards, batteries, ug sensors, maaaring mapasabot sa performance degradation. Ang prolonged exposure sa high temperatures o humidity mao ang nag-accelerate sa aging sa electronic components, nagresulta sa poor contact o short circuits, nga naapektuhan ang meter efficiency. Ang extreme weather conditions sama sa thunderstorms ug ice mao ang maphysical damage sa meters, nag-weaken pa usab sa ilang functionality. Ang accumulation sa dust ug pollutants mao ang nag-hinder sa heat dissipation, nag-increase sa failure risks. Ang regular inspections ug maintenance, sama sa protective measures sama sa moisture-proof ug dust-proof materials ug lightning protection devices, kay essential aron mapataas ang equipment life ug reliability.
2.2 Operational Risks gikan sa Software Defects ug System Compatibility Issues
Ang smart meters naka-rely sa complex software systems para sa iba't ibang tasks. Ang unforeseen defects o errors sa software maaaring mapasabot sa system crashes o data loss. Isip nag-advance ang grid technology, ang compatibility issues tali sa different software versions maaaring mopasabot, difficult sa new ug old equipment nga mogamit ngadto. Ang continuous updates ug optimizations sa software kay necessary aron mapataas ang robustness ug adaptability, sama sa enhanced software testing processes aron masiguro ang stable operation sa new software versions sa practical applications.
2.3 Threats sa Security sa Meter gikan sa External Cyber-Attacks ug Physical Damage
Ang smart meters nag-exchange og data sa networks, making them potential targets for cyber-attacks. Ang hackers maaaring mogamit sa security vulnerabilities aron remotely control o steal user information. Ang advanced encryption technologies ug strict authentication mechanisms kay indispensable aron mapataas ang security. Besides cybersecurity threats, ang meters usab adunay risk gikan sa physical damage gikan sa vandalism o natural disasters. Ang installation sa protective devices (sama sa anti-theft locks ug earthquake-resistant casings) mao ang effective nga mapababa ang risks associated sa physical damage. Ang integration sa mga method niini significantly enhances the security protection sa smart meters, safeguarding both the power grid ug user information.
3 Exploring Innovative Applications of Smart Meter Fault Diagnosis Technologies
3.1 Using Big Data Analysis to Predict Potential Faults
Ang collecting ug analyzing sa large amounts of data gikan sa smart meters mao ang identify potential fault patterns ug trends. Pinaagi sa continuous monitoring sa operational parameters sama sa voltage, current, ug temperature, mao ang establish models aron predict the aging rate sa hardware components o possible anomalies. Kini nga approach not only aids in preventive maintenance planning apan reduce usab ang likelihood sa sudden failures. Ang big data analysis mao ang reveal correlations among different fault types, providing strong support for optimizing grid management ug service quality.
3.2 Implementing Real-Time Monitoring ug Automatic Anomaly Detection to Improve Response Speed
Ang real-time monitoring systems mao ang allow power companies sa pag-track sa working status sa smart meters continuously, promptly discovering ug handling any anomalies. Ang automatic anomaly detection mechanisms, based on preset rules ug machine learning algorithms, mao ang automatically identify behaviors nga deviate from normal operational patterns ug immediately trigger alarms. Kini nga method not only accelerates fault response speed apan allows usab taking preemptive actions before problems escalate, significantly improving the reliability ug stability sa power system.
3.3 Integrating Multiple Advanced Technologies for Accurate Fault Location ug Rapid Repair
Combining IoT, cloud computing, ug artificial intelligence modern information technologies greatly improves fault location accuracy ug repair efficiency. Ang IoT devices enable comprehensive sensing sa smart meters ug their surrounding environment, precisely pinpointing fault locations. Ang powerful computing capabilities provided by cloud platforms support complex data processing tasks, helping to quickly analyze fault causes. The application of AI makes the fault diagnosis process more intelligent, recommending optimal solutions based on specific circumstances. Through this integration of multiple technologies, affected areas' power supply services can be swiftly restored, accumulating valuable experience data to improve future maintenance strategies ug technical solutions.
4 Effective Strategies for Enhancing the Reliability ug Stability of Smart Meters
4.1 Extending Meter Lifespan Through Improved Design ug Material Selection
The design ug materials used in smart meters directly impact their durability. Considering mechanical strength during the design phase, using reinforced structures to withstand external physical shocks; applying efficient heat dissipation designs to prevent overheating; optimizing internal circuit layouts to reduce electromagnetic interference; selecting corrosion-resistant, anti-oxidation materials like stainless steel or special plastics can effectively resist harsh environmental factors, extending equipment lifespan.
4.2 Optimizing Algorithms ug Upgrading Software to Enhance System Anti-Interference Capability
Optimizing algorithms ug regular software updates are key approaches to enhance system stability against various interferences faced by smart meters. Improving measurement algorithms to increase data processing accuracy ug reducing errors caused by signal fluctuations ensures accurate measurement results. Utilizing machine learning algorithms to dynamically optimize performance based on real-time operating conditions enables meters to adapt to changing grid conditions. During software upgrades, compatibility tests should be emphasized to ensure seamless integration between new ug old systems.
4.3 Strengthening Safety Management Measures Against Internal ug External Security Threats
Faced with increasing security threats, adopting multi-layered safety management measures is crucial for ensuring the security of smart meters. Deploying firewalls ug intrusion detection systems at the network level monitors ug blocks illegal access attempts. Implementing strict authentication mechanisms ensures only authorized users can access meter data. Physically reinforcing meters ug adding anti-tampering devices prevents unauthorized physical tampering. Regularly conducting safety audits identifies ug fixes potential vulnerabilities. Training maintenance personnel in the latest safety knowledge ug techniques raises overall safety awareness.
5 Exploring New Directions for Future Development of Smart Meters
5.1 Utilizing Artificial Intelligence Technology to Predict ug Prevent Failures
AI technology enables smart meters to learn ug identify potential fault patterns from massive data. Training neural network models to analyze historical operational data predicts future problems; real-time monitoring of meter status based on machine learning algorithms issues warnings in advance of anomalies, allowing timely action. AI can also optimize maintenance plans, reducing unnecessary inspections ug repairs through predictive maintenance, lowering operational costs, enhancing meter reliability ug security, ug making the power system more efficient ug stable.
5.2 Building a Smart Energy Ecosystem to Promote Efficient Resource Allocation
The establishment of a smart energy ecosystem aims to achieve efficient allocation ug utilization of energy. By integrating smart meters, distributed energy resources, ug energy storage systems into an interconnected network, it makes the production, transmission, ug consumption of energy more transparent ug controllable. Utilizing big data analysis ug cloud computing technologies, dynamic adjustments to supply-demand balance ug optimization of grid load distribution reduce waste. Users can flexibly adjust their electricity usage behavior based on real-time price information, improving energy use efficiency. This integrated solution promotes renewable energy development, reducing reliance on traditional fossil fuels, providing a solid foundation for achieving sustainable development goals.
5.3 Exploring Emerging Technologies ug Materials to Revolutionize Meter Performance
With technological advancements, the application of emerging technologies ug materials offers unprecedented opportunities for performance improvements in smart meters. Using new conductive materials like graphene significantly enhances meter sensing precision ug response speed; nanotechnology can produce smaller, more efficient electronic components, reducing meter size ug cost; the introduction of quantum computing ug blockchain technologies strengthens data processing capabilities ug security, ensuring data authenticity ug immutability; 5G communication technology accelerates data transmission rates, enhancing remote monitoring ug control capabilities. These technological innovations collectively open new paths for the future development of smart meters, heralding the arrival of a new era.
6 Conclusion
This article analyzes the functions of smart meters, common faults, ug their impacts, proposing methods to achieve precise fault location ug rapid repair using big data analysis, real-time monitoring, ug various advanced technologies. It discusses the importance of design improvement, algorithm optimization, ug strengthening safety management measures, finally looking ahead to the potential of artificial intelligence, smart energy ecosystems, ug emerging technologies ug materials in enhancing smart meter performance. This article aims to provide theoretical support ug practical guidance for the development of smart grids, promoting the intelligence ug efficiency of power systems.






















