Pangitaa sa Pagkawala ug Pagprognosya sa Kahimtangan sa mga Power Capacitors sa Mataas nga Temperature
Bilang ang mga sistema sa kuryente nagpadayon nga mogrow ug ang mga demand sa load nagsugod pagtaas, ang kapaligiran sa operasyon sa mga electrical equipment nagsugod magkomplikado. Ang pagtaas sa ambient temperature nagsugod maging usa ka key factor nga nakakaapekto sa reliable operation sa mga power capacitors. Isip mga critical components sa mga sistema sa transmision ug distribution, ang pagkawala sa performance sa mga power capacitors direkta nakaapekto sa safety ug stability sa grid. Sa mataas nga temperatura, ang dielectric materials sa loob sa mga capacitors mas dali mokauban, resulta sa significant na pagkawala sa electrical performance, shortened service life, ug posibleng system failures.
1. Pag-aaral sa Characteristics sa Pagkawala sa Performance
1.1 Experimental Setup
Ang parallel power capacitors nga adunay rated voltage nga 10 kV ug capacity nga 100 kvar gipili isip mga test samples, naa sa requirements sa GB/T 11024.1—2019, Shunt capacitors for a.c. power systems with a rated voltage above 1000 V – Part 1: General. Ang test system gisulayan og OMICRON CP TD1 capacitance tester ug ME632 dielectric loss analyzer, uban ang temperature controlled pinaagi sa KSP-015 high-temperature aging chamber. Tres temperature levels—70 °C, 85 °C, ug 100 °C—giset, uban lima ka samples gisulayan sa matag level. Ang prosedura sa test gisunod ang IEC 60871-2, aplikahan ang rated voltage continuously sa panahon sa aging aron simularon ang tun-ang condition sa operasyon.
1.2 Dielectric Loss Degradation Behavior
Sa mataas nga temperatura, ang dielectric loss (tanδ) nagsugod magpakita og significant na temperature dependence. Sa 70 °C, ang tanδ nag-increase slowly sa panahon, narehistro sa operational limits, nagsulti sa stable insulation performance. Sa 85 °C, ang rate sa increase nag-accelerate, ang slope sa curve naging mas steep; ang uban sa mga samples nagsugod moadto sa standard limits sa huling bahin. Sa 100 °C, ang tanδ nag-rise sharply uban ang steep curve, nagpakita sa typical characteristics sa thermal aging.
1.3 Capacitance Variation Characteristics
Ang pagtaas sa temperatura nakaapekto sa capacitance stability, uban ang clear stage-dependent behavior. Sa bata nga temperatura, ang capacitance deviation narehistro sa allowable tolerances, nagpakita sa good stability. Sa medium-temperature range, ang capacitance nagsugod mag-decay noticeably, ang deviation naga-approach sa operational limits. Sa mataas nga temperatura, ang capacitance nag-decrease rapidly, nagsugod moadto sa allowable deviation, nagsulti sa accelerated deterioration.
2. Development sa Life Prediction Model
2.1 Analysis sa Data sa Performance Degradation
Pinaagi sa pag-compare sa degradation rates sa matang temperature levels, ang relationship tali sa temperatura ug acceleration factor gianalisa. Ang comprehensive failure criterion gibasehan sa key parameters sama sa dielectric loss, capacitance deviation, ug insulation resistance. Ang resulta nagsulti nga ang performance degradation naka-accelerate significantly sa mataas nga temperatura, ang acceleration factor nagpakita og exponential relationship sa temperatura. Ang data fitting nagsulti sa high correlation coefficient, nagsulti sa strong statistical significance. Ang Arrhenius equation gigamit aron ma-calculate ang acceleration factor, uban sa experimentally derived activation energy ug Boltzmann’s constant, aron makabuo og quantitative temperature-acceleration relationship.
2.2 Application sa Arrhenius Model
Isip gihatagan sa Figure 1, ang experimental data gi-fit sa log-lifetime vs. inverse temperature (1/T) coordinate system, nagsulti sa strong linear correlation. Ang slope sa fitted line kasagaran sa activation energy EaEa (sa kJ/mol), representante sa energy barrier sa aging process, ug nagsulti sa theoretical expectations. Ang high correlation coefficient nagsulti sa excellent agreement tali sa experimental data ug Arrhenius model. Ang 95% confidence interval analysis nagsulti sa statistically reliable predictions. Ang experimental results nagsulti nga, sa tested temperature range, ang rate sa performance degradation naka-exponentially related sa temperatura. Pinaagi sa life data sa matang temperature points, ang mathematical model relating temperature ug service life giatiman.
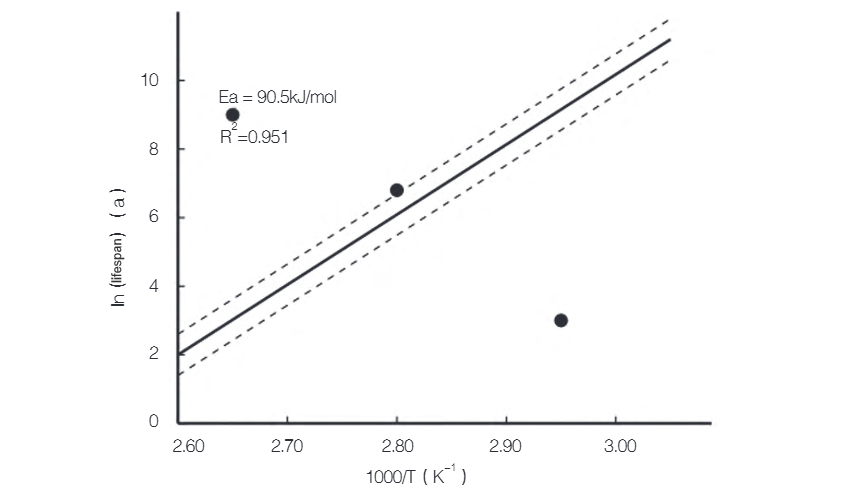
2.3 Implementation sa Life Prediction
Ang life prediction based sa cumulative damage theory, nga superimpose ang damage effects sa matang temperature conditions. Ang prediction method komprehensibo nga consider ang factors sama sa material aging rate, environmental temperature fluctuations, ug load variations. Ang operating cycle gisulayan sa n time intervals, ang damage sa matag interval determinado sa operating temperature ug duration. Ang temperature data gikolekta pinaagi sa online monitoring system sa sampling interval nga 1 h aron siguraduhon ang data continuity ug accuracy. Ang measured temperatures gipasok sa Arrhenius equation aron ma-calculate ang equivalent operating time sa matag interval. Ang accumulated damage sa tanang intervals nagsulti sa predicted remaining service life [4]. Ang prediction accuracy geverify pinaagi sa accelerated aging test results, ang average deviation tali sa model calculations ug experimental data maintained sa ±8%.
3. Application ug Verification
3.1 Analysis sa Prediction Accuracy
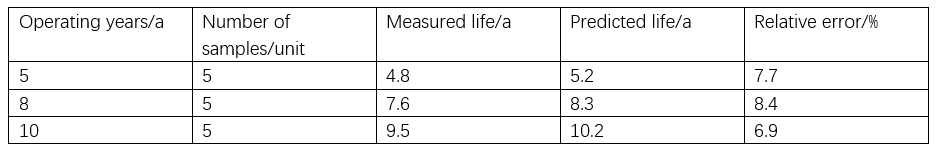
Ang prediction model geverify pinaagi sa combined approach sa accelerated aging tests ug actual operational data. Ang multiple batches sa power capacitors sa matang service durations gipili alang sa performance testing, ug ang resulta gicompare sa model predictions. Isip gihatagan sa Table 1, para sa 5-year operating group, ang measured average life 4.8 years ug ang predicted value 5.2 years, ang relative error 7.7%; para sa 8-year group, ang measured value 7.6 years ug ang predicted value 8.3 years, ang relative error 8.4%; para sa 10-year group, ang measured value 9.5 years ug ang predicted value 10.2 years, ang relative error 6.9%. Ang error source analysis nagsulti nga ang environmental temperature fluctuations ang primary factor nga nakaapekto sa prediction accuracy. Kapag ang daily temperature variation adto sa 20 °C, ang model prediction error nag-increase sa 12%. Bisan pa, ang temperature fluctuations gikan sa load variations nagsumbong sa increase sa prediction error sa 4.2%.
3.2 Engineering Application Recommendations
Isip gihatagan sa Table 2, kapag ang ambient temperature maintained sa below 75 °C, ang rate sa equipment life degradation nag-decrease sa 58%. Para sa every 5 °C reduction sa installation location temperature, ang expected service life nag-increase sa 18.5%. Pinaagi sa pag-improve sa ventilation, ang ambient temperature sa test site nag-decrease sa average nga 7.2 °C, resulta sa 32% improvement sa stability sa capacitor performance parameters. Ang temperature data gikan sa online monitoring system nagsulti nga human sa pag-implement sa intelligent ventilation, ang maximum temperature sa palibot sa equipment nag-decrease sa 11.3 °C ug ang average temperature sa 8.7 °C. Ang life prediction model giapply sa 500 kV substation sa usa ka tuig, successful nga nagsulay sa early warnings sa six potential failures, nag-increase sa preventive maintenance efficiency sa 43%. Ang maintenance data analysis nagsulti nga ang maintenance ug replacement decisions based sa model predictions nakuha ang accuracy sa 87%, representante sa 35% improvement sa traditional time-based maintenance. Ang model-guided equipment management strategy nagreduce sa maintenance costs sa 27% ug nag-increase sa equipment availability sa 15%.
4. Conclusion
Pinaagi sa systematic accelerated aging tests ug data analysis, kini nga study nagsugyot sa influence sa high-temperature environments sa performance degradation sa power capacitors ug napatyon og life prediction model based sa Arrhenius equation. Ang experimental results nagsulti nga ang ambient temperature ang key factor nga nakaapekto sa capacitor life: para sa every 10 °C increase sa temperature, ang service life nag-decrease sa 42.5% ± 2.5%. Ang critical performance parameters sama sa dielectric loss, capacitance, ug insulation resistance nagsugod magpakita og significant na degradation trends sa pagtaas sa temperatura. Ang developed life prediction model nakuha ang prediction accuracy sa over 90%, naghatag og scientific basis sa maintenance ug replacement decisions sa power capacitors.























