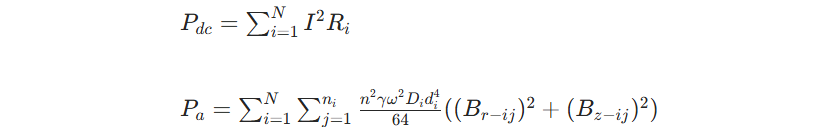1 Teknikal nga mga Katangian ug Standard References sa 500kV Dry-type Shunt Reactors
1.1 Teknikal nga mga Katangian
Ang 500kV dry-type shunt reactor, usa ka oil-free power device alang sa ultra-high-voltage transmission systems, naglangkob og core features sama sa advanced insulation, innovative heat dissipation, optimized electromagnetic design, ug modular structure. Kini nga mga advantage, na nagsayo gihapon sa traditional nga oil-immersed reactors, usab nagdrive og bag-ong teknikal nga standard demands.
Advanced Insulation: Gamiton ang epoxy resin casting ug nanocomposites (may nano-SiO₂ particles nga nagboost sa epoxy breakdown strength ngadto sa ~40% ug partial discharge initial voltage sa 25%), kini nag-improve sa insulation ug partial discharge resistance. Kini nga breakthrough nagkinahanglan og redefining sa insulation levels ug partial discharge test methods sa standards.
Innovative Heat Dissipation: Usa ka composite structure (multi-channel forced air cooling + phase-change material-assisted heat dissipation) nagpanatili sa hot-spot temperature rise within 60K (gamay pa kay sa IEC limits, verified pinaagi sa finite element analysis ug experiments). New temperature-rise test methods/limits kinahanglan sa standards.
Optimized Electromagnetic Design: Multi-layer staggered winding ug gradient insulation nagoptimize sa electric field distribution, nag-improve sa short-circuit resistance. Ang finite element analysis nagpakita og ~20% reduction sa maximum electric field strength sa windings. Standards dapat magdugang og evaluation methods para sa electric field distribution ug short-circuit resistance.
Modular Structure: Gicompose sa serially connected identical basic units, easing manufacturing, transportation, ug on-site installation. Standards kinahanglan ug test requirements para sa inter-module connection reliability ug overall performance consistency.
1.2 Reference ug Formulation sa Teknikal nga Standards
Sa pag-apply sa 500kV dry-type shunt reactor tech sa Brazil, ang teknikal nga standards nagplay og key role. Ang research team adunay deep dive sa Brazil's electrical standard ABNT NBR 5356-6 Transformer Part 6: Reactors, ug gipanghunahuna ang international standards sama sa IEC 60076-6 Power Transformers - Part 6: Reactors ug IEEE Std C57.12.90-2021 Standard Test Procedures for Liquid-Immersion Distribution, Power, ug Regulating Transformers, aron makadevelop og 500kV dry-type shunt reactor technical specification nga angay sa context sa Brazil.
Key focuses sa panahon sa specification formulation:
Insulation Level: Customized sa grid sa Brazil, ang insulation requirements gibataas (lightning impulse withstand voltage: 1550kV; operating impulse withstand voltage: 1175kV - mas taas kay sa Chinese standards apan angay sa grid). Sumala sa NBR5356-6, switching impulse test Tz ≥ 1000 μs ug Td ≥ 200 μs.
Temperature Rise & Heat Dissipation: Para sa high-temp environment sa Brazil, ang average temperature rise limit gitighten gikan sa 60K hangtod 50K (pinaagi sa innovative cooling design, nagboost sa safety). Gitambahon ang thermal imaging analysis ug long-term temperature monitoring sa composite cooling structure.
Loss Requirements & Calculation: Designed sumala sa standards sa Brazil uban sa 0.3% interference loss limit. Pinaagi sa IEEE Std C57.12.90-2021 Annex B.2, gi-build ang 50Hz-60Hz loss conversion model, nagensure sa accurate ug comparable loss calculations across frequencies.
Environmental Adaptability: Para sa hot ug humid climate sa Brazil, gitambahon ang anti-salt-fog, anti-pollution-flashover, ug anti-UV requirements aron mapalambo ang long-term reliability. Gi-formulate ang tests sama sa accelerated aging ug humid-heat cycle tests.

2 Application Practice sa 500kV Dry-type Shunt Reactors sa Brazil
2.1 Challenges sa Technology Introduction ug Standard Adaptation
Ang pag-apply sa 500kV dry-type shunt reactor technology sa power system sa Brazil naghatag og daghang challenges, kinahanglan ug solusyon sa kini nga mga key issues:
Technical Standard Differences: Ang ABNT NBR 5356-6 Transformer Part 6: Reactors sa Brazil ug China's GB/T 1094.6-2017 Power Transformers - Part 6: Reactors structurally similar apan may differences sa specific requirements ug implementation details. Both reference IEC 60076-6 pero localized sa national needs, varying sa insulation levels, temperature-rise limits, ug loss-calculation methods. Kini nga differences nagkinahanglan og careful handling sa panahon sa technology adaptation.
Climate Adaptability: Ang tropical climate sa Brazil (e.g., Silvânia region: annual average temperature >25°C, relative humidity ≥80%) naghatag og higher heat-dissipation ug insulation demands. Kini nga hot, humid environment severe challenge sa traditional power equipment's insulation ug service life.
Grid-Characteristic Adaptation: Ang 500kV grid sa Brazil may voltage fluctuations ~15% mas taas kay sa same-level grids sa China, may different harmonic environments. Ang reactors kinahanglan og stronger voltage adaptability ug anti-harmonic performance.
Localized Operation & Maintenance (O&M) Needs: Aron mapasuportahan ang long-term reliable operation, localized O&M capabilities/habits kinahanglan consider, covering technical training, spare-parts supply, ug localized services.
2.2 Adjustment ug Innovation sa Teknikal nga Standards
Arong masolusyonan ang above challenges, ang research ini nahimo og innovative measures, most crucially adjusting pre-project teknikal nga standards ug specifications based sa actual use ug testing sa new dry-type reactor. Kini nagsolusyon sa teknikal nga adaptation issues ug nagprovide og key reference sa similar projects.
Key technical standard modifications:
Cancel Partial Discharge Test: External corona interference sa dry-type reactors far exceeds their internal partial discharges. Wala pa mature testing methods/criteria sa interference partial discharge, ug considering NBR 5356-11-2016 applies lang sa low-voltage dry-type transformers (wala external interference) ug IEEE C57.21 exempts dry-type shunt reactors from such tests, ang partial discharge test sa 500kV dry-type reactors canceled.
Optimize Insulation & Test Time: Sumala sa Brazilian standards, lightning impulse withstand voltage 1550kV ug operating impulse withstand voltage 1175kV. Due to reactor impedance, switching impulse test time parameters adjusted to Td ≥ 120 μs ug Tz ≥ 500 μs.
Enhance Heat Dissipation: Para sa hot, humid climate sa Brazil, developed ang new composite heat-dissipation structure using Class H (180°C) insulation (boosting heat resistance by 30°C vs traditional designs). Thermal simulations show hot-spot temperature rise stays within 60K (below design limits).
Adjustment of Loss Calculation Method: A reactor's loss comprises the DC resistance loss of its winding (Pdc) and the winding's additional loss (Pa). For a given reactor structure, both Pdc and Pa are proportional to the square of the current. Using transposed conductors, and with only a few small conductive metal components (like connectors) at connection points (non-magnetic), the additional loss accounts for a low proportion of the DC loss. Test results show the prototype's extra loss is ~9%–12%, so the loss calculation formula is as follows:
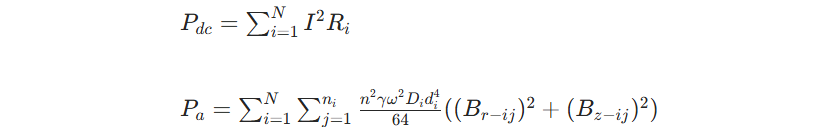
Enhancing Voltage Adaptability: By optimizing the electromagnetic design, the voltage adaptation range of the equipment was expanded to cope with the large voltage fluctuations in the Brazilian power grid. Meanwhile, the equipment's anti-harmonic performance was improved, and harmonic modes were reduced through a special winding design.
3 Evaluation sa Practical Effects ug Technical Standards
3.1 Analysis sa Practical Effects
Through application at Silvânia Substation, ang 500kV dry-type shunt reactor showed excellent performance. Sumala sa CEPRI-EETC03-2022-0880 (E) test report, key indicators:
Loss Level: Measured loss: 58.367kW @ 80°C (below 60kW limit), verifying effective loss calculation/control methods.
Noise Control: Measured noise: 57dB(A) (well under 80dB(A) requirement), thanks to focused noise-control design.
Temperature-Rise Performance: Average temp rise: 22.9K; hot-spot rise: 26.5K (both under design limits), validating new cooling design for Brazil's climate.
Electrical Performance: Performed well in tests (lightning/operating impulse). Used ABNT NBR 5356-4/IEC 60076-4 parameters (T1, Td, Tz) for operating impulse, accounting for reactor impedance.
These prove the reactor's applicability/superiority in Brazil's grid, especially in energy efficiency/environmental protection, supporting sustainable development. Results also verify scientific, forward-looking technical specs.
3.2 Technical Standard Optimization Evaluation
Based on practice/operation, the team proposes optimizations:
Loss Limits: Lower 500kV/20Mvar reactor loss limit from 60kW @ 80°C to 58kW @ 80°C; use 75°C for loss-calculation reference.
Noise Standards: Refine standards (e.g., 75dB(A) for substations near residences); consider noise under varying voltages (e.g., 600kV).
Temperature-Rise Limits: Adjust average temp-rise limit from 60K to 50K; specify Class B insulation (130°C temp index, 60/90°C avg/hot-spot rises).
Insulation Coordination: Raise lightning impulse withstand voltage to 1600kV (for Brazil's frequent lightning); use 140kV power-frequency dry-withstand for neutral-point insulation. Define test freq (≥48Hz, 80% of rated) and duration (≥60s).
Environmental Adaptability: Add anti-salt-fog reqs (coastal areas); consider EMF impact, set spacing. Use shields, anti-pollution/UV coatings in design.
These suggestions boost reactor performance/reliability, guide future standards, and help Brazil's grid develop efficiently, reliably, and sustainably.