I. Overall Situation
Overall, State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC) and China Southern Power Grid (CSG) currently maintain a pragmatic stance toward solid-state transformers (SSTs)—actively supporting R&D while prioritizing pilot demonstrations. Both grid companies are advancing SST feasibility through technology research and demonstration projects, laying the groundwork for potential large-scale deployment in the future.
| Project |
State Grid (and Affiliated Units) |
China Southern Power Grid (and Affiliated Units) |
| Overall Attitude |
Regards SST as a forward-looking key technology to support the new power system and actively lays out research and demonstration. |
Includes SST-related technologies in key development directions and explores application value through demonstration projects. |
| Technical Research |
Institutions such as the subordinate China Electric Power Research Institute conduct in-depth research on amorphous nanocrystalline iron cores and other core SST materials and technologies. |
In the "2025 Key Tasks for New Power System Construction", explicitly proposes the application of "low-voltage AC-DC hybrid distribution technology" and "optical storage and charging integrated station", which are typical application scenarios of SST.Focuses on improving SST-related technologies, such as "grid-forming technology" and "converter anti-interference and active support". |
| Demonstration Application |
SST has been implemented in demonstration projects of State Grid and China Southern Power Grid in many places such as Zhuhai, Dongguan, Shanxi, Suzhou, etc.In Xiong'an New Area and Zhangjiakou Winter Olympics demonstration projects, excellent new amorphous nanocrystalline iron cores were applied, verifying their stability under high-frequency working conditions. |
Promotes projects such as the Guangzhou 220kV Tianhetangxia VSC Back-to-Back Project, providing application scenarios for new power electronic equipment such as SST.Listed company CSG Technology explicitly states that it has fully reserved cutting-edge core technologies of SST, which can be used in scenarios such as distributed new energy grid connection and regional flexible interconnection. |
State Grid Corporation of China and China Southern Power Grid are primarily fostering the development of cutting-edge technologies like solid-state transformers (SSTs) through technological R&D, pilot demonstration projects, and policy support—creating an enabling environment and necessary conditions. However, SSTs remain in a forward-looking, incubation phase for now.
| Measure Direction |
Specific Means |
Stakeholders / Cases |
| Support Technical R&D |
Subordinate research institutions directly initiate projects to tackle key SST core components (such as high-frequency transformers, new insulating materials). |
China Southern Power Grid Research Institute procures "1MVA high-frequency transformer" and researches "environmentally friendly solid insulation transformer materials". Such research forms the technical foundation for constructing solid-state transformers. |
| Provide Demonstration Opportunities |
Establish a "grid-connected trial operation" mechanism, solicit new technologies and products from the whole society, and provide a path for verified technologies to be included in the procurement catalog. |
China Southern Power Grid publicly solicits new power system products for grid-connected trial operation. Technologies that meet the conditions can be included in the New Technology Promotion and Application Catalog and generate procurement material codes. This provides a potential access channel for future SST. |
| Expand Application Scenarios |
In the construction of new power systems, plan and build demonstration projects where SST can leverage its advantages. |
China Southern Power Grid promotes "low-voltage AC-DC hybrid distribution technology" and "optical storage and direct current power supply technology" in its 2025 key tasks. These scenarios are exactly the ideal application fields for SST. |
| Create a Policy Environment |
Follow the top-level design of the National Energy Administration, promote the intelligent and green upgrading of power grid equipment, and point the way for new equipment such as SST. |
Four ministries including the National Energy Administration have issued a document, explicitly mentioning the need to accelerate the development of "advanced equipment such as integrated primary and secondary intelligent switches and solid-state circuit breakers", "grid-forming and flexible DC equipment". This provides a strong policy expectation for SST. |
II. Current Status and Future Outlook
Although solid-state transformers (SSTs) offer significant technical advantages, industry analysis indicates that State Grid Corporation of China (SGCC) and China Southern Power Grid (CSG) have not yet adopted them at scale. The primary reasons lie in ongoing commercialization challenges:
Cost and Reliability: SSTs remain considerably more expensive to manufacture than conventional transformers, and their long-term operational reliability still requires extensive real-world engineering data for validation.
Lack of Standards: Unified national standards for SSTs—particularly in sectors like data centers—have not yet been established, which hampers customer investment decisions and large-scale deployment.
In response, both grid companies have adopted a clear strategy: leveraging pilot projects to “lead by example” in targeted applications—such as fast-charging infrastructure for data centers, renewable energy integration, and industrial energy efficiency—to accumulate operational experience. Simultaneously, they are actively participating in standard-setting efforts (e.g., Chinese teams are already leading the development of international SST standards), aiming to secure strategic leadership in future markets.
III. R&D and Demonstration Projects
Current developments show that both grid operators—especially CSG—are advancing SST technology with a well-defined dual-track approach: research & development and demonstration deployment.
Core Component Breakthroughs: CSG’s research institute has launched procurement initiatives focused squarely on SST core components—high-frequency transformers and novel solid-state insulation materials. This signals a strategic shift toward addressing fundamental technical bottlenecks at the material and component levels, laying the groundwork for future full-system integration.
Demonstration Pathways: The “grid-connected trial operation” mechanism serves as a critical real-world testing ground. Companies can voluntarily deploy their SST prototypes into live grid environments for long-term, comprehensive evaluation of performance and reliability. Successful products may then be included in official promotion catalogs—effectively earning a “procurement license”—which significantly lowers the barrier to market entry for emerging technologies.
IV. Building an Application Ecosystem
Beyond direct R&D, the grid companies are also cultivating an ecosystem conducive to SST adoption.
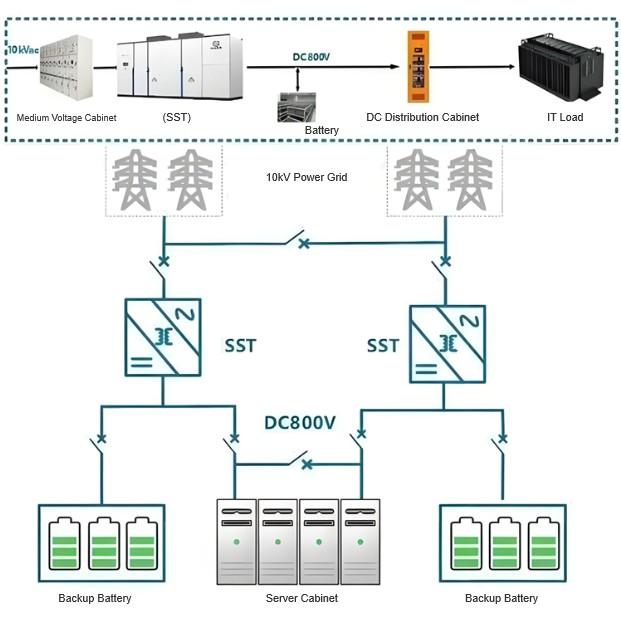
Creating Application Scenarios: SSTs excel at flexible AC/DC power conversion—a capability perfectly aligned with CSG’s strategic focus on “low-voltage AC/DC hybrid distribution” and “PV-storage-DC-flexible” (Guang-Chu-Zhi-Rou) building systems. While SSTs may not yet be deployed in these pilot projects, the infrastructure and control architectures being developed are paving the way for their future integration.
Policy Guidance: Recent guidelines issued by four national agencies, including the National Energy Administration, act as a strategic compass for next-generation grid equipment. These documents explicitly encourage intelligent integrated terminals, grid-forming equipment, and flexible DC technologies—all of which align closely with SST capabilities—providing strong confidence for upstream and downstream enterprises to invest in R&D.
V. Conclusion
While SGCC and CSG have not yet rolled out solid-state transformers at scale, they are proactively advancing the technology through a pragmatic, long-term strategy. By starting with core component innovation, establishing grid-connected demonstration mechanisms to validate full-system performance, and strategically pre-positioning SSTs within future application scenarios, China’s two major grid operators are laying a solid foundation for the eventual commercialization and widespread adoption of this transformative technology.