1 Paghahatag sa Kuryente nga Ring Network ug Ring Main Units
Sumala sa pag-usbong sa urbanisasyon, ang demand para sa mas taas nga kumpiyansya sa distribusyon sa kuryente nagpadayon nga molambo, ug mas daghan pa ka mga gumagamit ang nanginahanglan og duha o mas daghan pa ka mga pinakaonan sa kuryente. Ang tradisyonal nga "radial power supply" method nahadlok sa mga suliran alang sa pagsulay sa cable, komplikado nga pagdiskubre sa kapanguhaan, ug dili makakapugos sa pag-upgrade ug pagdako sa grid. Sa kabalaka, ang "ring network power supply" naghatag og dual o multiple power sources alang sa importante nga loads, gisimplehan ang distribution lines, gi-easy ang pagsulay sa cable, gitabangan ang numero sa switchgear, gibawasan ang failure rates, ug gi-easy ang pagdiskubre sa kapanguhaan.
1.1 Paghahatag sa Kuryente nga Ring Network
Ang ring network power supply nagrefer sa configuration diin ang duha o mas daghan pa ka outgoing lines gikan sa iba't ibang substations o iba't ibang busbars sa sama nga substation gisumbanan aron makabuo og closed loop alang sa pagdistribute sa kuryente. Ang iyang pangunahing advantage mao nga ang bawg distribution branch makadawat og kuryente gikan sa anaa nga bahin sa ring. Kon ang usa ka bahin moguba, ang kuryente gihapon mahatagan gikan sa uban nga bahin. Sumala sa operasyon sa single-loop mode, ang bawg branch maayo nga nakamit ang dual-power-source level sa kumpiyansya, sigurado nga gipataas ang kumpiyansya sa sistema. Sa Tsina, ang urban ring network power systems sumunod sa "N−1 security criterion," naa mao nga kon bisan asa sa N loads moguba, ang natun-an N−1 loads gihapon mahatagan og kuryente walay interrupsiyon o load shedding.
1.2 Mga Configuration sa Connection sa Ring Network
(1) Basic Ring Connection: Single power source diin ang cables nagsimbahan og ring, naghatag og patuloy nga paghatag sa kuryente sa uban nga loads kon ang usa ka bahin sa cable moguba (tingtong Fig. 1).
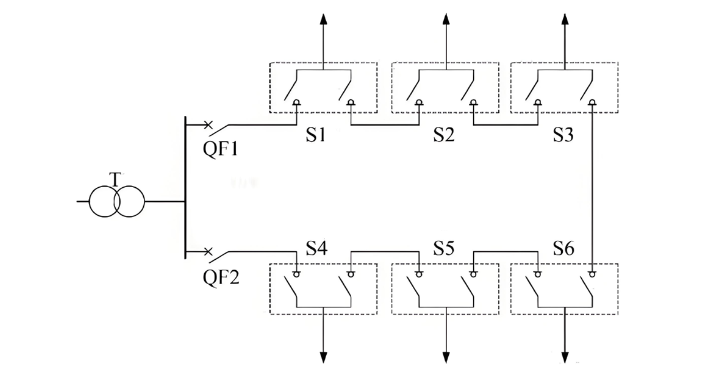
(2) Ring Connection gikan sa Iba't Ibang Busbars: Duha ka mga power sources, kasagaran ginoperahan sa open-loop mode, naghatag og taas nga kumpiyansya ug flexible nga operasyon (tingtong Fig. 2).
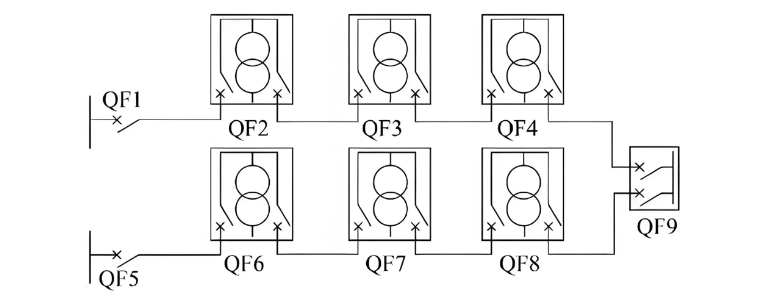
(3) Single Ring Configuration: Power sources gikan sa iba't ibang substations o busbars; ang maintenance sa bisan asa nga bahin sa cable dili maginterup sa paghatag sa kuryente sa bisan asa nga load (tingtong Fig. 3).
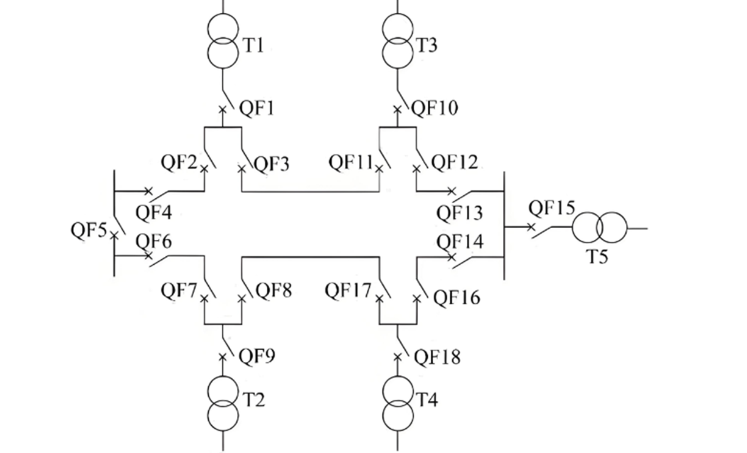
(4) Double Ring Configuration: Ang bawg load gihatagan gikan sa duha ka independent nga ring networks, naghatag og ekstremong taas nga kumpiyansya (tingtong Fig. 4).
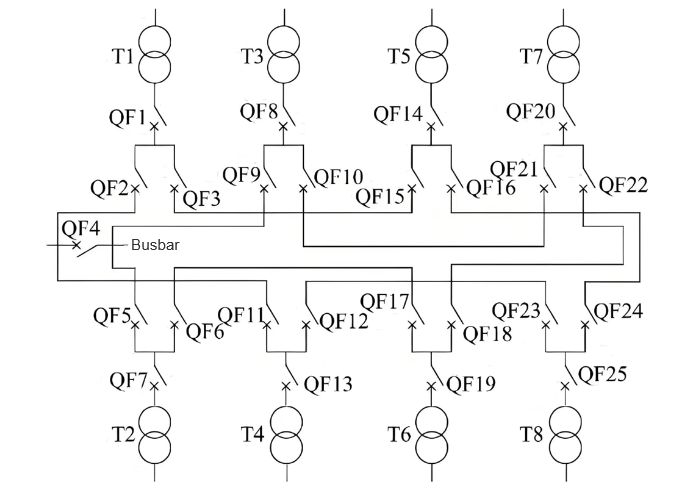
(5) Dual-Supply Double "T" Connection: Duha ka cable lines gisulay sa iba't ibang busbar sections, naghatag sa bawg load sa kuryente gikan sa duha ka lines. Kini nga configuration naghatag og near-continuous paghatag sa kuryente alang sa dual-source users ug labi na angkop sa importante nga aplikasyon (tingtong Fig. 5).
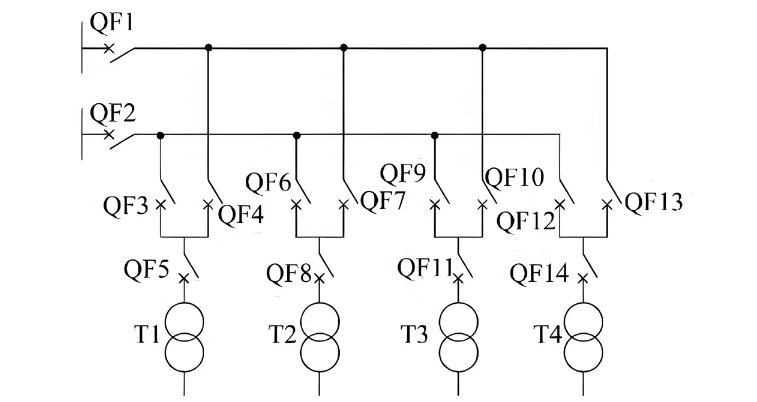
1.3 Ring Main Units ug Ilahang Characteristics
Ang ring main unit (RMU) mao ang switchgear gamiton sa ring network power systems, kasagaran naglakip og load break switches, circuit breakers, fuse-switch combinations, bus couplers, metering devices, voltage transformers, o bisan unsang combination niini. Ang RMUs compact, space-saving, cost-effective, easy to install, ug quick to commission, sumala sa demand sa "equipment miniaturization." Gi-gamit sila sa residential communities, public buildings, small and medium enterprise substations, secondary switching stations, pad-mounted substations, ug cable distribution boxes.
1.4 Mga Tipo sa Ring Main Units
Air-Insulated RMUs: Gisulti ang air isip insulating medium; kini nga mga units dako sa size, nanginahanglan og mas daghan pa ka espasyo, ug susceptible sa environmental conditions.
SF₆ RMUs: Naggamit og sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) gas isip insulating ug arc-quenching medium. Ang main switch sealed sa metal enclosure filled with SF₆, samtang ang operating mechanism located outside. Ang sealed design nagminimize sa environmental impact ug naghatag og significantly smaller footprint compared to air-insulated units. Ang SF₆ RMUs karon ang pinaka widely used type.
Solid-Insulated RMUs: Naggamit og solid insulation materials (e.g., epoxy resin) aron makapalig-on ug cast sa switches ug tanang live parts. Kini nga design nagbawas sa phase-to-phase ug phase-to-ground insulation distances, resulta ngadto sa compact dimensions comparable to SF₆ RMUs. Ania gyud, kini nageliminate sa SF₆ emissions ug makamao ang maintenance-free operation.
2 Limitations sa SF₆ Ring Main Units
Ang SF₆ mao ang major contributor sa greenhouse effect. Bisag sa iyang excellent electrical properties—such as high dielectric strength, effective arc quenching, good thermal stability, ug strong electronegativity—ug insensitivity sa humidity, pollution, ug high altitudes, making it ideal for compact electrical equipment, ang SF₆ girecognize isip potent greenhouse gas. Ang higit sa 80% sa global SF₆ production gigamit sa power industry. Ang Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) ug ang U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) classify ang SF₆ isip one of the most harmful greenhouse gases. Ang EU F-Gas Regulation (2006) prohibits ang paggamit sa SF₆ sa most applications, except where no viable alternatives exist for electrical switchgear.
Gibarisan, ang SF₆ RMUs involve high usage complexity ug significant investment, requiring various auxiliary equipment:
SF₆ leak detection systems for monitoring gas leakage, concentration, oxygen levels, ug moisture content.
SF₆ recovery equipment: During arc interruption, by-products such as SF₄ are generated; thus, at end-of-life, not only must residual SF₆ be recovered, but toxic by-products must also be specially treated.
SF₆ purification systems to clean and reuse the gas.
Ventilation systems in substations.
When using SF₆ RMUs, the following measures must be observed:
Minimize SF₆ leakage. Although SF₆ RMUs use overpressure-sealed enclosures, gas leakage is inevitable. Reduced gas pressure lowers switching reliability, directly endangering personnel safety and shortening equipment life.
Personnel must perform forced ventilation and wear specialized protective gear before entering substations with SF₆ equipment.
Operations are complex, requiring thorough and repeated training for relevant personnel.
3 Features and Applications of Solid-Insulated Ring Main Units
The potential environmental hazards associated with SF₆ ring main units (RMUs) have limited their further development, making the search for SF₆ alternatives a key research focus worldwide. Solid-insulated RMUs were first developed and introduced by Eaton Corporation of the United States at the end of the 1990s. These units produce no harmful gases during operation, have no environmental impact, offer higher reliability, and achieve true maintenance-free operation.
A solid-insulated RMU integrates vacuum interrupters, disconnect switches, grounding switches, main conductors, branch busbars, or combinations thereof, encapsulated within epoxy resin or other solid insulation materials. These components are sealed in fully insulated and fully sealed functional modules that can be recombined or expanded. Conductive or semiconductive shielding layers are applied to the outer surfaces of modules accessible to personnel, ensuring reliable grounding.
3.1 Features of Solid-Insulated Ring Main Units
(1) Environmentally Friendly Design. These units do not use SF₆ as insulation or arc-quenching medium. Instead, they employ vacuum interrupters for switching and environmentally benign, recyclable materials for primary insulation. By minimizing the number of components, they ensure low energy consumption and reduced failure rates during operation.
(2) Truly Maintenance-Free. Solid-insulated RMUs eliminate the need for SF₆ pressure vessels. Internal insulation and arc interruption rely on vacuum technology, while external insulation uses solid materials such as insulating housings. Through potting technology, the vacuum interrupter, main conductive path, and insulation supports are integrated into a single unit sealed within a metal enclosure, making performance immune to external environmental factors. The fully insulated and sealed structure eliminates the need for SF₆ leak detection, gas refilling, and waste disposal, enabling truly maintenance-free operation.
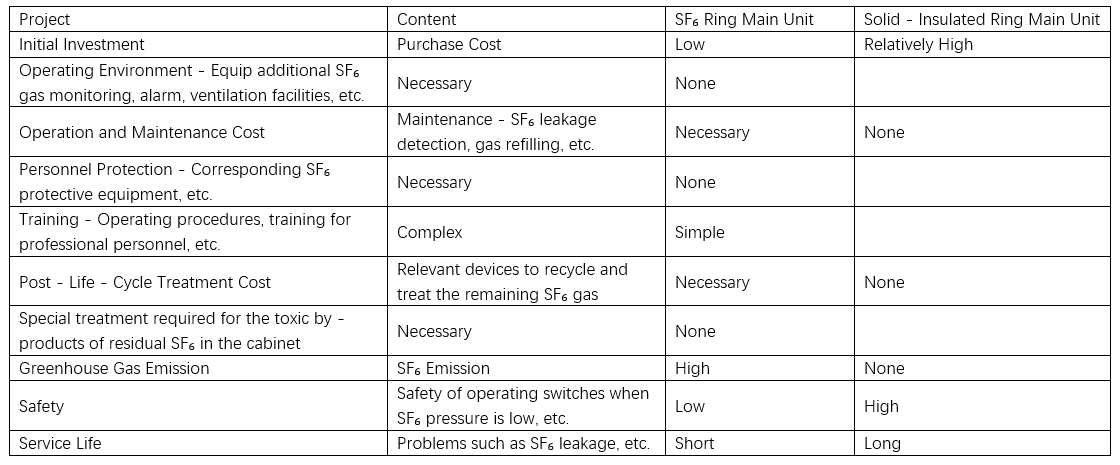
(3) High Cost-Effectiveness. Although the initial investment for solid-insulated RMUs is slightly higher than that of SF₆ RMUs, the total lifecycle cost is significantly lower, as shown in Table 1. Users are increasingly considering comprehensive factors such as safety risks, power quality, cost control, and sustainability—not just initial purchase price—but also total cost of ownership. The cumulative costs of maintenance, gas refilling, leak management, and end-of-life recovery for SF₆ RMUs can approach their initial purchase cost, whereas solid-insulated RMUs require no additional costs after installation. Thus, from a long-term perspective, solid-insulated RMUs offer superior economic benefits.
(4) Compact Structure. Designed to be as compact as possible while ensuring safety and ease of operation, these units have a smaller footprint and volume than even SF₆ RMUs, helping users save space and achieve direct economic benefits.
(5) Internal Arc Fault Resistance, Enhanced Safety and Reliability. According to Exnis reports, significant losses due to internal arcing in primary and secondary switchgear occur at least once annually. Most solid-insulated RMUs incorporate arc-resistant designs that minimize the impact of internal arcs, ensuring safer and more reliable operation.
(6) Visible Isolation Gaps. Equipped with observation windows, these units allow direct visual inspection of the three-position disconnect switch contacts, ensuring visible break points and enhancing operator safety.
(7) Intelligent Capabilities. Solid-insulated RMUs are more readily adaptable to distribution automation. By installing distribution terminal units (DTUs) and communication devices, functions such as status monitoring, remote control ("four-remote" functions), communication, self-diagnosis, and event logging can be easily implemented.
3.2 Current Application Status
Currently, the widespread adoption of solid-insulated RMUs is constrained by their relatively high cost and complex manufacturing processes. Their production requires higher technical precision than SF₆-insulated RMUs. Inadequate manufacturing techniques can lead to greater insulation risks, higher failure probabilities, and increased hazards compared to SF₆ RMUs, necessitating strict control over raw material quality and process standards. Additionally, the wiring configurations of solid-insulated RMUs are less flexible, particularly for functional units such as potential transformer (PT) cabinets and metering cabinets, offering limited options and restricting their application and development.
With continuous optimization of production processes and increasing standardization, the quality of solid-insulated RMUs is becoming more stable, and prices are gradually decreasing. Some countries offer 5%–10% incentives for products that do not use SF₆ to reduce emissions. This encourages users to consider total lifecycle costs rather than just initial purchase price. Drawing from international practices, solid-insulated RMUs can be prioritized in environmentally sensitive or new projects—such as residential communities, public buildings, and municipal infrastructure—while gradually phasing out SF₆ RMUs.
Aging or end-of-life SF₆ RMUs can be systematically replaced based on manufacturer-specified service life. Subsidies for users adopting eco-friendly solid-insulated RMUs can further support lifecycle cost considerations, promote product adoption, and advance environmentally responsible technologies. As environmental awareness grows, solid-insulated RMUs, as one of the alternatives to SF₆ RMUs, will gradually replace a portion of existing SF₆ units and gain widespread application, demonstrating strong market potential.
4 Conclusion
Solid-insulated RMUs are technologically comparable to SF₆ RMUs and possess unique advantages such as zero harmful emissions, truly maintenance-free operation, and lower total lifecycle costs, making them increasingly attractive to users. The State Grid Corporation of China's "First Catalog of Key New Technologies for Priority Promotion" (2011) stated that, considering trends toward higher technical reliability and stricter environmental requirements, solid-insulated RMUs are poised to fully replace SF₆ RMUs.
Furthermore, the "Technical Specification for 12 kV Solid-Insulated Ring Main Units" issued by the State Grid Corporation in 2012 affirmed that solid-insulated RMUs are technically capable of meeting complex operational demands and represent a new direction in RMU development, warranting active promotion. This marks formal recognition of solid-insulated RMUs by the industry and technical community. As a viable alternative to SF₆ RMUs, solid-insulated RMUs will gradually replace a portion of existing SF₆ units, achieving broad application and demonstrating excellent prospects for future development.


























