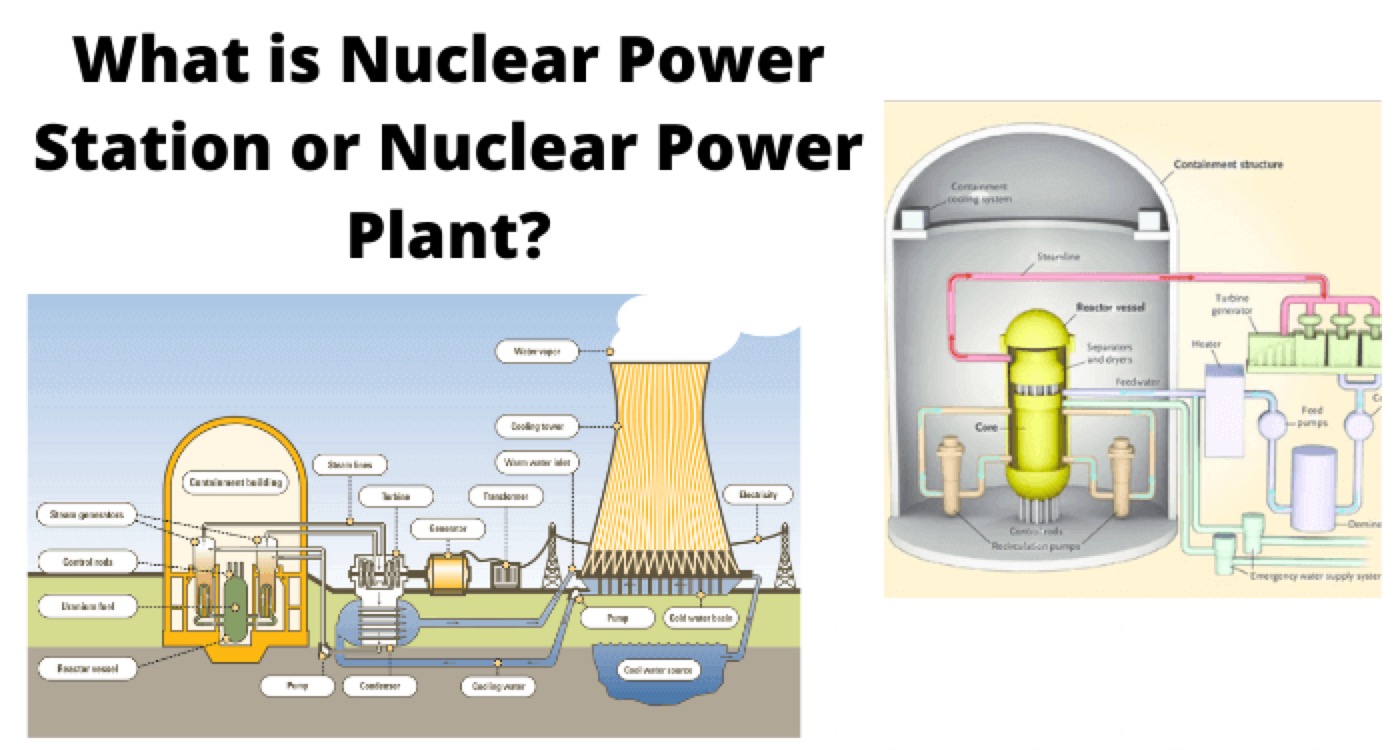
We can generate electrical power by means of nuclear power. In nuclear power station, generates electrical power by nuclear reaction. Here, heavy radioactive elements such as Uranium (U235) or Thorium (Th232) are subjected to nuclear fission. This fission is done in a special apparatus called reactor.
What is nuclear fission?
In the fission process, the nuclei of heavy radioactive atoms are broken into two nearly equal parts. During this breaking of nuclei, a huge quantity of energy is released. This release of energy is due to a mass defect. That means the total mass of the initial product would be reduced during fission. This loss of mass during fission is converted into heat energy as per the famous equation established by Albert Einstein.

The basic principle of a nuclear power station is the same as a conventional thermal power station. The only difference is that, instead of using heat generated due to coal combustion, here in a nuclear power plant, the heat generated due to nuclear fission is used to produce steam from water in the boiler. This steam is used to drive a steam turbine.
This turbine is the prime mover of the alternator. This alternator generates electrical energy. Although, the availability of nuclear fuel is not much but very less amount of nuclear fuel can generate huge amount of electrical energy.
This is the unique feature of a nuclear power plant. One kg of uranium is equivalent to 4500 metric tons of high-grade coal. That means complete fission of 1 kg uranium can produce as much heat as can be produced by the complete combustion of 4500 metric tons high-grade coal.
This is why, although nuclear fuel is much costlier, nuclear fuel cost per unit electrical energy is still lower than that cost of energy generated by means of other fuel like coal and diesel. To meet up conventional fuel crisis in the present era, nuclear power stations can be the most suitable alternatives.
Advantages of Nuclear Power Station
As we said, the fuel consumption in this power station is quite low and hence, the cost for generating a single unit of energy is quite less than other conventional power generation methods. The amount of nuclear fuel required is also less.
A nuclear power station occupies a much smaller space compared to other conventional power stations of the same capacity.
This station does not require plenty of water, hence it is not essential to construct plant near-natural sources of water. This also does not require a huge quantity of fuel; hence it is also not essential to construct the plant near a coal mine or the place where good transport facilities are available. Because of this, the nuclear power station can be established very near to the load center.
There are large deposits of nuclear fuel globally therefore such plants can ensure the continued supply of electrical energy for coming thousands of years.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Power Plant
The fuel is not easily available and it is very costly.
The initial cost of constructing a nuclear power station is quite high.
Erection and commissioning of this plant are much complicated and sophisticated than other conventional power stations.
The fission by-products are radioactive in nature, and it may cause high radioactive pollution.
The maintenance cost is higher and the manpower required to run a nuclear power plant is quite higher since specialist trained people are required.
The sudden fluctuation of load cannot be met up efficiently by the nuclear plants.
As the by-products of the nuclear reactions are highly radioactive, it is a very big problem for the disposal of these by-products. It can only be disposed of deep inside the ground or in a sea away from the seashore.

Different Components of Nuclear Power Station
A nuclear power station has mainly four components.
Nuclear reactor
Heat exchanger
Steam turbine
Alternator
Let’s discuss these components one by one:
Nuclear Reactor
In a nuclear reactor, Uranium 235 is subjected to nuclear fission. It controls the chain reaction that starts when the fission is done. The chain reaction must be controlled otherwise the rate of energy released will be fast, there may be a high chance of explosion. In nuclear fission, the nuclei of nuclear fuel, such as U235 are bombarded by the slow flow of neutrons. Due to this bombarding, the nuclei of Uranium is broken, which causes the release of huge heat energy and during the breaking of nuclei, a number of neutrons are also emitted.
These emitted neutrons are called fission neutrons. These fission neutrons cause further fission. Further fission creates more fission neutrons which again accelerate the speed of fission. This is a cumulative process.
If the process is not controlled, in a very short time the rate of fission becomes so high, it will release so huge amount of energy, there may be a dangerous explosion. This cumulative reaction is called a chain reaction. This chain reaction can only be controlled by removing fission neutrons from a nuclear reactor. The speed of the fission can be controlled by changing the rate of removing fission neutrons from reactors.
A nuclear reactor is a cylindrical shaped stunt pressure vessel. The fuel rods are made of nuclear fuel i.e. Uranium moderates, which is generally made of graphite cover the fuel rods. The moderates slow down the neutrons before the collision with uranium nuclei. The controls rods are made of cadmium because cadmium is a strong absorber of neutrons.
The control rods are inserted in the fission chamber. These cadmium control rods can be pushed down and pull up as per requirement. When these rods are pushed down enough, most of the fission neutrons are absorbed by these rods, hence the chain reaction stops. Again, while the controls rods are pulled up, the availability of fission neutrons becomes more which increases the rates of chain reaction.
Hence, it is clear that by adjusting the position of the control rods, the rate of nuclear reaction can be controlled and consequently the generation of electrical power can be controlled as per load demand. In actual practice, the pushing and pulling of control rods are controlled by an automatic feedback system as per the requirement of the load. It is not controlled manually. The heat released during a nuclear reaction is carried to the heat exchanger by means of coolant consist of sodium metal.
Heat Exchanger
In a heat exchanger, the heat carried by sodium metal is dissipated in water and water is converted to high-pressure steam here. After releasing heat in water the sodium metal coolant comes back to the reactor by means of a coolant circulating pump.
Steam Turbine
In a nuclear power plant, the steam turbine plays the same role as a coal power plant. The steam drives the turbine in the same way. After doing its job, the exhaust steam comes into a steam condenser where it is condensed to provide space to the steam behind it.
Alternator
An alternator, coupled with a turbine, rotates and generates electrical power, for utilization. The output from the alternator is delivered to the bus-bars through a transformer, circuit breakers, and isolators.
Site Selection of Nuclear Power Station
Availability of Water: Although a very large quantity of water is not regulated as a hydro-electric power plant, still sufficient supply of neutral water is obvious for cooling purposes in a nuclear power station. That is why it is always preferable to locate this plant near a river or seaside.
Disposal of Water: The by-products or wastes of the nuclear power stations are radioactive and may cause severe health hazards. Because of this, special care to be taken during the disposal of wastes of nuclear power plants. The wastes must be buried insufficient deep from earth level or these must be disposed of in sea quite away from the seashore. Hence, during selecting the location of the nuclear plant, these factors must be taken into consideration.
Distance from Populated Area: As there is always a probability of radioactivity, it is always preferable to locate a nuclear station sufficiently away from populated areas.
Transportation Facilities: During the commissioning period, heavy equipment is to be erected, which to be transported from the manufacturer site. So good railways and roadways availabilities are required. For the availability of skilled manpower good public transport should also be present at the site.
Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.

























