Makarantar jirgin noma na tsari suna da suka amfani da energy mai zurfi don gina electric power. Su zan iya kategorize a biyu na manyan abubuwa: photovoltaic (PV) makarantar jirgin noma da concentrated solar power (CSP) makarantar. Makarantar PV suna haifar da cin zaifi zuwa electric power tare da kamar solar cells, amma makarantar CSP suna amfani da mirrors ko lenses don kula cin zaifi da kuma karfin fluid wanda yake sauki turbine ko engine. A cikin wannan rubutu, zan bayyana mu abubuwan da suke, layout, da hanyoyin gwamnati na biyu na manyan abubuwa na makarantar jirgin noma, kuma abubuwan da suke da hasashen.
Me ke Photovoltaic Power Plant?
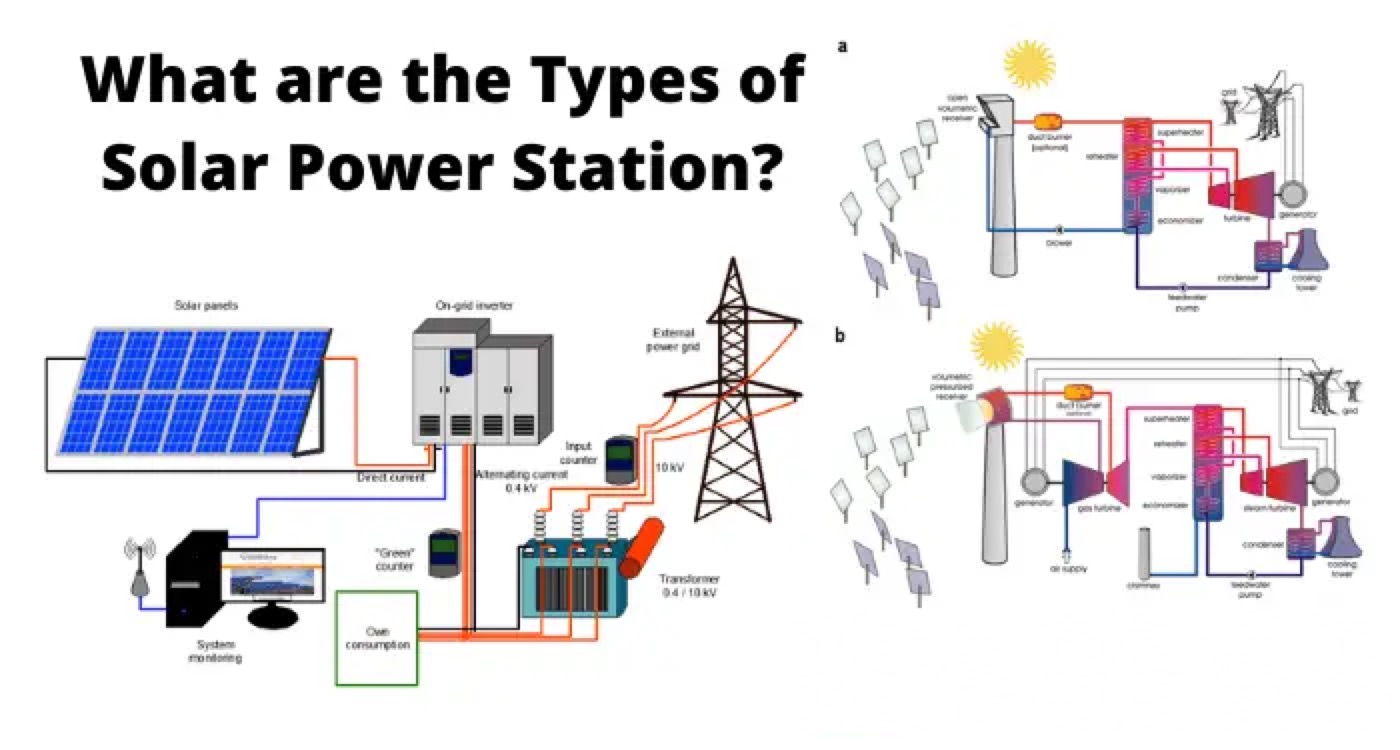
Photovoltaic power plant shine ne PV system mai yawa wanda ya shiga grid da kuma ya kirkiro don gina bulk electric power daga cin zaifi. Photovoltaic power plant na da abubuwan da suke kamar:
Solar modules: Wadannan shine babban birnin PV system. Suna da solar cells wanda suke haifar da light zuwa electric power. Solar cells suna da siyasa silicon, wanda shine material mai semiconductor wanda zai iya amfani da photons da kuma release electrons. Electrons suna haifar da circuit da kuma samar da electric current. Solar modules zai iya haifar da configurations daban-daban, kamar series, parallel, ko series-parallel, kafin haka kan voltage da current requirements na system.
Mounting structures: Wadannan shine frames ko racks wanda suke taimaka da kuma orient solar modules. Su zai iya fi sani ko adjustable, kafin haka kan location da climate na site. Mounting structures na fixe suna da rarrabe da kuma asali, amma ba suke track movement na sun kuma zai iya rage output na system. Mounting structures na adjustable zai iya tilta ko rotate solar modules don follow position na sun da kuma optimize energy production. Su zai iya manual ko automatic, kafin haka kan degree of control da accuracy needed.
Inverters: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke convert direct current (DC) wanda solar modules suke produce zuwa alternating current (AC) wanda zai iya feed into grid ko use by AC loads.

Inverters zai iya classify a biyu na manyan abubuwa: central inverters da micro-inverters. Central inverters shine large units wanda suke connect several solar modules ko arrays da kuma provide a single AC output. Micro-inverters shine small units wanda suke connect to each solar module ko panel da kuma provide individual AC outputs. Central inverters suna da cost-effective da efficient for large-scale systems, amma micro-inverters suna da flexible da reliable for small-scale systems.
Charge controllers: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke regulate voltage da current na solar modules ko arrays don prevent overcharging ko over-discharging na batteries. Charge controllers zai iya classify a biyu na manyan abubuwa: pulse width modulation (PWM) controllers da maximum power point tracking (MPPT) controllers. PWM controllers suna da simple da cheap, amma suke waste some energy by switching on and off the charging current. MPPT controllers suna da complex da expensive, amma suke optimize energy output by adjusting voltage da current to match maximum power point na solar modules ko arrays.
Batteries: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke store excess electricity generated by solar modules ko arrays for later use when there is no sunlight or when grid is down. Batteries zai iya classify a biyu na manyan abubuwa: lead-acid batteries da lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries suna da cheap da more widely used, amma suke da lower energy density, shorter lifespan, da require more maintenance. Lithium-ion batteries suna da expensive da less common, amma suke da higher energy density, longer lifespan, da require less maintenance.
Switches: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke connect ko disconnect different parts of system, kamar solar modules, inverters, batteries, loads, ko grids. Switches zai iya manual ko automatic, kafin haka kan level of safety da control needed. Manual switches require human intervention to operate them, while automatic switches operate based on predefined conditions or signals.
Meters: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke measure da kuma display various parameters of system, kamar voltage, current, power, energy, temperature, ko irradiance. Meters zai iya analog ko digital, kafin haka kan type of display da accuracy needed. Analog meters use needles ko dials to show values, while digital meters use numbers ko graphs to show values.
Cables: Wadannan shine wires wanda suke transmit electricity between different components of system. Cables zai iya classify a biyu na manyan abubuwa: DC cables da AC cables. DC cables carry direct current from solar modules to inverters ko batteries, while AC cables carry alternating current from inverters to grid ko loads.
Layout na photovoltaic power plant depends on several factors, kamar site conditions, system size, design objectives, da grid requirements. Amma, typical layout consists of three main parts: generation part, transmission part, da distribution part.
Generation part includes solar modules, mounting structures, da inverters wanda suke produce electricity from sunlight.
Transmission part includes cables, switches, da meters wanda suke transmit electricity from generation part to distribution part.
Distribution part includes batteries, charge controllers, da loads wanda suke store ko consume electricity.
The following diagram shows an example of a photovoltaic power plant layout:

Operation na photovoltaic power plant depends on several factors, kamar weather conditions, load demand, da grid status. Amma, typical operation consists of three main modes: charging mode, discharging mode, da grid-tie mode.
Charging mode occurs when there is excess sunlight and low load demand. In this mode, solar modules generate more electricity than is needed by loads. Excess electricity is used to charge batteries through charge controllers.
Discharging mode occurs when there is no sunlight or high load demand. In this mode, solar modules generate less electricity than is needed by loads. Deficit electricity is supplied by batteries through inverters.
Grid-tie mode occurs when there is grid availability and favorable tariff rates. In this mode, solar modules generate electricity that can be fed into grid through inverters.

Grid-tie mode can also occur when there is a grid outage, and backup power is needed. In this mode, solar modules generate electricity that can be used by loads through inverters.
Me ke Concentrated Solar Power Plant?
Concentrated solar power plant shine ne CSP system mai yawa wanda suke amfani da mirrors ko lenses don kula cin zaifi zuwa receiver wanda yake karfin fluid wanda yake sauki turbine ko engine don gina electric power. Concentrated solar power plant na da abubuwan da suke kamar:
Collectors: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke reflect ko refract cin zaifi zuwa receiver. Collectors zai iya classify a four types: parabolic troughs, parabolic dishes, linear Fresnel reflectors, da central receivers. Parabolic troughs shine curved mirrors wanda suke focus cin zaifi zuwa linear receiver tube wanda yake run along their focal line. Parabolic dishes shine concave mirrors wanda suke focus cin zaifi zuwa point receiver at their focal point. Linear Fresnel reflectors shine flat mirrors wanda suke reflect cin zaifi zuwa linear receiver tube above them. Central receivers shine towers surrounded by array of flat mirrors called heliostats wanda suke reflect cin zaifi zuwa point receiver at their top.
Receivers: Wadannan shine devices wanda suke absorb concentrated sunlight da kuma transfer it to heat transfer fluid (HTF). Receivers zai iya classify a two types: external receivers da internal receivers. External receivers shine exposed to atmosphere da kuma have high heat losses due to convection da radiation. Internal receivers shine enclosed in vacuum chamber da kuma have low heat losses due to insulation da evacuation.
Heat transfer fluids: Wadannan shine fluids wanda suke circulate through receivers da kuma transport heat from collectors to power block. Heat transfer fluids zai iya classify a two types: thermal fluids da molten salts. Thermal fluids shine organic liquids kamar synthetic oils ko hydrocarbons wanda suke da high boiling points da low freezing points. Molten salts shine inorganic compounds kamar sodium nitrate ko potassium nitrate wanda suke da high heat capacity da low vapor pressure.
Power block: This is where electricity is generated from heat using turbine or engine coupled with generator. Power block zai iya classify a two types: steam cycle da Brayton cycle. Steam cycle uses water as HTF da produces steam that drives steam turbine connected to electric generator. Brayton cycle uses air as HTF da produces hot air that drives gas turbine connected to electric generator.
Storage system: This is where excess heat is stored for later use when there is no sunlight or when there is high load demand. Storage systems zai iya classify a two types: sensible heat storage da latent heat storage. Sensible heat storage uses materials kamar rocks, water, ko molten salts wanda suke store heat by increasing their temperature without changing their phase. Latent heat storage uses materials kamar phase change materials (PCMs) ko thermochemical materials (TCMs) wanda suke store heat by changing their phase or chemical state without changing their temperature.
Layout na concentrated solar power plant depends on several factors, kamar site conditions, system size, design objectives, da grid requirements. Amma, typical layout consists of three main parts: collection field, power block, da storage system.
Collection field includes collectors, receivers, da HTFs wanda suke collect da kuma transport heat from sunlight.
Power block includes turbines, engines,
generators da other equipment wanda suke convert heat into electricity.
Storage system includes tanks, vessels, da other devices wanda suke store heat for later use.
Operation na concentrated solar power plant depends on several factors, kamar weather conditions, load demand, da grid status. Amma, typical operation consists of three main modes: charging mode, discharging mode, da grid-tie mode.
Charging mode occurs when there is excess sunlight and low load demand. In this mode, collectors concentrate sunlight onto receivers wanda yake heat HTF. HTF then flows to power block or storage system, depending on system configuration and control strategy.
























