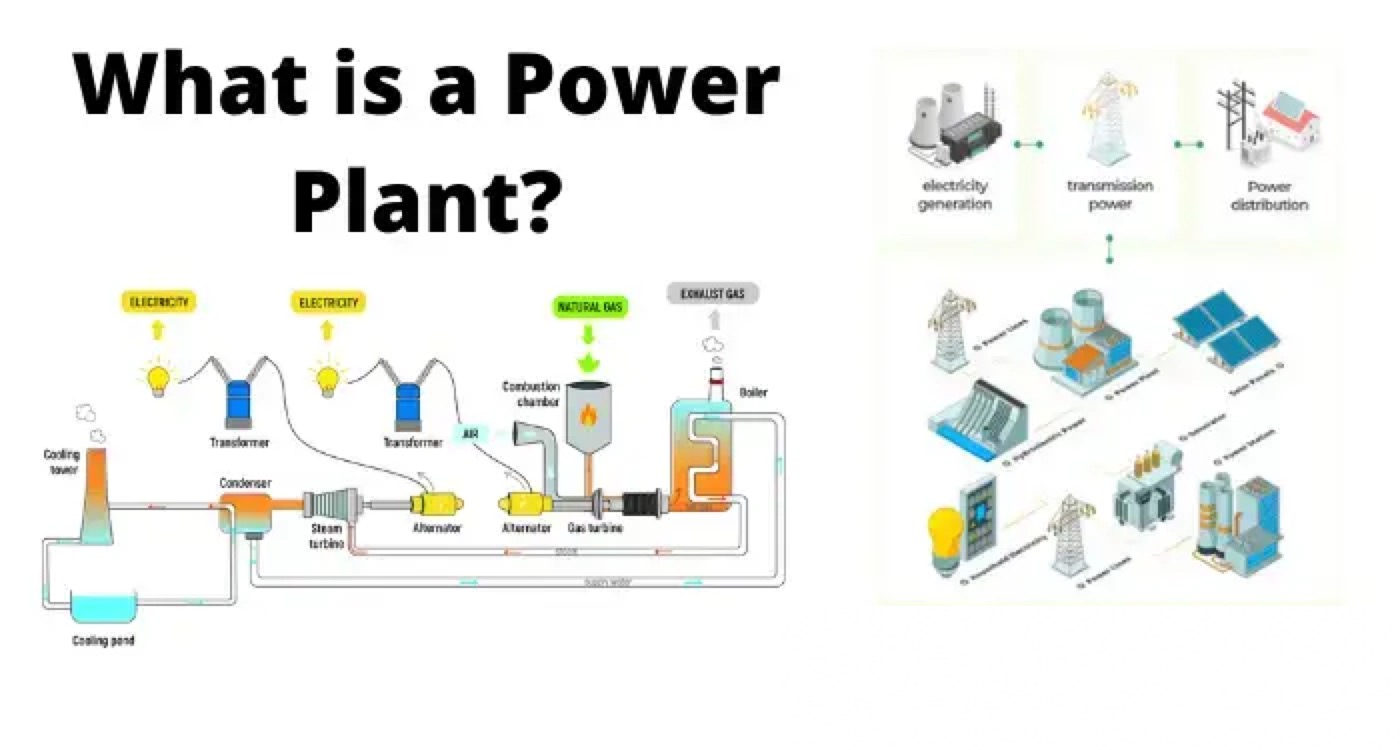
מהו מפעל כוח?
מפעל כוח (ידוע גם כתחנת כוח או תחנת ייצור כוח), הוא אתר תעשייתי המשמש לייצור והפצה של חשמל בקנה מידה גדול. רבים מהתחנות מכילות גנרטורים אחדים או יותר, מכונה מסתובבת הממירה כוח מכני לזרם חשמלי תלת פאזי (המכונים גם אלטרנטור). התנועה היחסית בין שדה מגנטי מול מוליך חשמלי יוצרת זרם חשמלי.
אלה נמצאים בדרך כלל באזורים מיושנים או מספר קילומטרים מחוץ לעיר או מרכזי עומס, בשל הצרכים שלהם כמו אדמה ומים עצומים, בנוסף לאילוצים שונים כמו היפוסר של פסולות וכדומה.
לכן, על תחנת ייצור כוח להתייחס לא רק לייצור יעיל של כוח, אלא גם להעברתו. זה הסיבה שהתחנות הן לעיתים קרובות מלוות במחנות טרנספורטורים. המחנות הללו מעלים אתряע החשמל ההעברה, מה שמאפשר העברת חשמל יעילה יותר לאורך מרחקים ארוכים.
מקור האנרגיה המשמש להפעלת ציר הגנרטור משתנה מאוד ומבוסס בעיקר על סוג הדלק הנבחר. בחירת הדלק קובעת איך מכנים את מפעל הכוח, והפיכת מפעלי הכוח השונים לסוגים שונים.

סוגי מפעלי כוח
הסוגים השונים של מפעלי כוח ממיינים בהתאם לסוג הדלק שנבחר. לשם ייצור כוח המוני, אנרגיה תרמית, גרעינית ומימית הם היישומים הכי יעילים. תחנת ייצור כוח יכולה להיות מסווגת לשלושת הסוגים המוזכרים למעלה. בואו נבדוק את סוגי התחנות הללו בפרטים.
תחנת כוח תרמית
תחנת כוח תרמית או מפעל כוח תרמי המופעל בעפר סיליקטי היא דרך קונבנציונלית ביותר לייצר כוח חשמלי בהיענות גבוהה. היא משתמשת בעפר סיליקטי כדלק ראשי כדי לבשל את המים הזמינים לדיימן סופר לחץ עבור הנעה של טורבינת הקיטור.
טורבינת הקיטור מת/generated by the rotation of the turbine blades. This steam is then superheated in the superheater to extremely high temperatures. This superheated steam is then allowed to enter into the turbine, as the turbine blades are rotated by the pressure of the steam.
The turbine is mechanically coupled with the alternator in such a way that its rotor will rotate with the rotation of the turbine blades. After entering the turbine, the steam pressure suddenly falls, leading to a corresponding increase in the steam volume.
After having imparted energy into the turbine rotors, the steam is made to pass out of the turbine blades into the steam condenser of the turbine. In the condenser, cold water at ambient temperature is circulated with the help of a pump, which leads to the condensation of the low-pressure wet steam.
Then this condensed water is further supplied to a low-pressure water heater where the low-pressure steam increases the temperature of this feedwater. It is again heated in high pressure. This outlines the basic working methodology of a thermal power plant.
**Advantages of Thermal Power Plants**
- The fuel used, i.e., coal, is quite cheaper.
- Initial cost is less compared to other generating stations.
- It requires less space compared to hydroelectric power stations.
**Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plants**
- It pollutes the atmosphere due to the production of smoke and fumes.
- The running cost of the power plant is more than a hydroelectric plant.
**Nuclear Power Station**
Nuclear power plants are similar to thermal stations in many ways. However, the exception here is that radioactive elements like uranium and thorium are used as the primary fuel instead of coal. Also, in a nuclear station, the furnace and the boiler are replaced by the nuclear reactor and the heat exchanger tubes.
For the process of nuclear power generation, the radioactive fuels undergo fission reactions within the nuclear reactors. The fission reaction propagates like a controlled chain reaction and is accompanied by an unprecedented amount of energy produced, which is manifested in the form of heat.
This heat is then transferred to the water present in the heat exchanger tubes. As a result, superheated steam at very high temperatures is produced. Once the process of steam formation is accomplished, the remaining process is exactly similar to a thermal power plant, as this steam will further drive the turbine blades to generate electricity.
**Hydro-Electric Power Station**
In hydroelectric plants, the energy of the falling water is utilized to drive the turbine, which in turn runs the generator to produce electricity. Rain falling upon the earth’s surface has potential energy relative to the oceans towards which it flows. This energy is converted to shaft work where the waterfalls through an appreciable vertical distance. The hydraulic power is, therefore, a naturally available renewable energy given by the equation:
P = gρ QH
Where, g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/sec²
ρ = density of water = 1000 kg/m³
H = height of fall of water.
This power is utilized for rotating the alternator shaft, to convert it to equivalent electrical energy.
An important point to be noted is that hydroelectric plants are of much lower capacity compared to their thermal or nuclear counterparts.
For this reason, hydro plants are generally used in scheduling with thermal stations, to serve the load during peak hours. They, in a way, assist the thermal or nuclear plant to deliver power efficiently during periods of peak hours.
**Advantages of Hydro Electric Power Station**
- It requires no fuel; water is used for the generation of electrical energy.
- It is neat and clean energy generation.
- Construction is simple, and less maintenance is required.
- It helps in irrigation and flood control also.
**Disadvantages of Hydro Electric Power Station**
- It involves high capital cost due to dam construction.
- Availability of water depends upon weather conditions.
- It requires high transmission costs as the plant is located in hilly areas.
**Types of Power Generation**
As mentioned above, depending on the type of fuel used, the power generating stations as well as the types of power generation are classified. Therefore, the three major classifications for power production in reasonably large scale are:
1. Thermal power generation
2. Nuclear power generation
3. Hydro-electric power generation
Apart from these major types of power generations, we can resort to small-scale generation techniques as well, to serve discrete demands. These are often referred to as alternative methods or non-conventional energy of power generation and can be classified as:
1. Solar power generation (making use of the available solar energy)
2. Geothermal power generation (energy available in the Earth’s crust)
3. Tidal power generation
4. Wind power generation (energy available from wind turbines)
These alternative sources of generation have been given due importance in the last few decades owing to the depleting amount of natural fuels available to us. In the centuries to come, a stage might be reached when several countries across the globe would run out of their entire reserve for fossil fuels.
The only way forward would then lie in the mercy of these alternative sources of energy, which might play an instrumental role in shaping the energy supplies of the future. For this reason, these might rightfully be referred to as the energy of the future.
**Statement:** Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.






















