| Brand | Wone Store |
| Model NO. | JDZW3-36 outdoor epoxy resin casting Voltage transformer |
| Rated frequency | 50/60Hz |
| Primary voltage | 35kV |
| Secondary voltage | 110V |
| Series | JDZW |
Product Overview
JDZW3-36 voltage transformer, outdoor epoxy resin casting and double pole insulated VT, is widely used for measuring current, electric energy and protective relaying in the isolated neutral system with the frequency 50Hz or 60Hz and insulation voltage 36 kV (Up to 40.5kV).
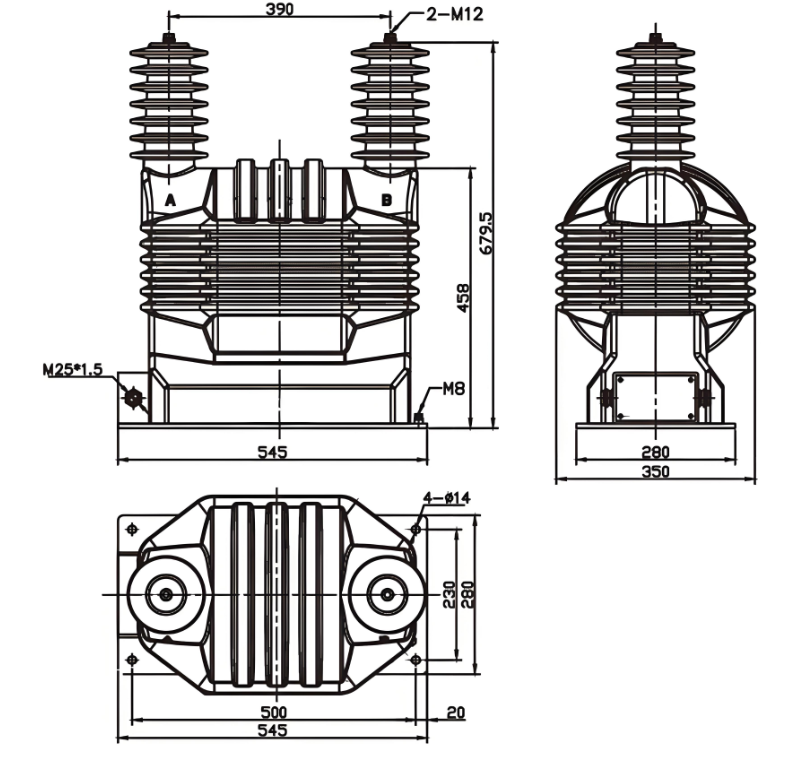
The iron core adopts advanced cold-rolled silicon steel sheet. High voltage outgoing line of primary winding was fetched out from top of the product; outgoing line of secondary winding was fetched out from transverse side of the product.
Key Features
Excellent Outdoor Insulation Protection:JDZW3-36 uses high-quality epoxy resin as the main insulation material, with a silicone rubber coating on the outer layer. The internal traditional epoxy resin casting process ensures the transformer's insulation and electrical performance. Silicone rubber features excellent arc resistance, hydrophobicity, and climatic adaptability, enabling the equipment to operate normally in high-altitude, high-salt fog, rainy, and strong UV environments. Even if system faults cause explosions, the external silicone rubber structure restrains internal resin, reducing splashing damage to surrounding personnel, livestock, or equipment.
High Precision & Low Partial Discharge:The vacuum casting process achieves uniform electric field distribution with low partial discharge, enabling precise voltage measurement. Voltage ratio error is controlled within a minimal range, meeting high-precision metering and protection needs to provide reliable voltage data for 36kV and below power systems.
Fully Enclosed & Sealed Design:Primary and secondary terminals are completely sealed to prevent dust, moisture, and impurities from invading, avoiding electrical performance degradation caused by external factors. This extends service life and ensures stable operation in complex outdoor environments.
Strong Anti-Fouling Capability:The external insulation has high dry arc and large creepage distance, with creepage distance meeting or exceeding relevant standards—especially suitable for high-pollution areas. The surface undergoes special treatment to further enhance anti-fouling performance and reduce flashover risks.
Durable Metal Components:All metal components are hot-dip galvanized to enhance corrosion resistance, withstanding long-term outdoor exposure to wind, rain, and sunlight—ensuring reliable long-term service in outdoor environments.
Main technical parameter
Rated primary voltage:30 kV or 33 kV or 35 kV etc.
Rated secondary voltage:100 V or 110 V
Rated power-frequency withstand voltage: 70kV
Rated lightning impulse withstand voltage: 170kV
Technical standard accords with IEC 60044-2.2003.
Other parameters pls see as follow:
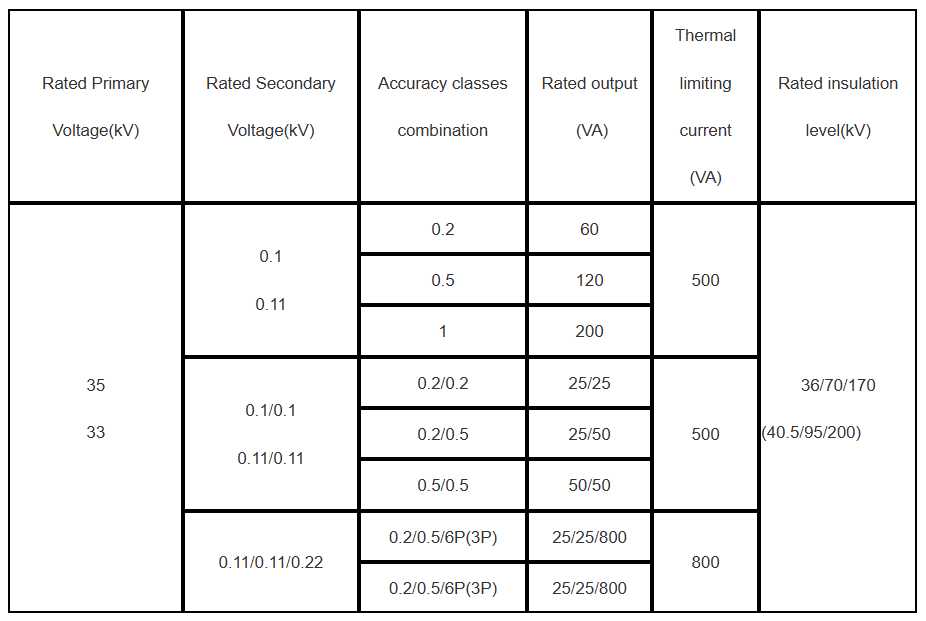
Remarks: Upon request we are glad to offer transformers according to other standards or with non-standard technical specs.
Outline drawing