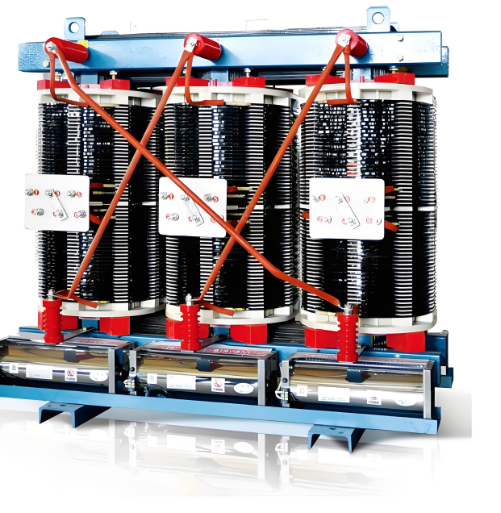
| Brand | Vziman |
| Model NO. | Non-encapsulated Class H dry-type power transformer 200KVA 250KVA 315KVA 400KVA |
| Rated capacity | 400kVA |
| Voltage grade | 10KV |
| Series | SG (B) 10 |
Description:
Non-encapsulated Class H dry-type power transformers, available in capacity specifications of 200kVA, 250kVA, 315kVA and 400kVA, are high-efficiency power conversion devices specifically designed for modern power systems. These transformers adopt an open-frame structure without enclosed encapsulation of windings, making internal components visually accessible and easy to maintain. Their core structure is built with Class H insulation materials, which enable stable operation in high-temperature environments and effectively ensure the transformer's reliable performance under complex working conditions. In practical applications, whether for power distribution systems in commercial buildings or power supply for industrial production, these transformers with different capacities can precisely adapt to diversified power demands, providing solid support for power transmission and distribution.
Feature:
Exceptional Insulation Performance
Uses Class H insulation material with a maximum operating temperature of 180°C
Resistant to high temperatures and aging, ensuring safe and stable operation
Extends service life significantly
Efficient Heat Dissipation Design
Non-encapsulated structure promotes natural air convection
Rapid heat dissipation prevents thermal buildup
Maintains optimal operating efficiency
High Reliability & Durability
Premium electromagnetic wires and silicon steel laminations
Advanced manufacturing processes ensure short-circuit resistance
Withstands overload conditions, reducing maintenance costs
Flexible Installation & Easy Maintenance
Open-frame design simplifies installation procedures
Quick fault diagnosis and component accessibility
Minimizes downtime and improves grid efficiency
Environmentally Friendly & Energy Efficient
Oil-free design eliminates contamination risks
Optimized electromagnetic design reduces no-load and load losses
Significant long-term energy cost savings
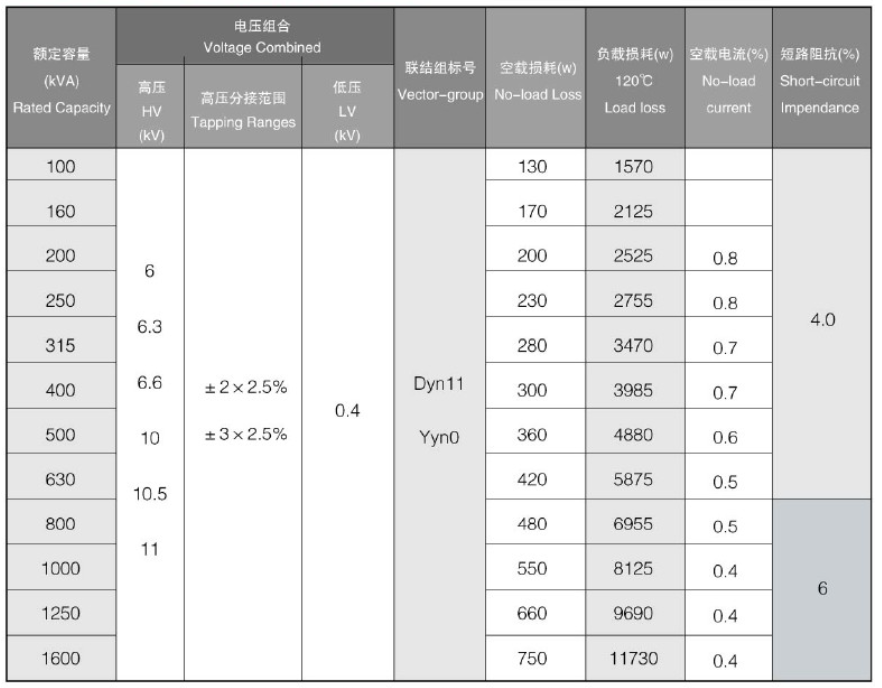
Parameter:

The working principle of an unencapsulated Class H dry-type power transformer?
Iron Core: It is usually made up of laminated high-quality silicon steel sheets, featuring low loss and low noise. The function of the iron core is to concentrate and guide the magnetic field, thus improving the efficiency of the transformer.
Primary Winding: Connected to the high-voltage side, it receives the input voltage. The primary winding is usually wound with copper or aluminum wires.
Secondary Winding: Connected to the low-voltage side, it outputs the required voltage. The secondary winding is also wound with copper or aluminum wires.
Insulation Materials: H-class insulation materials such as NOMEX paper and fiberglass are used, which possess excellent heat resistance and electrical properties.
Cooling System: Usually, natural air cooling (AN) or forced air cooling (AF) is adopted. The appropriate cooling method is selected according to specific application requirements.
Input Voltage: The alternating current power source is applied to the transformer through the primary winding.
Generating Magnetic Field: The current in the primary winding generates an alternating magnetic field in the iron core.
Transferring Magnetic Field: The alternating magnetic field is transferred to the secondary winding through the iron core.
Inducing Electromotive Force: The alternating magnetic field induces an electromotive force in the secondary winding, generating the output voltage.
Output Voltage: The secondary winding outputs the required voltage for the load to use.