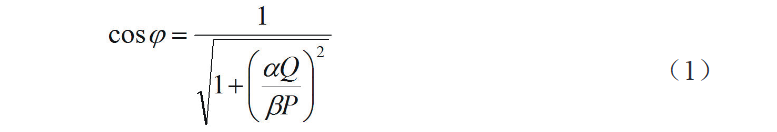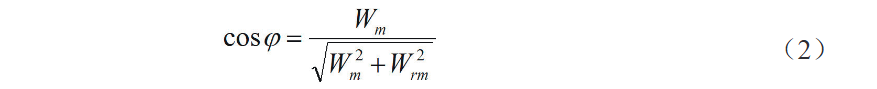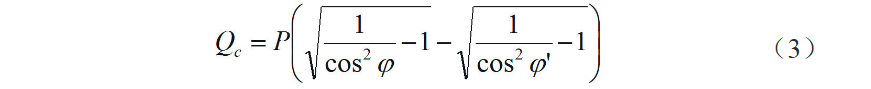1 Pananaw sa Teknolohiya sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
1.1 Papel sa Teknolohiya sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
Ang teknolohiya sa kompenso sa reactive power usa ka gihigugma nga teknika sa mga sistema sa kuryente ug grid. Gisagol kini aron mapataas ang power factor, mabawasan ang line losses, mapadako ang kalidad sa kuryente, ug mapataas ang kapasidad ug estabilidad sa pagpadala sa grid. Kini nagaseguro nga ang mga ekwipo sa kuryente mogamit sa mas estableng ug reliable nga kalibutan, sama sa pagbubo sa abilidad sa grid sa pagpadala og active power.
1.2 Limitasyon sa Teknolohiya sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
Bagamaog gigamit kini ngadto sa daghang aplikasyon, dili ang teknolohiya sa kompenso sa reactive power ang katugyan alang sa tanang scenario. Sa pamaagi, sa mga sistema uban sa madalas nga magbag-o ang load, ang switching speed sa mga ekwipo sa kompenso mahimong mudawat sa rapid nga pagbag-o sa load. Kini mahimong resulta sa insuficienteng response, na nagresulta sa unstable nga voltage fluctuations sa grid.
Sa ilang mga kasinatian, ang mga ekwipo sa kompenso sa reactive power mahimong mobuo og harmonic currents ug harmonic voltages, nga makapakita og negative nga epekto sa kabuok nga sistema sa kuryente ug sa mga konektado nga ekwipo. Dili paubos nga kinahanglan nga ihatag ang harmonics sa panahon sa pagdisenyo ug implementasyon sa mga skema sa kompenso, ug ang maayong suppression measures isip giya.

2 Strategiya sa Optimisasyon para sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
Ang teknolohiya sa kompenso sa reactive power batas sa paper niini gihatagan sa kompleto nga sistema sa kompenso. Ang sistema nagsakop sa tulo ka pangunehang bahin: ang S751e-JP main controller, ang S751e-VAR control board (capacitor switching execution unit), ug ang power capacitor bank. Sa matag usa, ang S751e-JP main controller ug ang S751e-VAR control board nagoperar sa master-slave relationship.
Sa normal nga operasyon, ang S751e-VAR control board mosulbar sa mga instruksyon gikan sa S751e-JP main controller ug nagkontrol sa internal composite switches aron mobag-o ang pre-grouped power capacitors. Ang S751e-JP main controller responsable sa pagkolekta ug pag-analisa sa real-time operational data gikan sa sistema sa kuryente. Gamiton ang built-in software ug algorithms, ito gigamit aron mapangita ang required nga amount sa kompenso sa reactive power, ug pagkatapos inusab ang information ha signals compatible sa S751e-VAR control board. Pagkatapos molambo sa command, ang control board mogamit sa switching operations sumala sa preset logic, na nagpadayon sa precise nga kompenso sa reactive power sa sistema sa kuryente.
2.1 Disenyo ug Konfigurasyon sa Ekwipo sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
2.1.1 Compensation Capacity sa Power Capacitors
Gikinahanglan ang simplified nga calculation method aron hibalde ang compensation capacity sa power capacitors. Apan, ang metodo may limitasyon sa practical applications. Taliha, ang paper niini adunay mas detalyado ug accurate nga algorithm aron mapangita ang required nga kompenso. Unsa man, ang initial power factor (cosφ) sa sistema sa un-compensated conditions established.
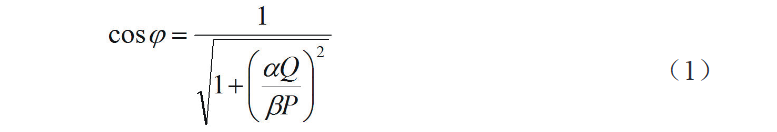
P ug Q mao ang active ug reactive power values, respectively, sa panahon ang grid nagoperar sa full load;
α mao ang annual average active load factor sa sistema sa kuryente (o grid), typical nga range gikan 0.70 hangtod 0.75;
β mao ang annual average reactive load factor sa sistema sa kuryente (o grid), general nga gitangtang 0.76.
Kon ang sistema sa kuryente nagsugod sa normal nga operasyon, ang historical electricity consumption data gamiton alang sa computation. Sa kasinatian:
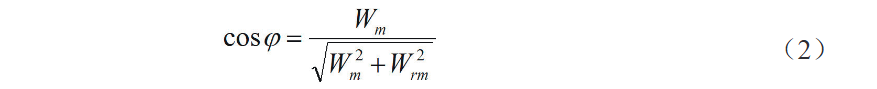
diin:
Wm mao ang monthly average active energy consumption sa sistema sa kuryente;
Wrm mao ang monthly average reactive energy consumption sa sistema sa kuryente.
Batasan sa target power factor sa itaas, ang actual compensation capacity sa power capacitor mahimo mapangita gamit ang sumala nga formula:
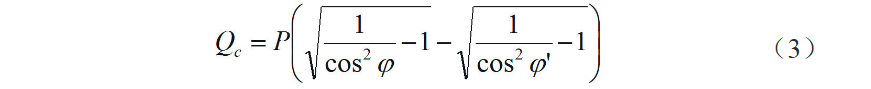
2.1.2 Connection Methods sa Power Capacitor Banks
Sa normal nga operasyon sa sistema sa kuryente, ang power capacitor banks adunay duha ka basic nga connection methods: delta (Δ) connection ug Y (wye) connection. Padulong, depende sa location sa switching devices sa circuit, sila mahimong classified isip internal o external switching configurations.
Ang delta connection naghatag og fast, simultaneous three-phase compensation, na effectively nagreduce sa duration sa line imbalance ug nag-improve sa efficiency sa kompenso. Apan, kini general nga suitable lang sa mga sistema uban sa relatively balanced three-phase loads ug dili mahimo ang precise nga grid compensation.
Ang Y connection naghatag og independent ug accurate nga kompenso sa matag phase sa capacitor bank. Apan, kini mahimong lead sa under-voltage o over-voltage sa usa ka phase ug typical nga may higher nga implementation costs.
Taliha, ang paper niini propose ang hybrid approach nga nagcombine sa advantages sa matag connection methods, adjusting ang number ug capacity sa capacitor groups sumala sa actual load conditions.
2.1.3 Grouping Configuration sa Power Capacitors
Ang grouping configuration sa power capacitors general nga include ang equal-capacity ug unequal-capacity schemes.
Sa equal-capacity grouping, ang total capacitor bank gibahin sa groups of identical capacity, ang number of groups determined based on the total required capacity. Kini nga metodo naghatag og simple assembly ug straightforward switching control logic. Apan, tungod sa fewer groups ug larger individual capacities, kini resulta sa coarse compensation steps, making precise compensation difficult. Frequent switching mahimong accelerate equipment wear ug increase maintenance costs.
Sa unequal-capacity grouping, ang capacitor capacities distributed according to a predefined ratio (e.g., 1∶2∶4∶8). Kini nga approach naghatag og higher nga compensation accuracy ug flexibility, enabling fine-tuned reactive power regulation. Apan, kini involve complex system design ug control logic, limiting its scalability. Padulong, smaller-capacity capacitors mahimong experience excessive switching operations, affecting long-term reliability.
Pagkatapos comprehensive evaluation, ang paper niini adopt ang equal-capacity grouping method. Apan, ang capacity sa common compensation group slightly larger than that of the split-phase compensation group. Kini nga configuration better supports cyclic switching operations, improves both compensation accuracy ug response speed, ug reduces control complexity. Kini usab shortens ang compensation cycle ug enhances overall efficiency.
2.2 Optimization sa Strategy sa Kompenso sa Reactive Power
Ang well-designed nga strategy sa kompenso sa reactive power nagaseguro nga effective nga kompenso sa iba't ibang operating conditions. Sa normal nga operasyon sa sistema, ang real-time state sa sistema sa kompenso mahimong hatagan og zones—such as the switching-in zone, stable zone, ug switching-out zone—based on parameters like active ug reactive power.
Optimizing ang strategy sa kompenso usa ka critical aspect sa disenyo sa sistema, directly influencing ang performance sa kompenso. Traditional single-parameter control strategies focus only on one variable, making them inadequate for handling complex or dynamic conditions. This often leads to over-compensation or excessive switching, increasing operational and maintenance costs.
Taliha, ang paper niini employs a multi-parameter composite control strategy. One parameter is used as the primary decision criterion, while several others serve as auxiliary factors. The system evaluates multiple parameters simultaneously, performs comprehensive calculations to determine switching requirements, and executes switching actions accordingly, improving control accuracy and stability.
2.3 Operation ug Maintenance sa Ekwipo sa Kompenso
Arong mapadako ang stability ug interference resistance sa ekwipo sa kompenso, ang built-in software protection system dapat implementar. Kini nagaseguro nga ang device makapag-operar normal o safely disconnect sa iba't ibang abnormal conditions, thereby improving operational reliability ug safety.
Padulong, professional technicians regular nga conduct installation commissioning ug inspections aron identify potential safety hazards sa loob sa ekwipo ug perform timely reinforcement.
Ang mga sistema sa kompenso sa reactive power typical nga equipped uban sa protective functions such as overcurrent, overvoltage, ug undervoltage protection. Aron sigurado nga ang protections respond correctly sa faults, regular nga testing sa kanilang operational performance necessary. Furthermore, overcurrent ug temperature protection should be implemented aron detect abnormalities promptly ug prevent fault escalation.