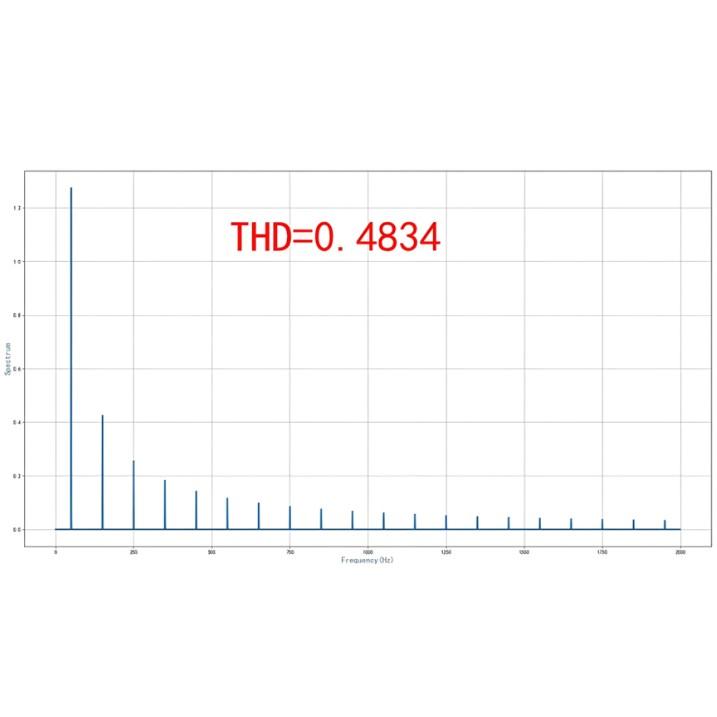
जब वास्तविक ग्रिड THD सीमा को पार करता है (उदाहरण के लिए, वोल्टेज THDv > 5%, करंट THDi > 10%), तो यह पूरे बिजली श्रृंखला में उपकरणों को अनुकूल नुकसान पहुंचाता है — Transmission → Distribution → Generation → Control → Consumption. मुख्य तंत्र अतिरिक्त नुकसान, रिझोनेंट ओवरकरंट, टोक्यो फ्लक्चुएशन, और सैंपलिंग विकृति हैं। नुकसान के तंत्र और प्रदर्शन उपकरण के प्रकार के आधार पर बहुत भिन्न होते हैं, जैसा कि नीचे विस्तार से दिया गया है:
1. Transmission Equipment: Overheating, Aging, and Drastically Reduced Lifespan
Transmission equipment directly carries grid current/voltage. Harmonics exacerbate energy losses and insulation degradation. Key affected components are transmission lines (cables/overhead) and current transformers (CTs).
1.1 Transmission Lines (Cables / Overhead Lines)
Damage Mechanism: Higher harmonic frequencies intensify the "skin effect" (high-frequency currents concentrate on the conductor surface, reducing effective cross-sectional area), increasing line resistance. Additional copper losses rise with the square of harmonic order (e.g., 5th harmonic copper loss is 25× that of fundamental).
Specific Damages:
Overheating: At THDi = 10%, copper losses increase by 20%-30% compared to rated conditions. Cable temperature can rise from 70°C to 90°C (exceeding insulation tolerance), accelerating aging and cracking of insulation layers (e.g., XLPE).
Shortened Lifespan: Prolonged overheating reduces cable life from 30 years to 15–20 years, potentially causing "insulation breakdown" and short-circuit faults. (An industrial park burned two 10kV cables within one year due to excessive 3rd harmonic, costing over 800,000 RMB in repairs.)
1.2 Current Transformers (CTs)
Damage Mechanism: Harmonic currents (especially 3rd and 5th) cause "transient saturation" of CT iron cores, sharply increasing hysteresis and eddy current losses (additional iron losses). Saturation distorts the secondary-side output waveform, preventing accurate representation of primary current.
Specific Damages:
Core Overheating: CT core temperature may exceed 120°C, burning insulation on secondary windings and causing ratio inaccuracies.
Protection Misoperation: Distorted secondary current leads protective relays (e.g., overcurrent protection) to falsely detect "line short circuits," triggering false tripping. (A distribution network experienced 10 feeder trips due to CT saturation, affecting 20,000 households.)
2. Distribution Equipment: Frequent Failures, System Stability Collapse
Distribution equipment is critical for "connecting upstream and downstream" in the grid. THD exceeding limits causes the most direct damage. Key affected devices include power transformers, capacitor banks, and reactors.
2.1 Power Transformers (Distribution / Main Transformers)
Damage Mechanism: Harmonic voltages increase magnetic hysteresis and eddy current losses in transformer cores (additional iron losses); harmonic currents increase winding copper losses. Combined, these significantly raise total losses. Unbalanced three-phase harmonics also increase neutral current (up to 1.5× phase current), worsening localized overheating.
Specific Damages:
Core Overheating: At THDv = 8%, transformer iron losses increase by 15%-20%. Core temperature rises from 100°C to 120°C, accelerating degradation of insulating oil (e.g., 25# transformer oil), increasing acidity, and reducing dielectric strength.
Winding Burnout: Long-term overheating carbonizes winding insulation paper (e.g., Nomex), leading to short circuits. A substation's 110kV main transformer suffered a winding short after 3 years due to excessive 5th harmonic, with repair costs exceeding 5 million RMB.
Reduced Lifespan: Prolonged THD reduces transformer lifespan from 20 years to 10–12 years.
2.2 Shunt Capacitor Banks (for Reactive Power Compensation)
Damage Mechanism: Capacitive reactance decreases with frequency (Xc = 1/(2πfC)), so high-frequency harmonics induce overcurrent. If capacitors form "harmonic resonance" with grid inductance (e.g., 5th-order resonance), current can surge to 3–5× rated value—far beyond capacitor ratings.
Specific Damages:
Insulation Breakdown: Overcurrent heats internal dielectrics (e.g., polypropylene film), causing puncture, bulging, or even explosion. (An industrial workshop damaged three 10kV capacitor banks within one month due to 7th harmonic resonance; replacement cost per bank exceeded 150,000 RMB.)
Protection Failure: Resonant currents burn out fuse links; if protection fails to act, fire risk increases.
2.3 Series Reactors (for Harmonic Suppression)
Damage Mechanism: Although used to suppress specific harmonics (e.g., 3rd, 5th), reactors suffer increased winding copper losses under long-term harmonic current. Pulsating magnetic fields from harmonics also intensify core vibration, causing mechanical wear.
Specific Damages:
Winding Overheating: At THDi = 12%, reactor copper losses increase by over 30%; winding temperatures exceed 110°C, causing insulation varnish to carbonize and flake off.
Core Noise & Wear: Vibration frequency couples with harmonics, producing loud noise (>85 dB). Long-term vibration loosens silicon steel laminations, reducing permeability and rendering harmonic suppression ineffective.
3. Generation Equipment: Output Limitation, Rising Safety Risks
Generation equipment is the "energy source" of the grid. Excessive THD negatively impacts operational stability. Key affected devices: synchronous generators, renewable inverters (PV/wind).
3.1 Synchronous Generators (Thermal/Hydro Plants)
Damage Mechanism: Grid harmonics back-feed into generator stator windings, creating "harmonic electromagnetic torque." Superimposed on fundamental torque, this forms "pulsating torque," increasing vibration. Harmonic currents also raise stator copper losses, causing local overheating.
Specific Damages:
Reduced Output: A 300MW unit at THDv = 6% experiences ±0.5% speed fluctuation due to pulsating torque, reducing output below 280MW, decreasing efficiency by 5%-8%.
Winding Overheating: Stator temperature may reach 130°C (exceeding Class A insulation limit of 105°C), accelerating insulation aging and risking turn-to-turn short circuits.
Bearing Wear: Increased vibration accelerates bearing (e.g., sleeve bearing) wear, reducing lifespan from 5 years to 2–3 years.
3.2 Renewable Inverters (PV / Wind)
Damage Mechanism: Inverters are sensitive to grid THD (per GB/T 19964-2012). If point-of-interconnection THDv > 5%, the inverter triggers "harmonic protection" to avoid damage. Additionally, harmonic voltage causes power imbalance between DC and AC sides, leading to IGBT module overheating.
Specific Damages:
Grid Disconnection: At a wind farm with THDv = 7%, 20 units of 1.5MW inverters disconnected simultaneously, abandoning over 100,000 kWh of wind energy in one day, costing ~50,000 RMB in lost revenue.
IGBT Burnout: Long-term operation under harmonics increases switching losses in IGBT modules (core component), raising temperature above 150°C, risking "thermal breakdown." Repair cost per inverter exceeds 100,000 RMB.
4. Control Equipment: Sampling Distortion, System Malfunctions
Control equipment acts as the "brain and nervous system" of the grid. Excessive THD causes distorted sampling data and abnormal command transmission. Key affected devices: protective relays, automation communication systems.
4.1 Protective Relays (Overcurrent / Differential Protection)
Damage Mechanism: Harmonic currents cause transient CT saturation, distorting sampled current waveforms (e.g., flat-topped waves), leading protection algorithms to misjudge amplitude and phase, triggering incorrect actions. Harmonic voltages may also interfere with relay power supplies, causing logic circuit malfunctions.
Specific Damages:
False Tripping: A distribution network with THDi = 12% experienced distorted CT output due to saturation, causing overcurrent protection to falsely detect "line short circuit" and trip 10 feeders, cutting power to 20,000 households for 4 hours, resulting in indirect economic losses exceeding 2 million RMB.
Failure to Trip : If harmonic interference causes ±10% voltage fluctuation in the relay’s power supply, the logic circuit may crash, failing to trip during actual faults, allowing fault escalation.
4.2 Automation Communication Devices (RS485 / Fiber Modules)
Damage Mechanism: Electromagnetic radiation from harmonics (e.g., 10V/m RF interference) couples into communication lines, causing "bit flips" in data transmission. Harmonic voltages also disrupt clock modules, increasing synchronization errors.
Specific Damages:
Increased Bit Error Rate: Due to harmonic interference, RS485 communication bit error rate in a distribution automation system rose from 10⁻⁶ to 10⁻³, delaying or losing dispatch commands (e.g., "adjust capacitor switching").
Module Burnout: High-frequency harmonics can break down signal isolation circuits (e.g., optocouplers) in communication modules, causing failure. One substation destroyed 8 fiber modules within a month due to 5th harmonic interference.
5. End-Use Equipment: Performance Degradation, Production Accidents
End-use equipment represents the "terminal load" of the grid. Industrial and precision equipment suffer most severely from excessive THD. Key affected devices: industrial motors, precision equipment (lithography machines / medical MRI).
5.1 Industrial Motors (Induction / Synchronous Motors)
Damage Mechanism: Harmonic voltage generates "harmonic currents" in motor stator windings, forming "negative sequence rotating magnetic fields." When superimposed on the fundamental field, they produce "braking torque," causing speed fluctuations and increased vibration. Harmonic currents also increase stator/rotor copper losses, leading to overall overheating.
Specific Damages:
Efficiency Drop: A 100kW induction motor at THDv = 7% sees efficiency drop from 92% to below 85%, consuming over 50,000 kWh extra annually (at 0.6 yuan/kWh, additional electricity cost: 30,000 yuan/year).
Burnout: A steel plant’s rolling mill motor burned out twice within six months due to prolonged 7th harmonic exposure; stator temperature reached 140°C. Replacement cost per motor exceeded 2 million RMB.
Vibration & Noise: Motor vibration acceleration increased from 0.1g to 0.5g, noise exceeded 90dB, affecting working environment and accelerating foundation wear.
5.2 Precision Equipment (Semiconductor Lithography Machines / Medical MRI)
Summary: Core Rules of THD-Induced Equipment Damage
Inductive Equipment (Transformers, Motors, Reactors): Vulnerable to "Additional Losses" — harmonics increase iron/copper losses, with overheating and aging being primary damages.
Capacitive Equipment (Capacitors): Vulnerable to "Resonant Overcurrent" — harmonics easily trigger resonance, with overcurrent-induced insulation breakdown being the main damage.
Control Equipment (Relays, Communication Systems): Vulnerable to "Sampling Distortion" — harmonics distort data, leading to misoperations or failures to operate.
Precision Equipment (Lithography Machines, MRI): Vulnerable to "Waveform Distortion" — harmonics increase voltage ripple, leading to loss of accuracy.
इसलिए, बिजली ग्रिड को दोहरी रणनीति का अपनाना चाहिए:
"हार्मोनिक मॉनिटोरिंग (THD माप त्रुटि को नियंत्रित करना ≤ ±0.5%) + सक्रिय फिल्टरिंग (APF) / पसिव फिल्टरिंग"
THDv को राष्ट्रीय मानक सीमा 5% के भीतर रखने के लिए, इस प्रकार उपकरणों को नुकसान से बचाया जा सके।